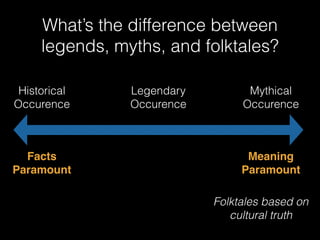
This document provides an overview of fairy tales and folklore. It defines folklore as traditional beliefs, customs, and stories passed down orally. The three main genres of folklore are legends, myths, and folktales. Fairy tales are considered a subgenre of folktales featuring fantasy elements. The document discusses characteristics of fairy tales like timeless settings and fantasy characters. It also covers the history and origins of fairy tales, how they have varied over time and place, and the work of the Brothers Grimm in collecting and publishing European folklore.