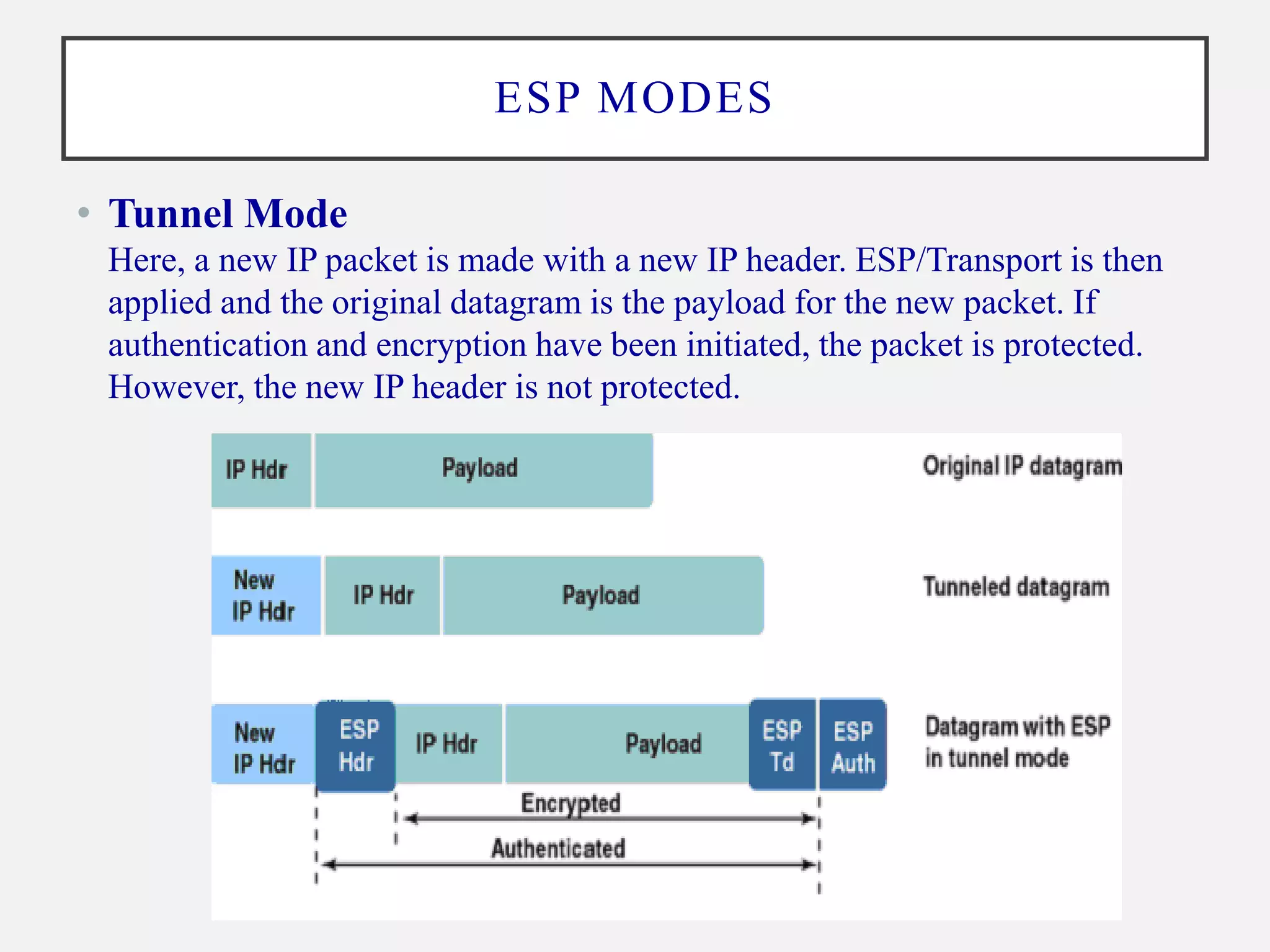
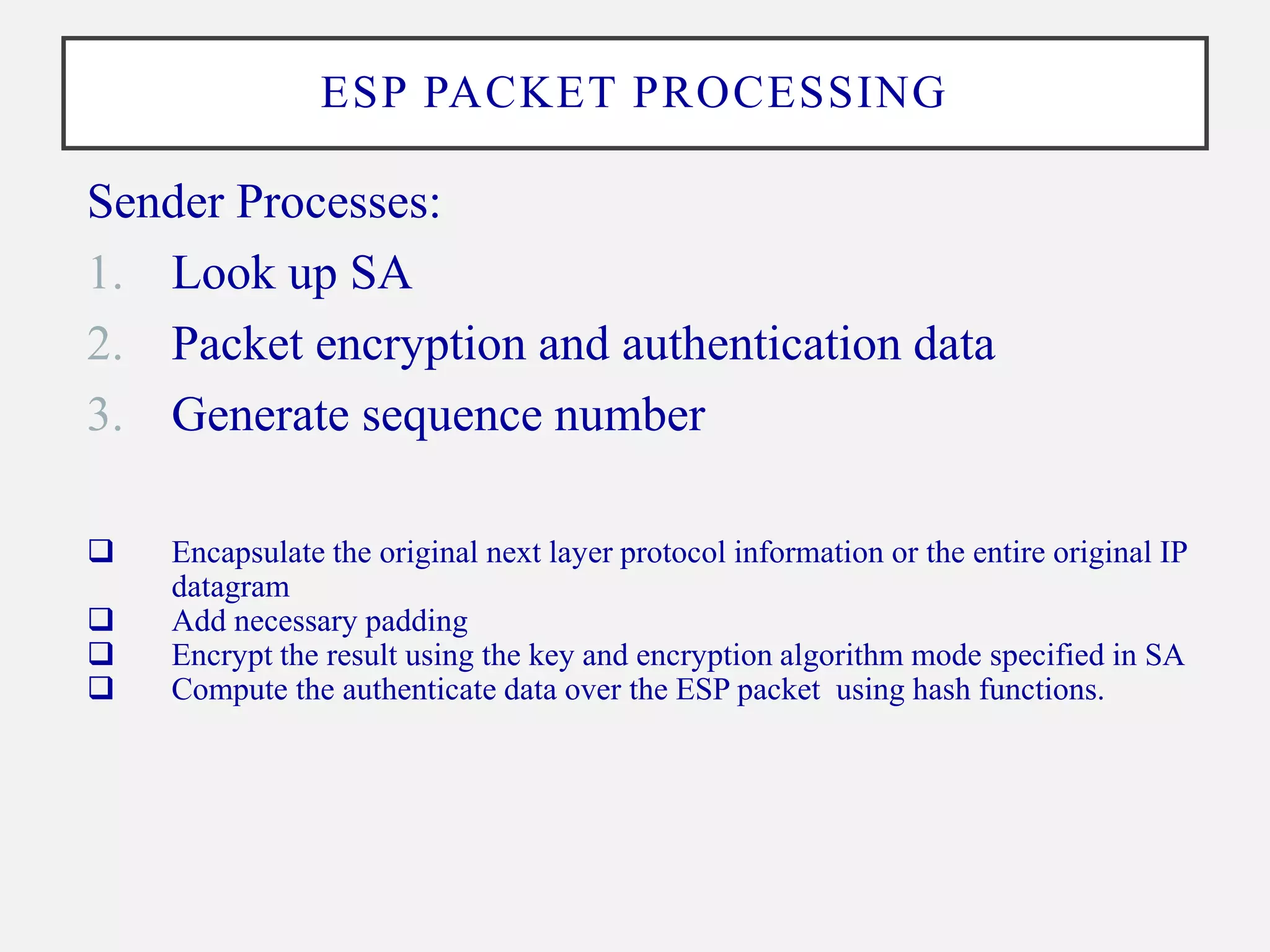
ESP provides encryption, authentication, and integrity for IP packets. It operates on a per-packet basis (ESP header and trailer encapsulate the payload) and supports transport and tunnel modes. The ESP packet fields include the SPI, sequence number, payload, padding, pad length, and ICV. ESP packet processing at the sender involves lookup SA, encryption, authentication, and sequencing. At the receiver, it involves verification of decryption, authentication and sequencing. ESP aims to provide data origin authentication, confidentiality, and traffic flow confidentiality with anti-replay detection.