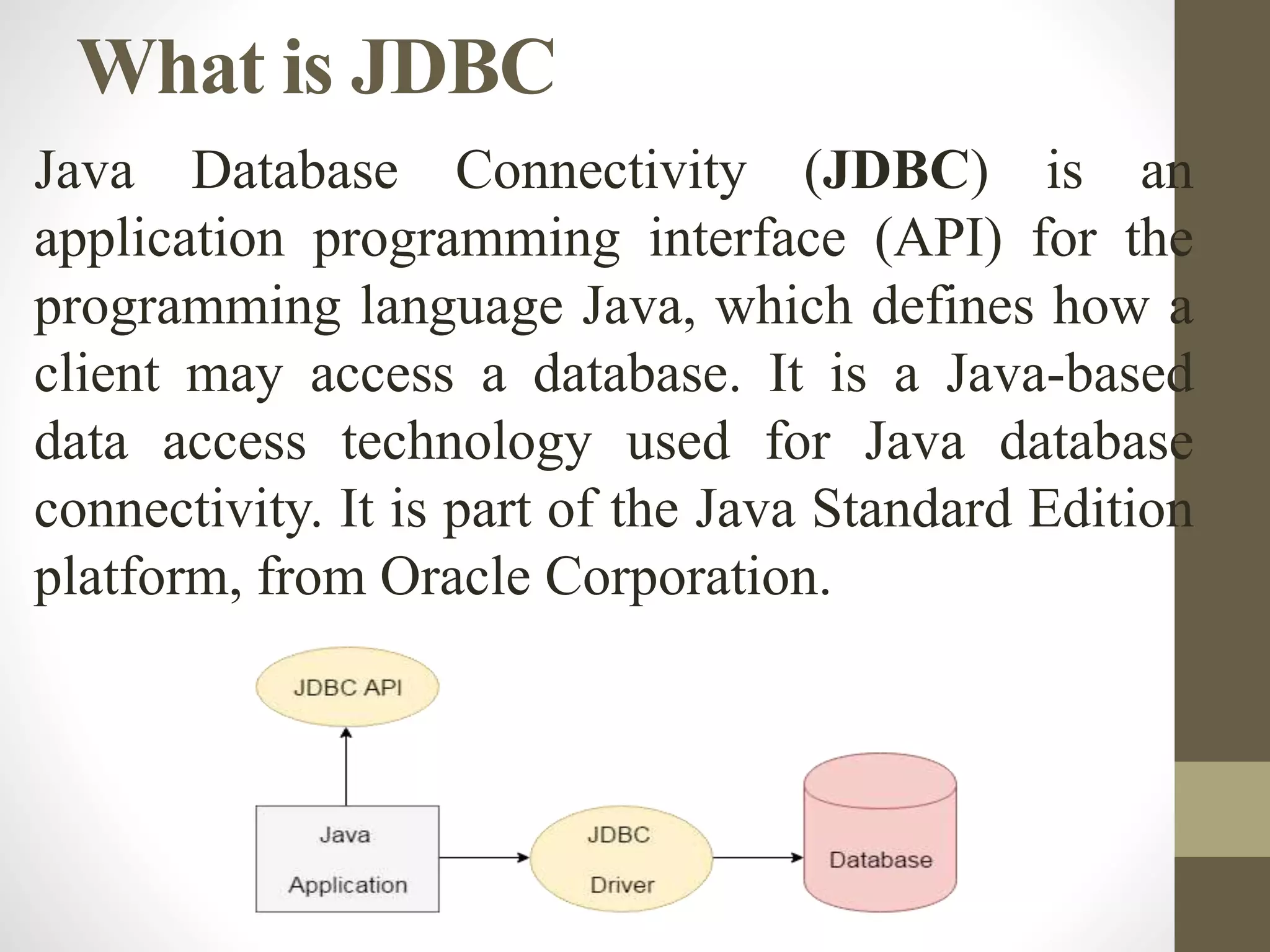
