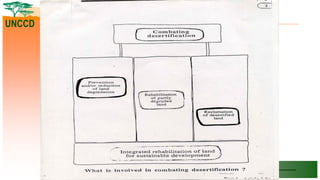
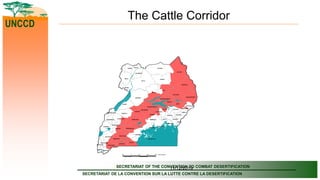
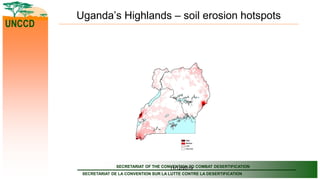
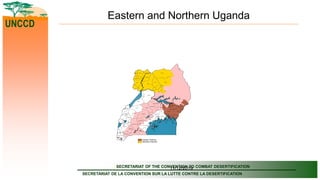
The document outlines the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) and its relevance to Uganda, detailing the country's commitment to combat desertification and mitigate drought effects since it signed the convention in 1994. It highlights the definition of desertification, priority areas for implementation in Uganda, major causes of land degradation, and institutional arrangements for executing the UNCCD. Additionally, it presents strategic frameworks and sector roles to enhance sustainable land management and achieve land degradation neutrality by 2030.