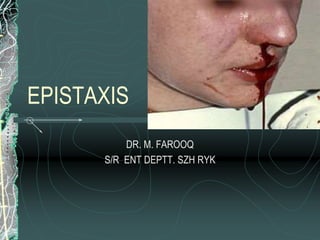
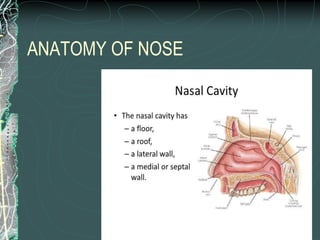
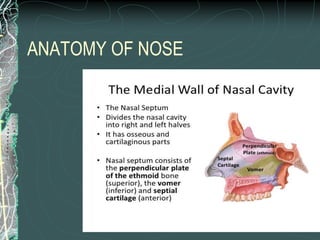
This document discusses epistaxis (nosebleeds), including its definition, anatomy, causes, classification, and management. It notes that epistaxis accounts for 30% of ENT admissions and can be caused by local nasal issues or systemic factors like high blood pressure. Treatment involves initial measures to stop bleeding followed by tests to identify the underlying cause. Options include nasal packing, cauterization, surgery, or embolization to control severe or recurrent bleeding. The document provides details on different surgical procedures for anterior vs. posterior bleeds.