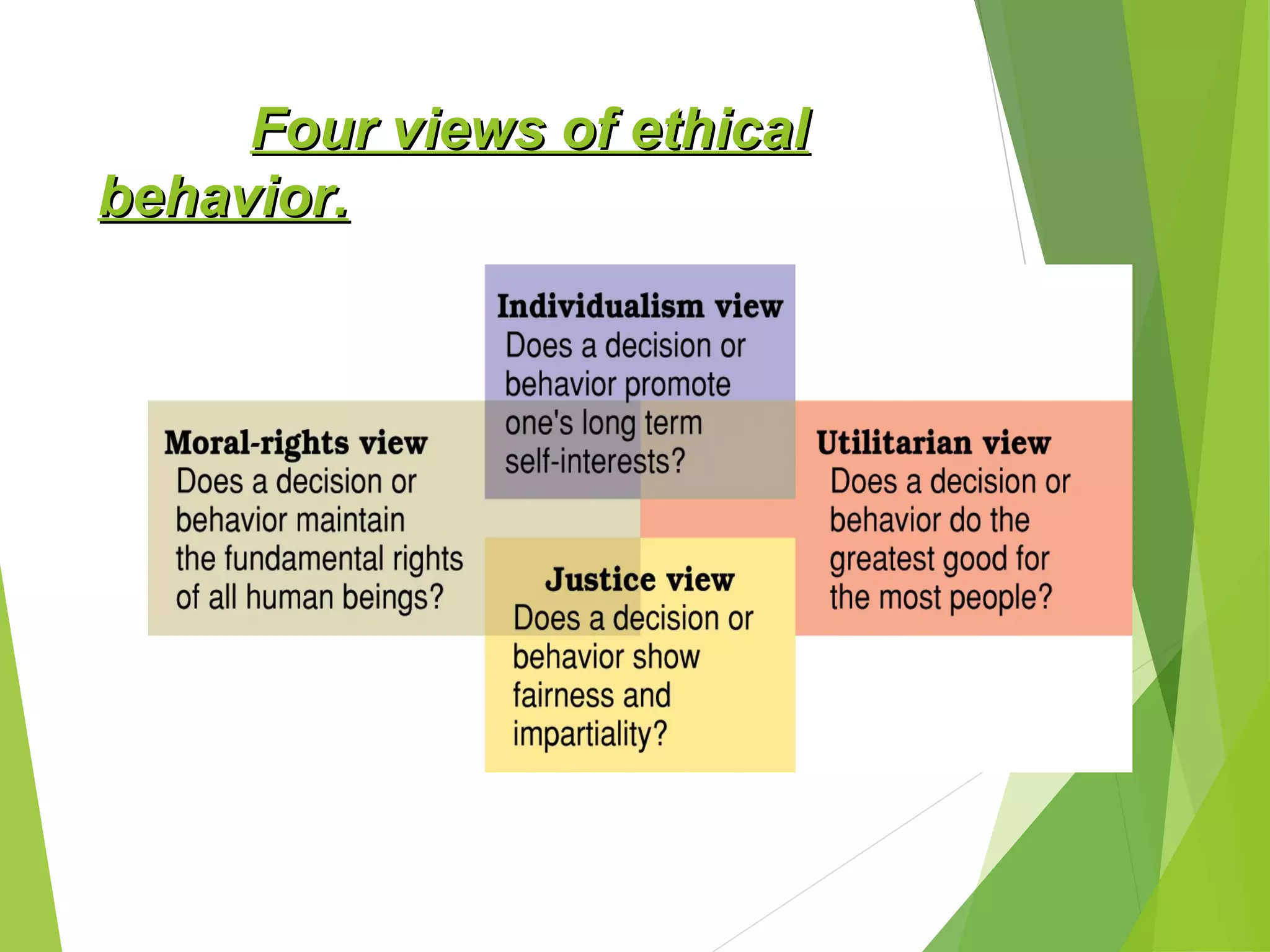
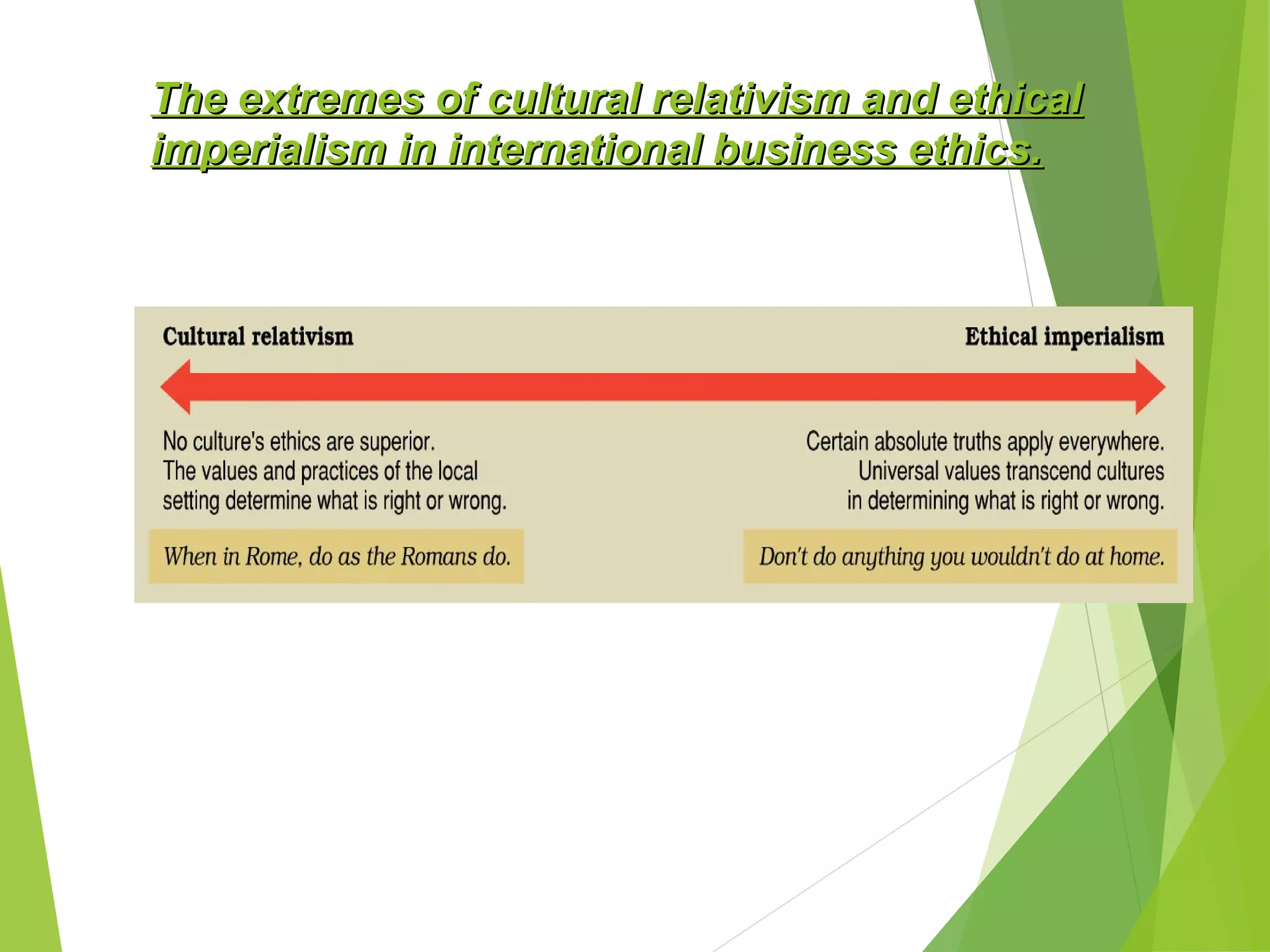
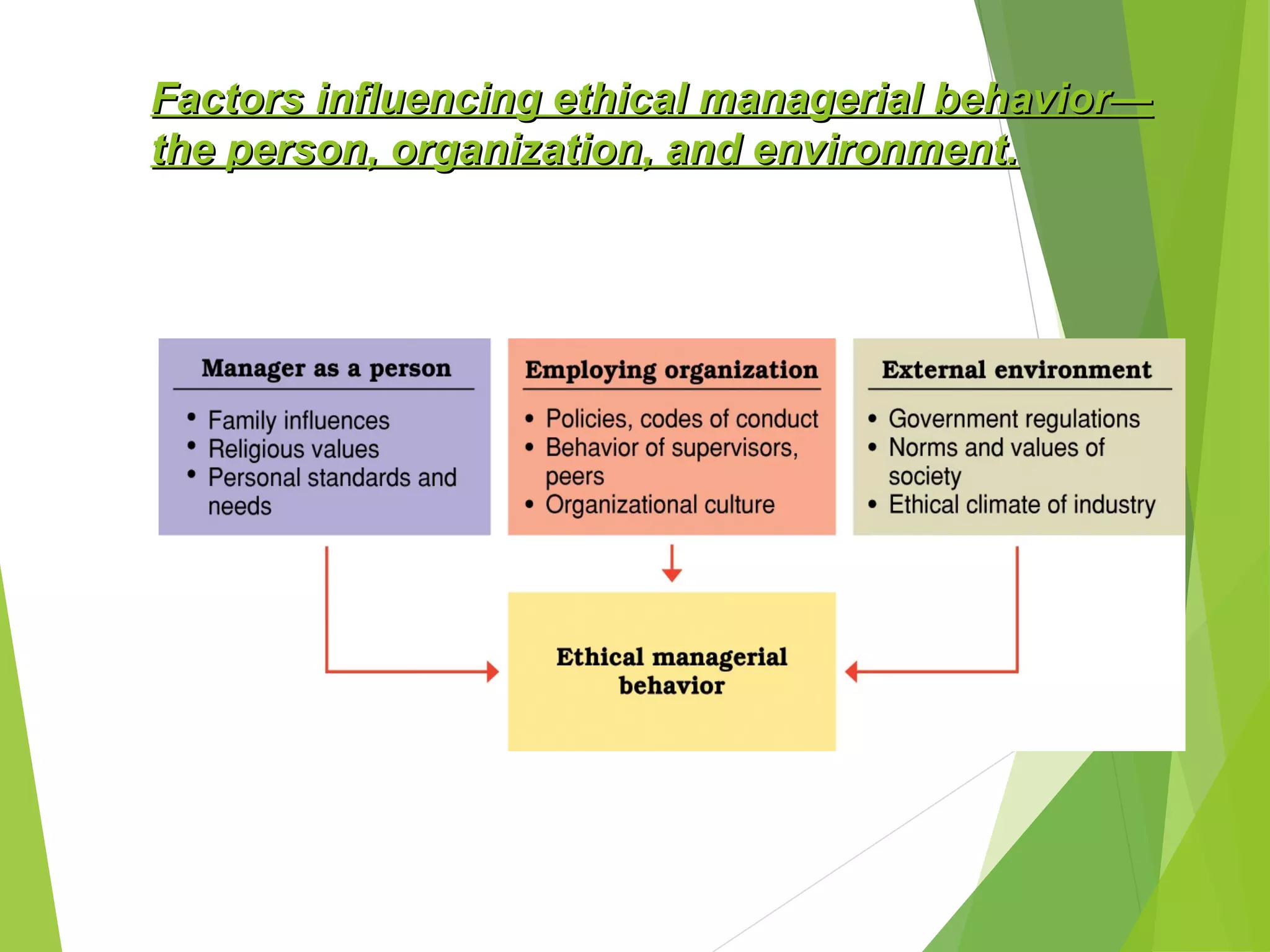
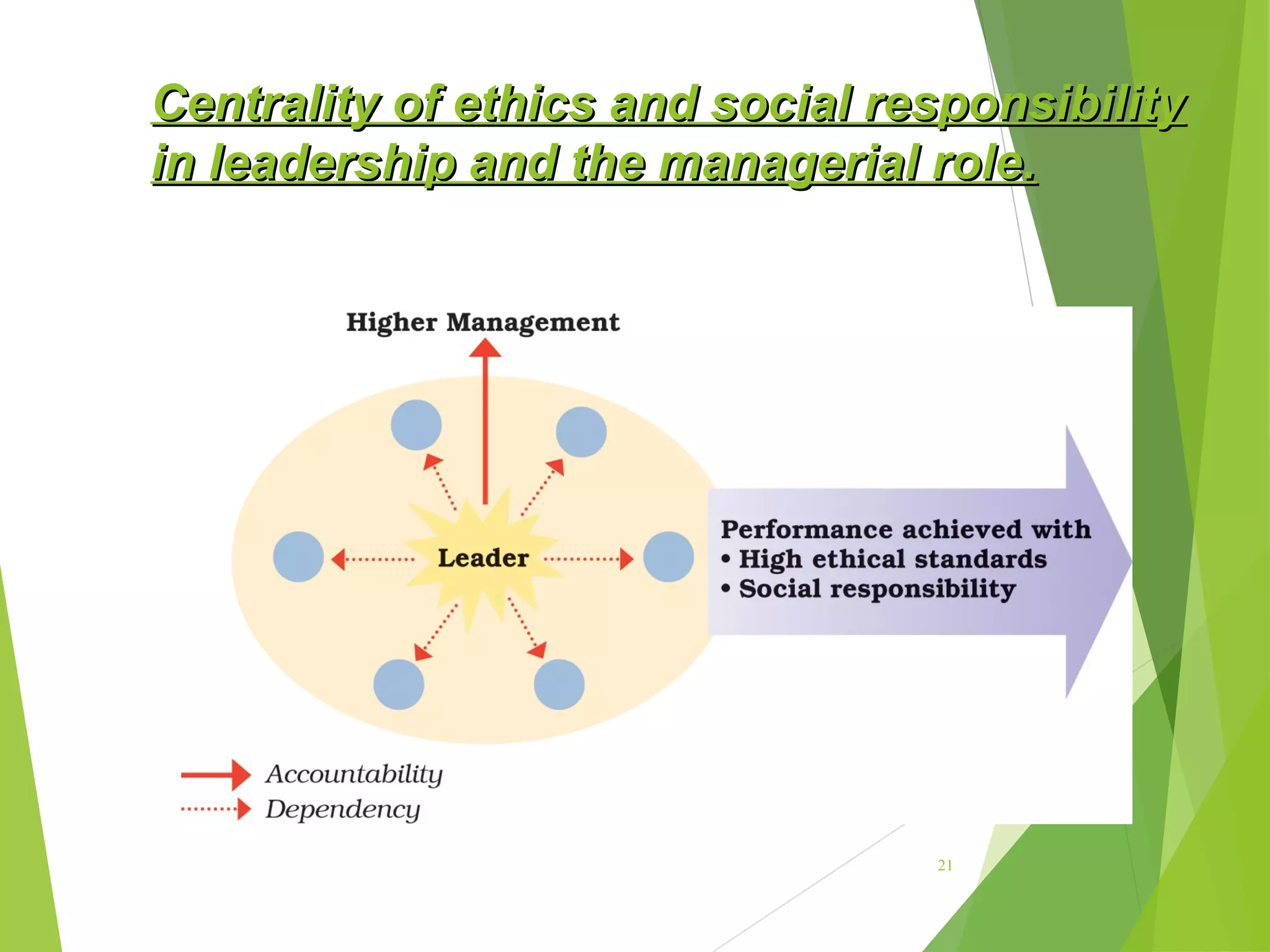
This document discusses ethics and ethical behavior in organizations. It addresses key questions such as what constitutes ethical behavior, how ethical dilemmas arise in the workplace, and how organizations can maintain high ethical standards. Ethical behavior is defined as actions that conform to moral principles and are considered good and right. Upholding ethics helps organizations through benefits like developing trust with employees and customers. Techniques for maintaining ethics include training, role modeling by leaders, and establishing codes of conduct. The document also examines corporate social responsibility and how organizations should serve societal interests in addition to their own.