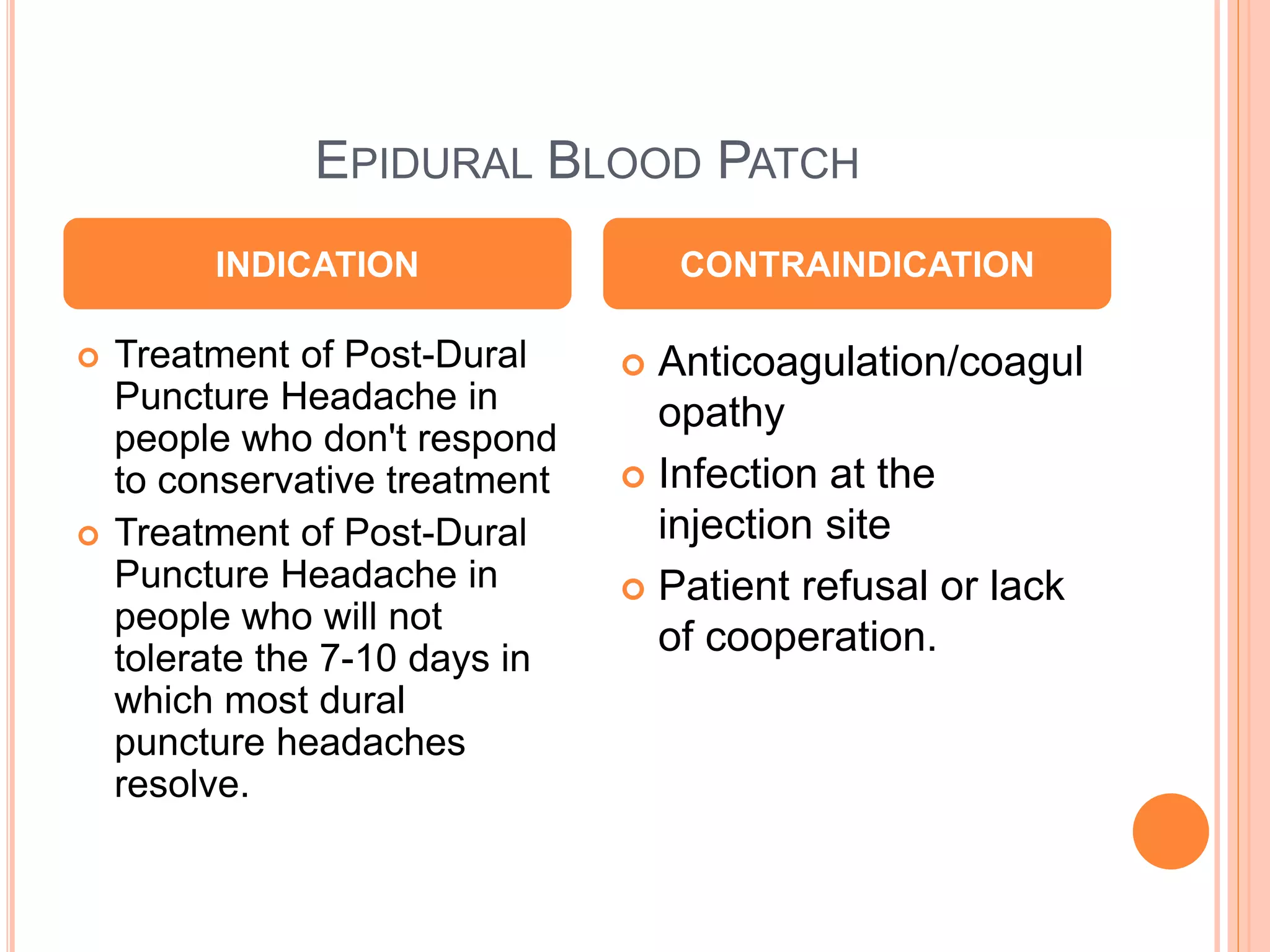
An epidural blood patch involves injecting the patient's own blood into the epidural space to treat a post-dural puncture headache that has not responded to conservative treatments like bed rest. It has an 85% success rate initially and up to 90% with repeated patches. The procedure involves identifying the epidural space and slowly injecting 5-25mL of blood drawn from the patient over 30-60 seconds. Complications can include worsening headaches from additional dural rents, back pain, or infection at the injection site.