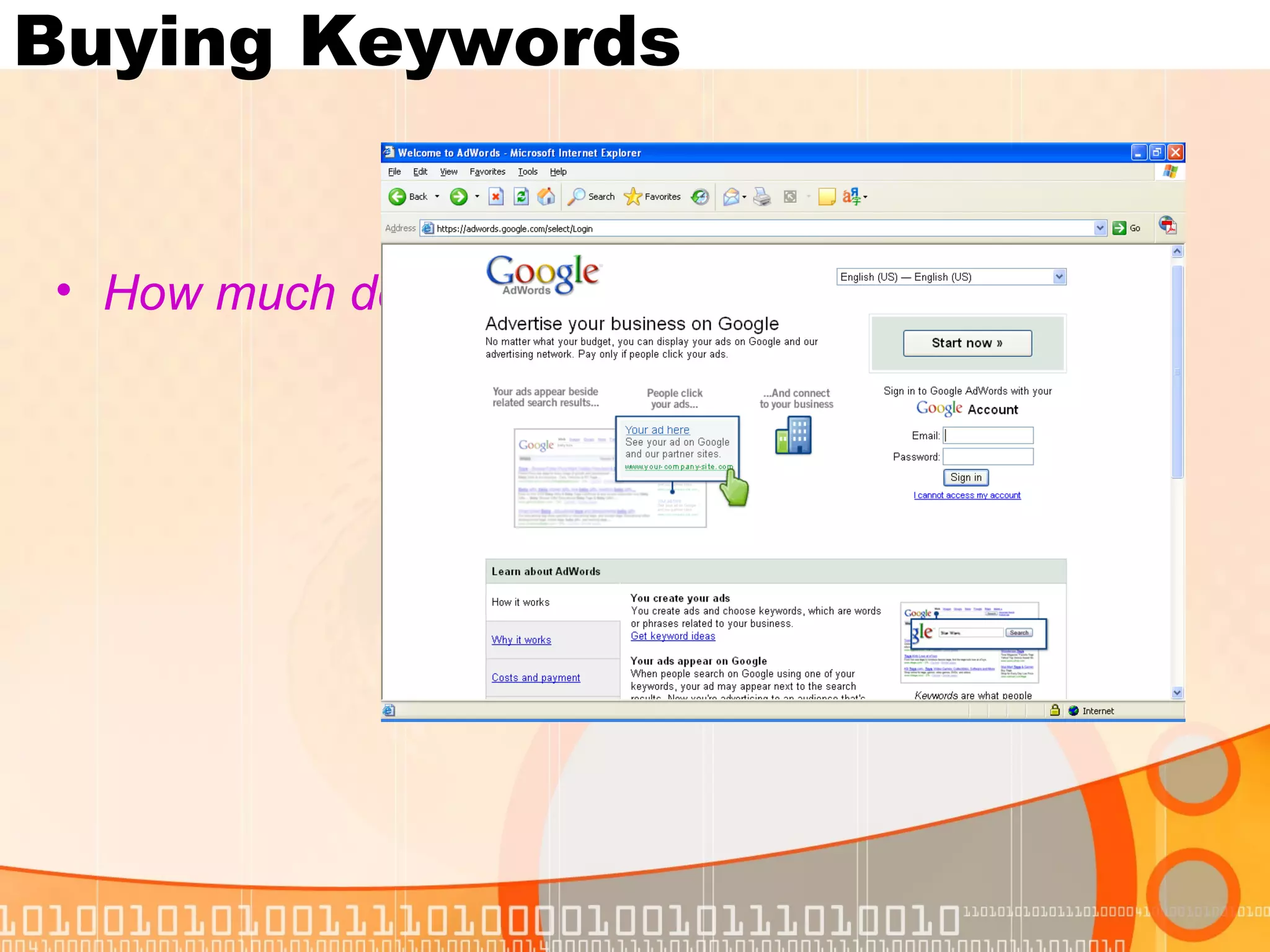
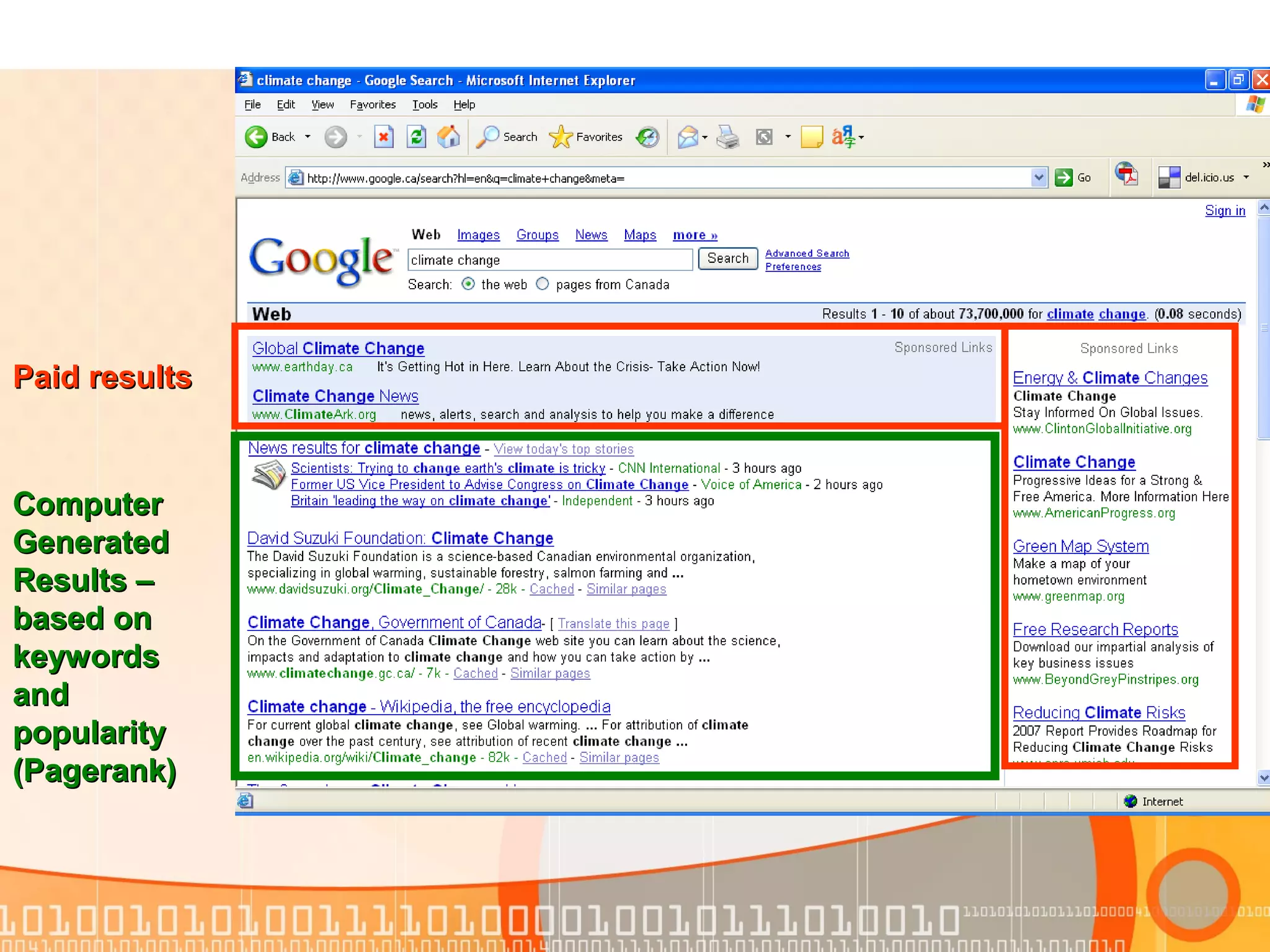
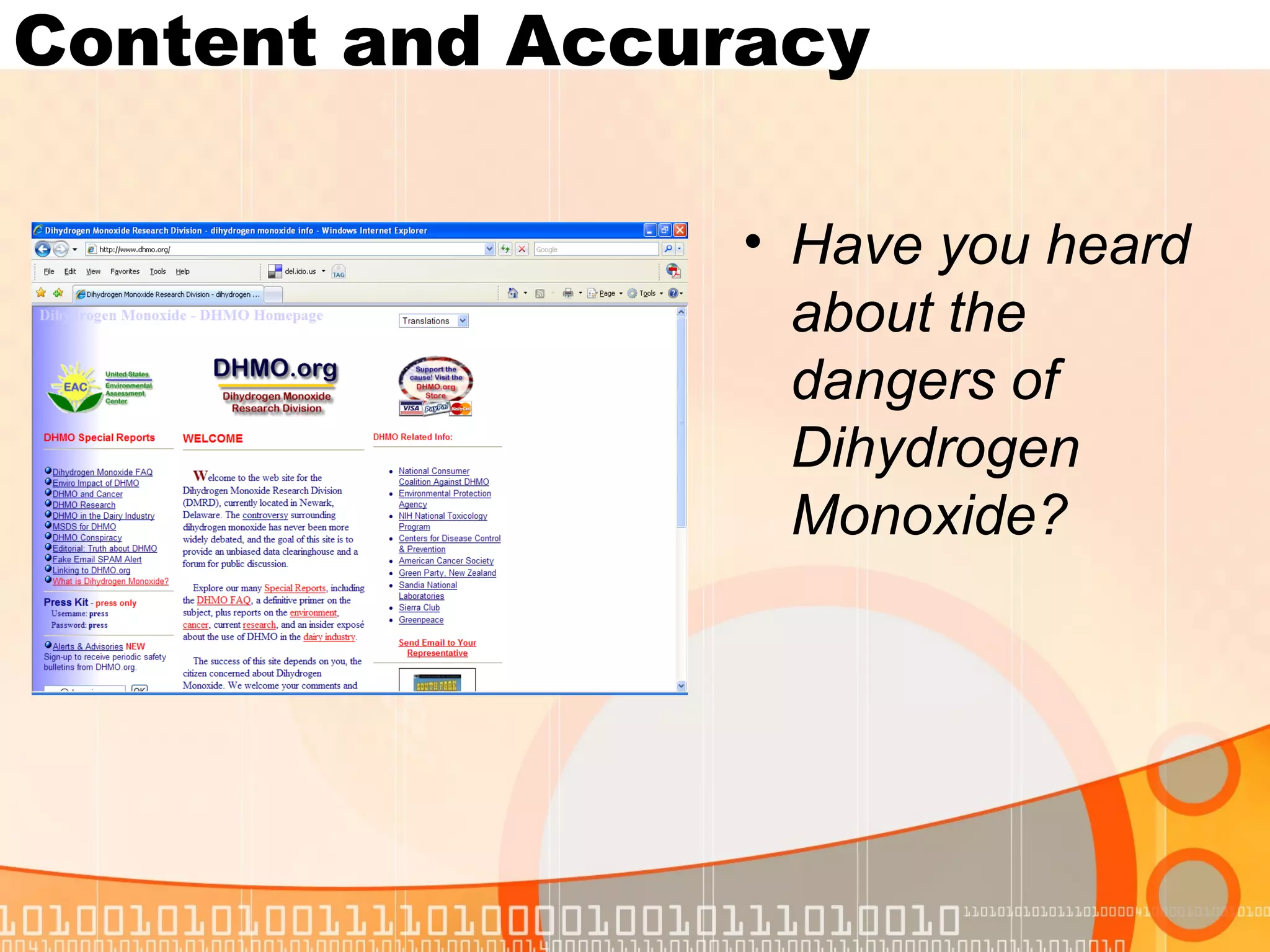
This document provides guidance on evaluating internet sites for research purposes. It emphasizes checking a site for authority, objectivity/bias, content and accuracy, and currency. Key factors include examining the author's credentials, potential agenda, sourcing and documentation of information, and date of publication. Students should use authoritative sources like online encyclopedias whenever possible rather than potentially unreliable or biased personal websites.