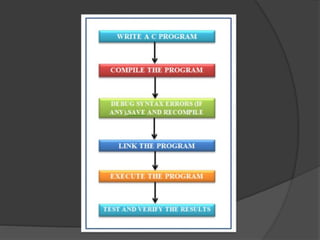
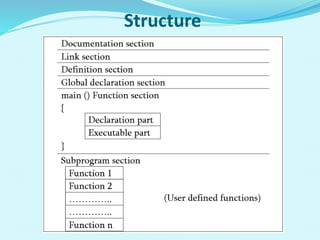
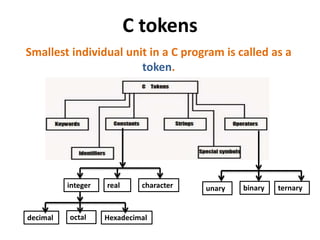
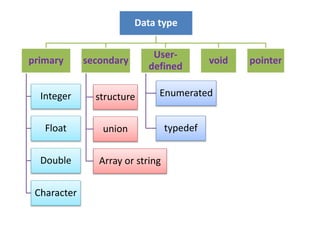
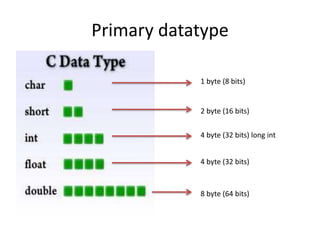
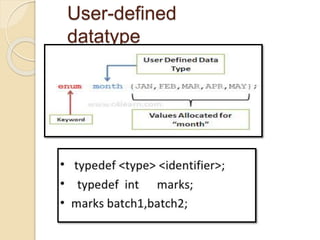
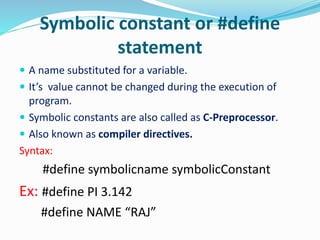
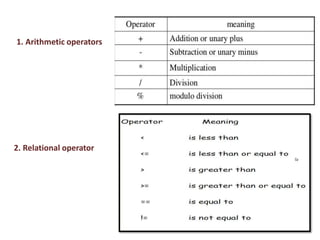
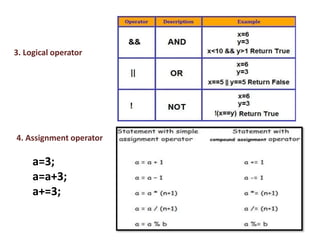
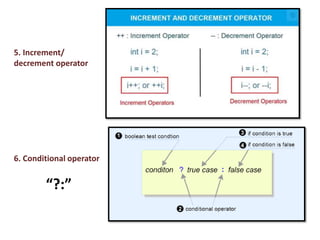
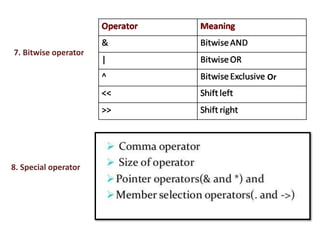
This document provides an overview of the C programming language. It discusses that C was developed at AT&T's lab by Dennis Ritchie and is a structured, portable, and reliable programming language. It then lists reasons for learning C like its use in operating systems and applications. The document outlines key features of C like portability, speed, and extensibility. It also describes the compilation process, data types, operators, and basic structure of a C program.