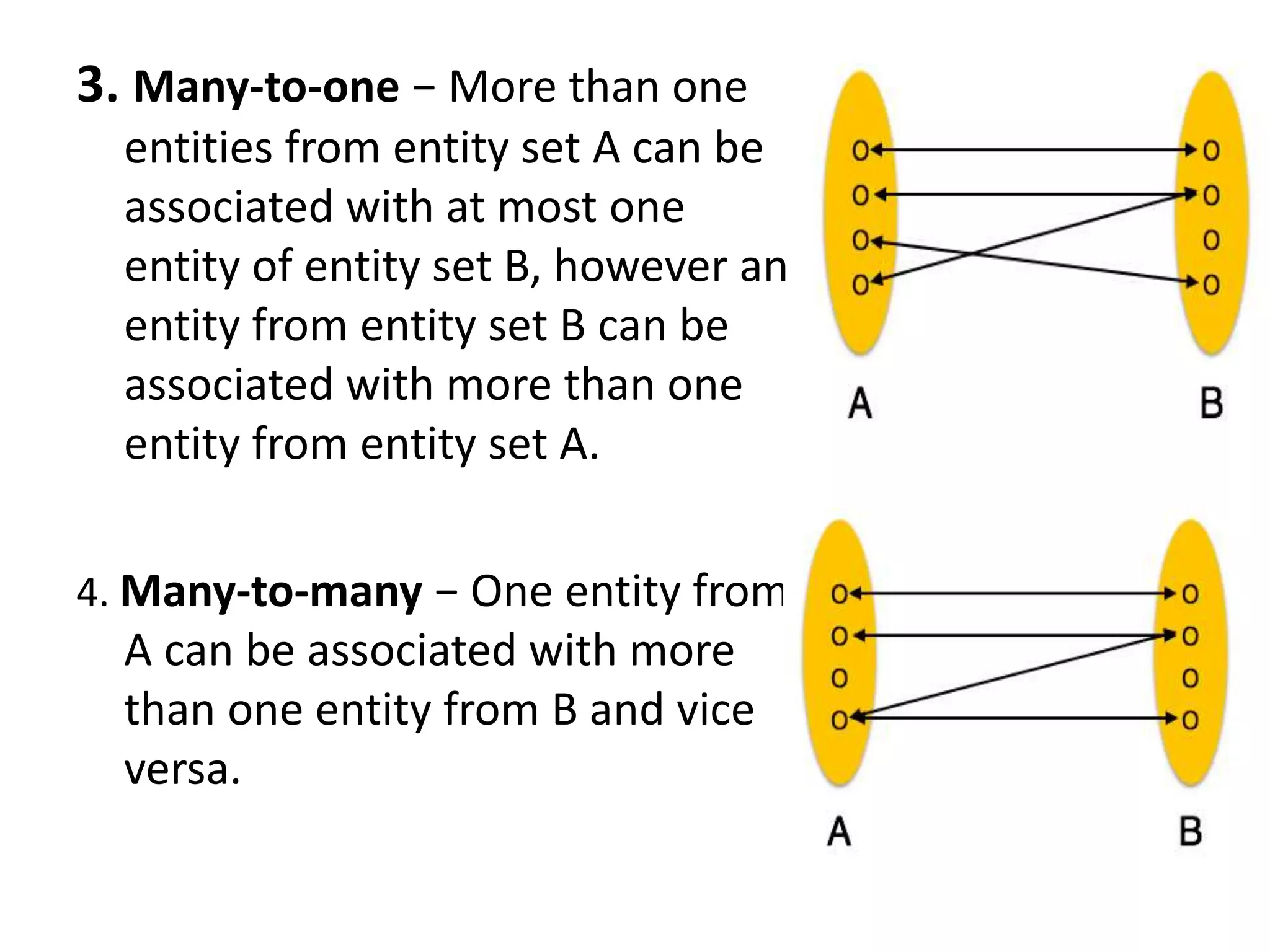
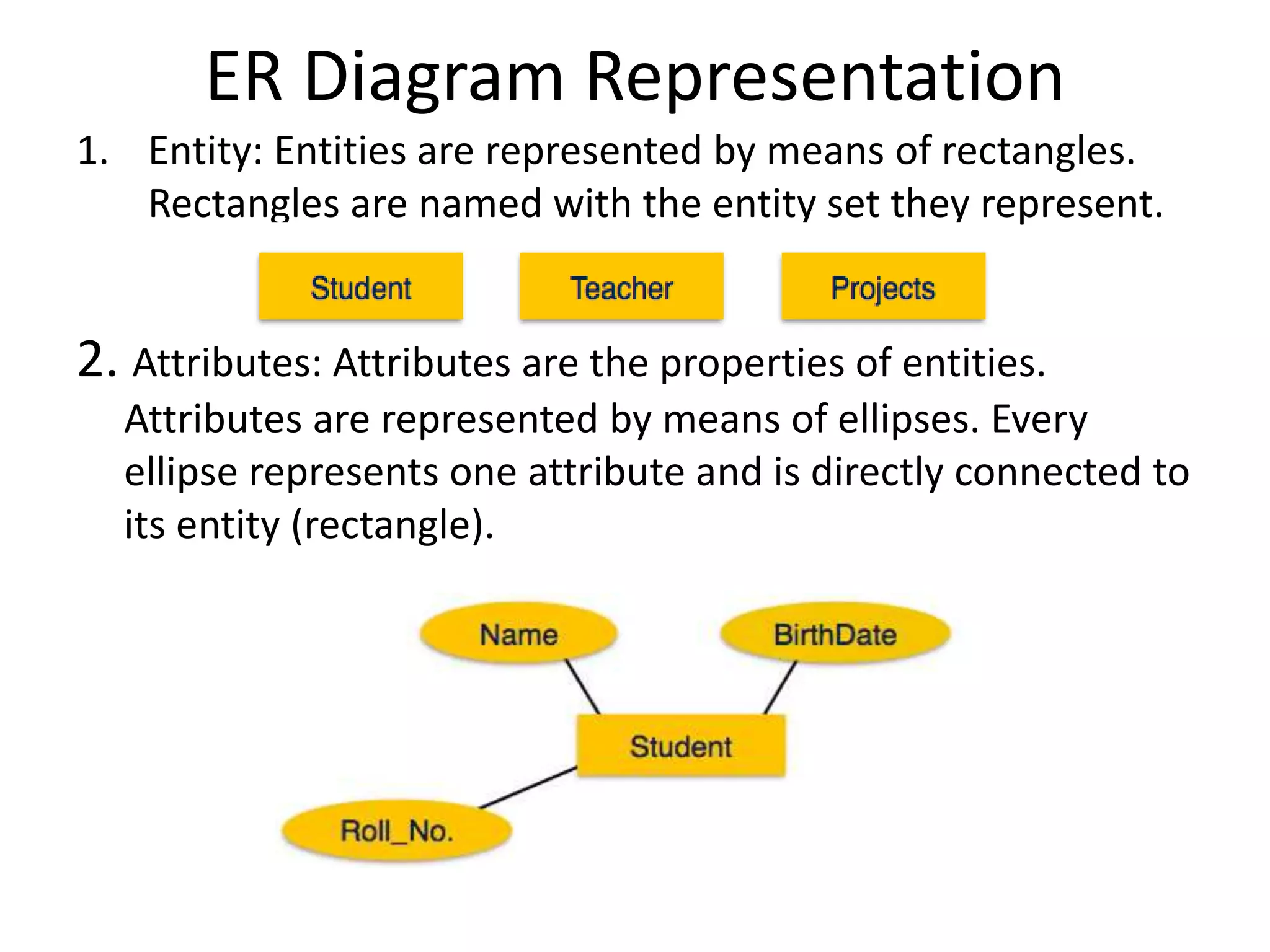
ER diagrams model the conceptual view of a database by representing real-world entities and the relationships between them. Entities have attributes that define their properties. Relationships associate entities and can be binary, ternary, or n-ary. Relationships have cardinalities like one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, or many-to-many to indicate the number of entities that can be related. ER diagrams visually depict these concepts using rectangles for entities, ellipses for attributes, diamonds for relationships, and notation like 1:N to specify cardinalities.