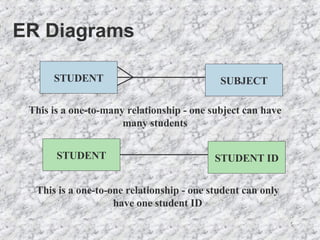
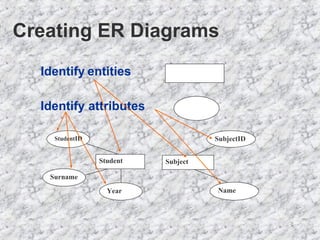
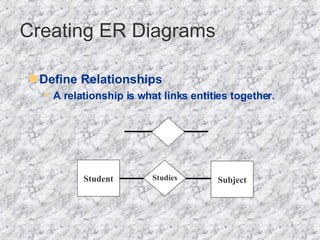
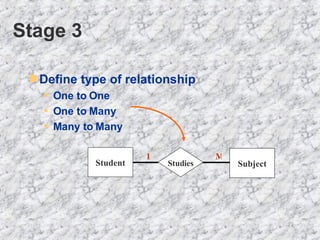
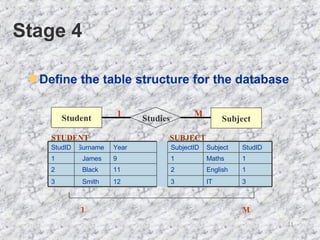
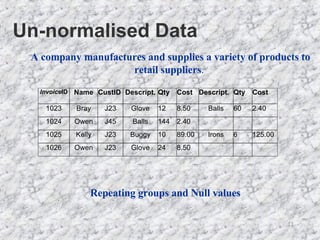
The document discusses relationships in relational databases. There are three main types of relationships: one-to-one, where each record in one table matches only one in another; one-to-many, where a record in one table can match many in another, which is the most common; and many-to-many, where records can match with many in both tables. Entity relationship (ER) diagrams are used to graphically represent entities as boxes, and relationships as lines between them with arrows indicating the relationship type. The process of creating ER diagrams involves identifying entities, defining relationships between them, specifying the relationship type, and defining the table structure.