Embed presentation
Downloaded 81 times




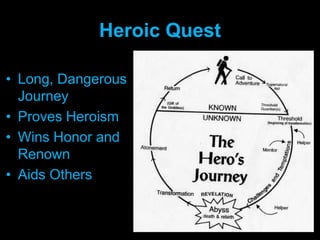






This document defines an epic as a long narrative poem about the adventures of a legendary hero that reflects the values of their culture. It describes common elements of epics such as an epic hero who embodies courage and virtue and goes on a long, dangerous quest where they perform valorous deeds and receive divine intervention to aid great historical or mythological events. Examples of folk epics composed through oral tradition include Beowulf and Gilgamesh, while later literary epics were written by individual authors like Homer's Iliad and Odyssey. Epics also share certain conventions in their characteristics and structure.










