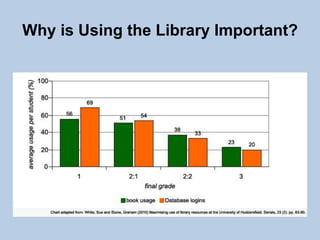
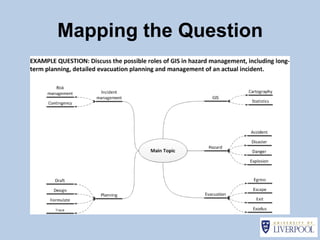
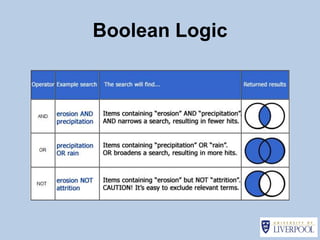
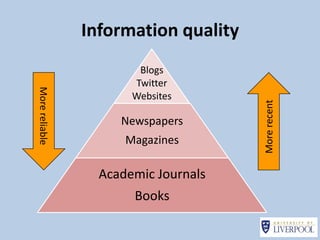
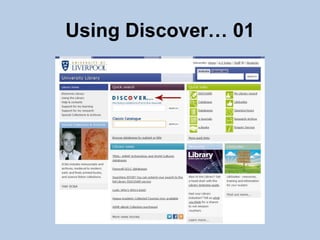
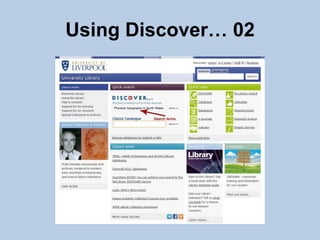
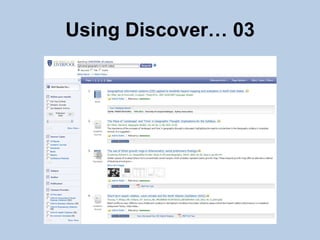
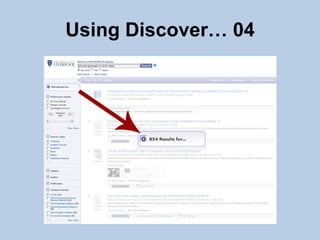
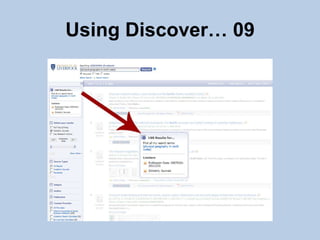
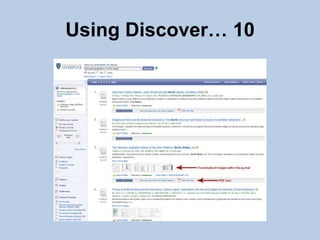
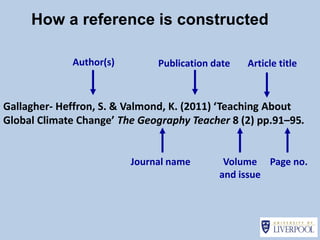
This document provides guidance on effectively using library resources to research assignments. It outlines six key learning outcomes, including developing search strategies using keywords, being aware of reference sources to expand knowledge, evaluating information quality, understanding peer review, and constructing references. The document offers tips for analyzing assignment questions, identifying keywords, using reference sources, evaluating websites and information, and providing references to avoid plagiarism.