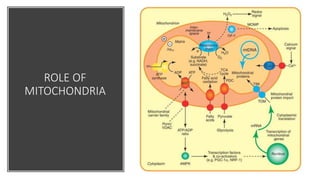
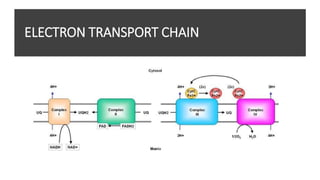
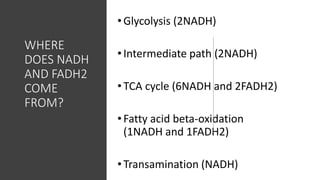
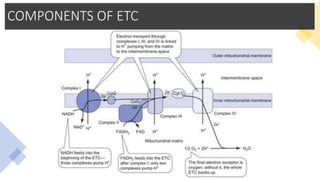
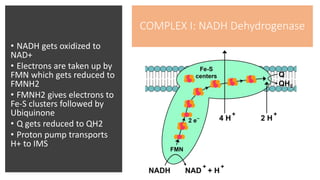
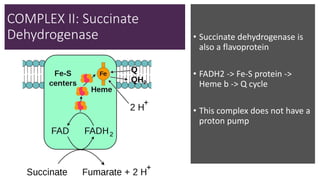
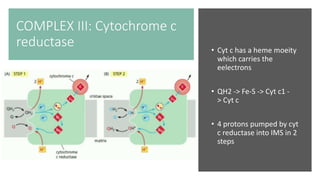
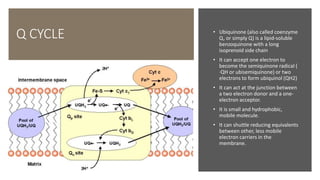
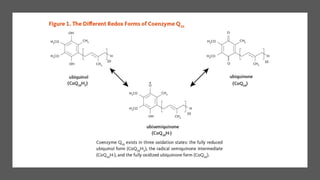
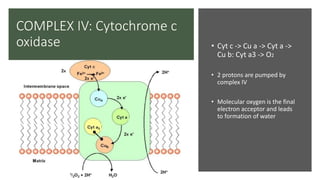
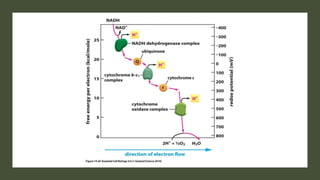
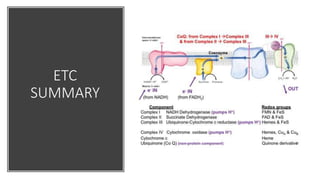
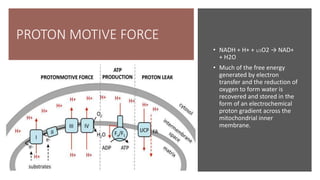
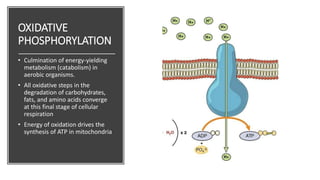
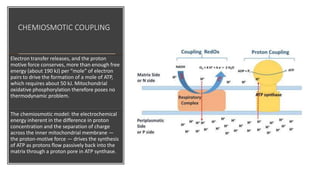
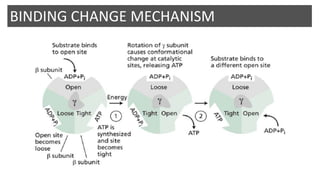
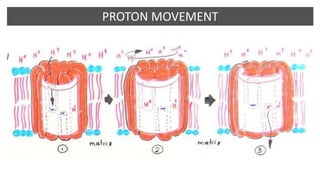
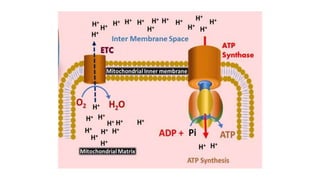
Mitochondria play a key role in cellular respiration through the electron transport chain (ETC) and oxidative phosphorylation. The ETC consists of four complexes that transfer electrons from electron carriers like NADH and FADH2 through redox reactions, pumping protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane. This creates a proton gradient that drives ATP synthase to generate ATP through chemiosmosis. The final complex uses oxygen as the terminal electron acceptor, reducing it to water. In this way, mitochondria harness the energy from oxidation to power ATP production through oxidative phosphorylation.