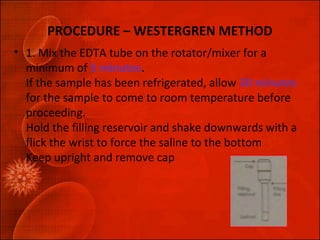
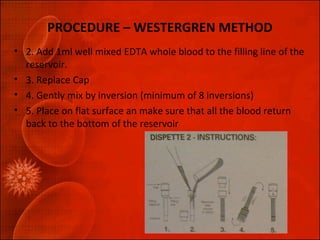
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a non-specific screening test used to indicate inflammation. There are two methods to determine ESR - Westergren and Wintrobe, with Westergren being most widely used. The ESR test measures how far red blood cells fall in a vertical tube over one hour, and an increased rate can indicate conditions involving inflammation like kidney disease, pregnancy, rheumatoid arthritis, and infections. Precise procedure and standardization of factors like anticoagulant used and tube filling are required to obtain an accurate ESR result.