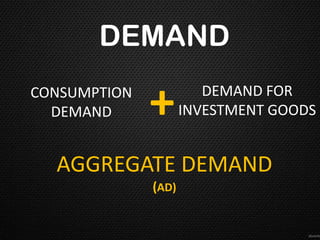
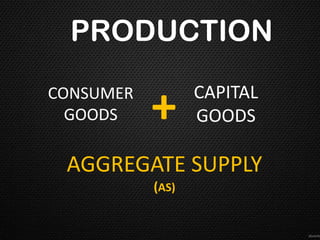
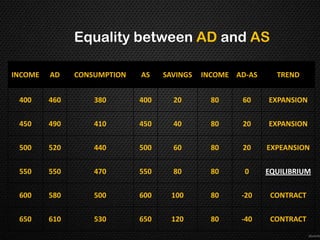
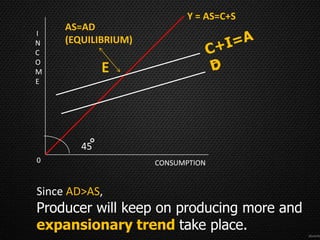
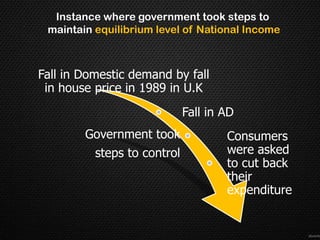
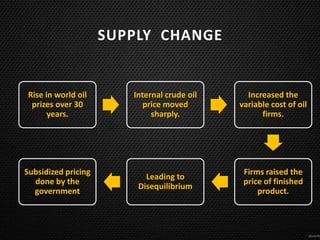
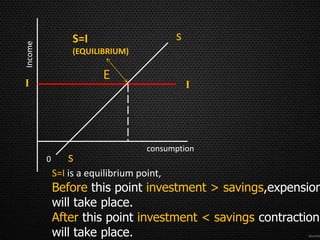
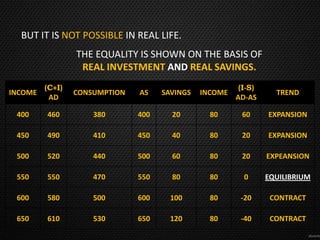
This document discusses the concept of equilibrium level of national income. It provides three main methods to measure national income - the product method, income method, and expenditure method. It explains that equilibrium occurs when aggregate demand (AD) equals aggregate supply (AS). The document uses a table to illustrate different scenarios when AD is greater than, less than, or equal to AS, and whether the economy is in a state of expansion, contraction, or equilibrium. It also gives examples of how governments may intervene to maintain equilibrium, such as by controlling consumption or subsidizing prices. Finally, it notes that while the Keynesian model shows savings equal to investment at equilibrium, this perfect equality does not always hold in reality due to differences between real and