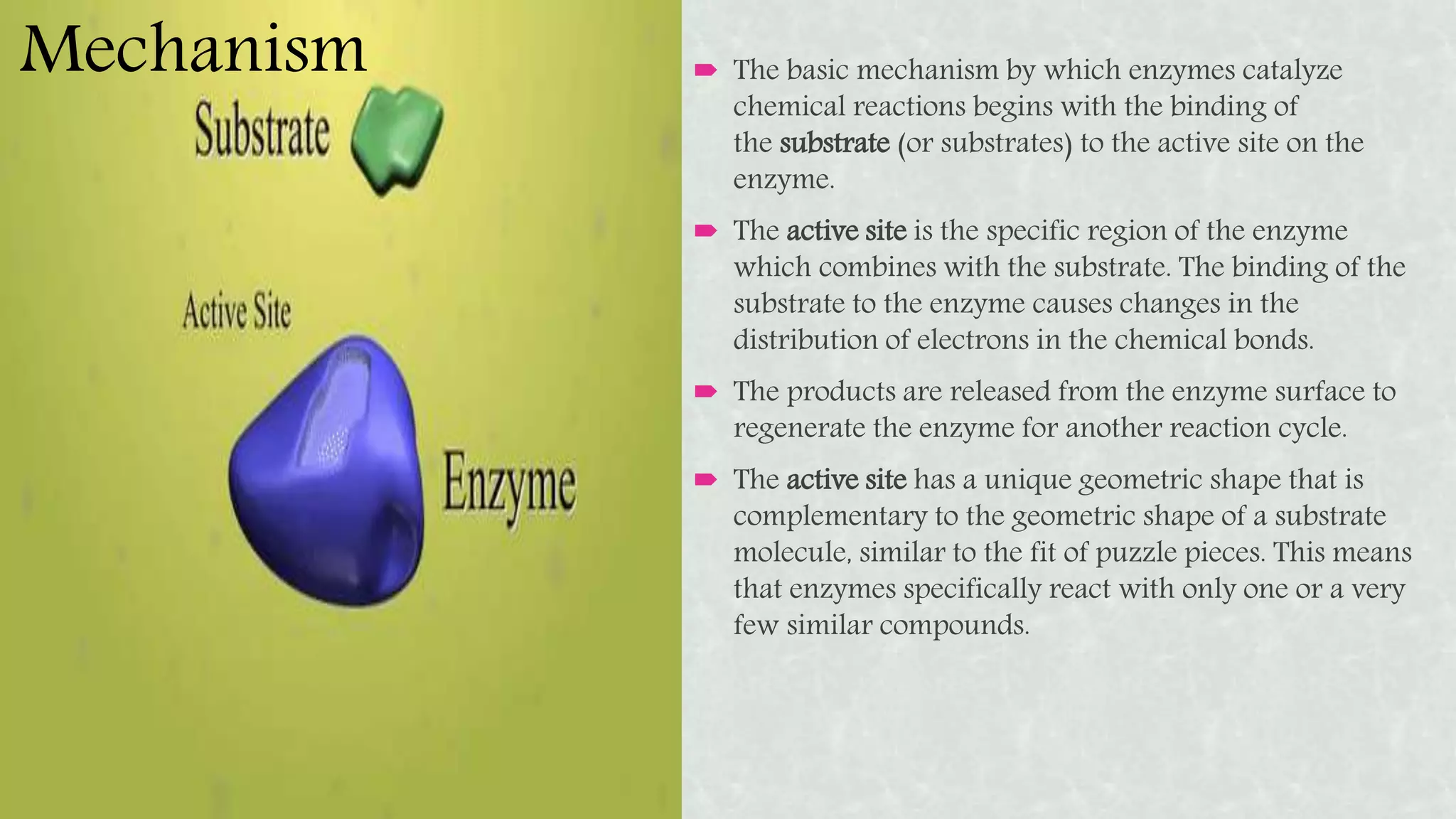
Enzymes are protein molecules that act as catalysts for chemical reactions in living organisms. They speed up reactions by lowering their activation energy but are not used up in the process. Enzymes have specific active sites that substrates bind to, and use lock-and-key or induced-fit mechanisms to catalyze reactions. The rate of enzymatic reactions depends on substrate concentration according to Michaelis-Menten kinetics, characterized by the parameters Km and Vmax. Enzymes are essential for many biological functions and processes and have important industrial applications like food production, biofuels, and cleaning products.