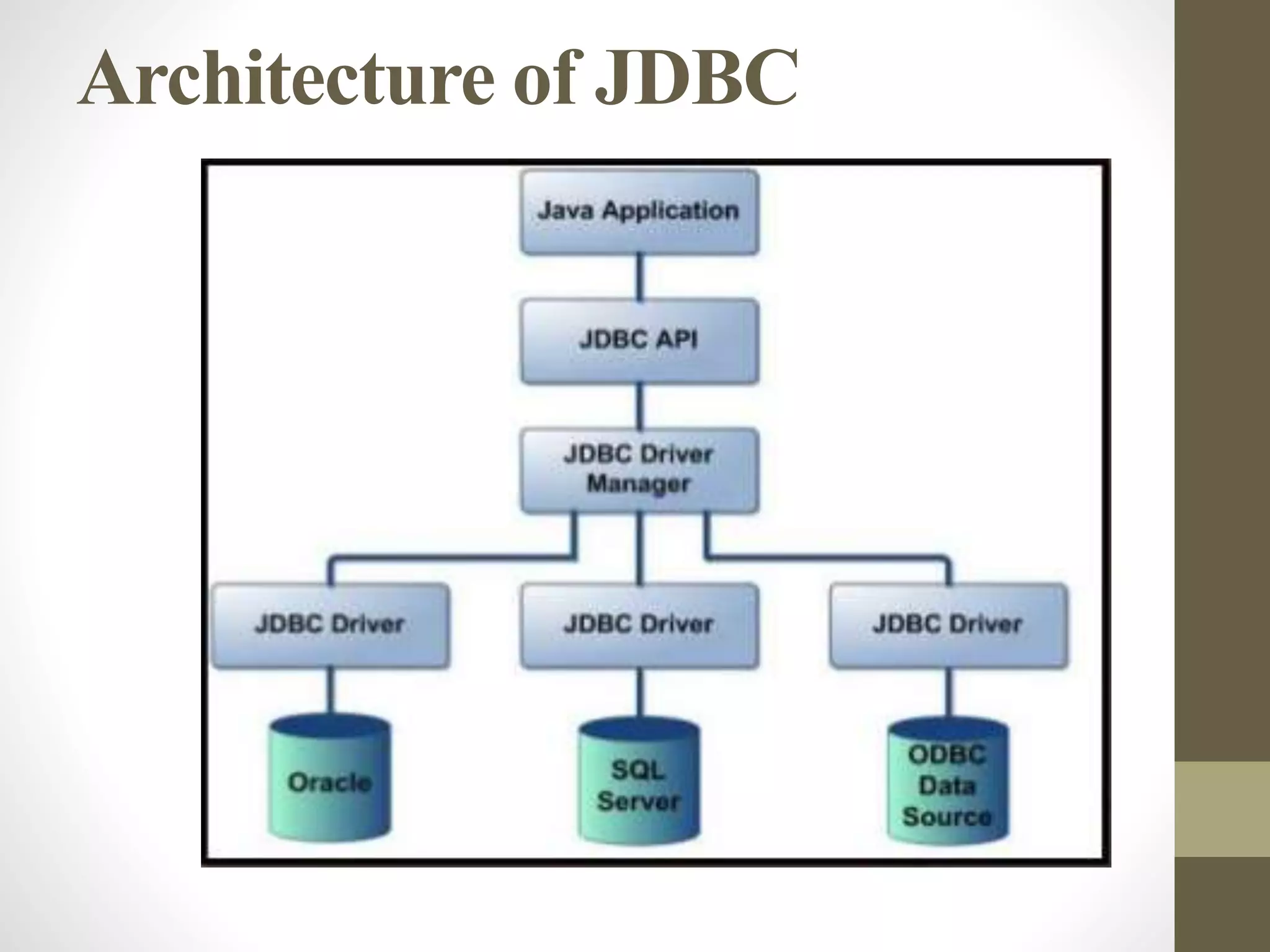
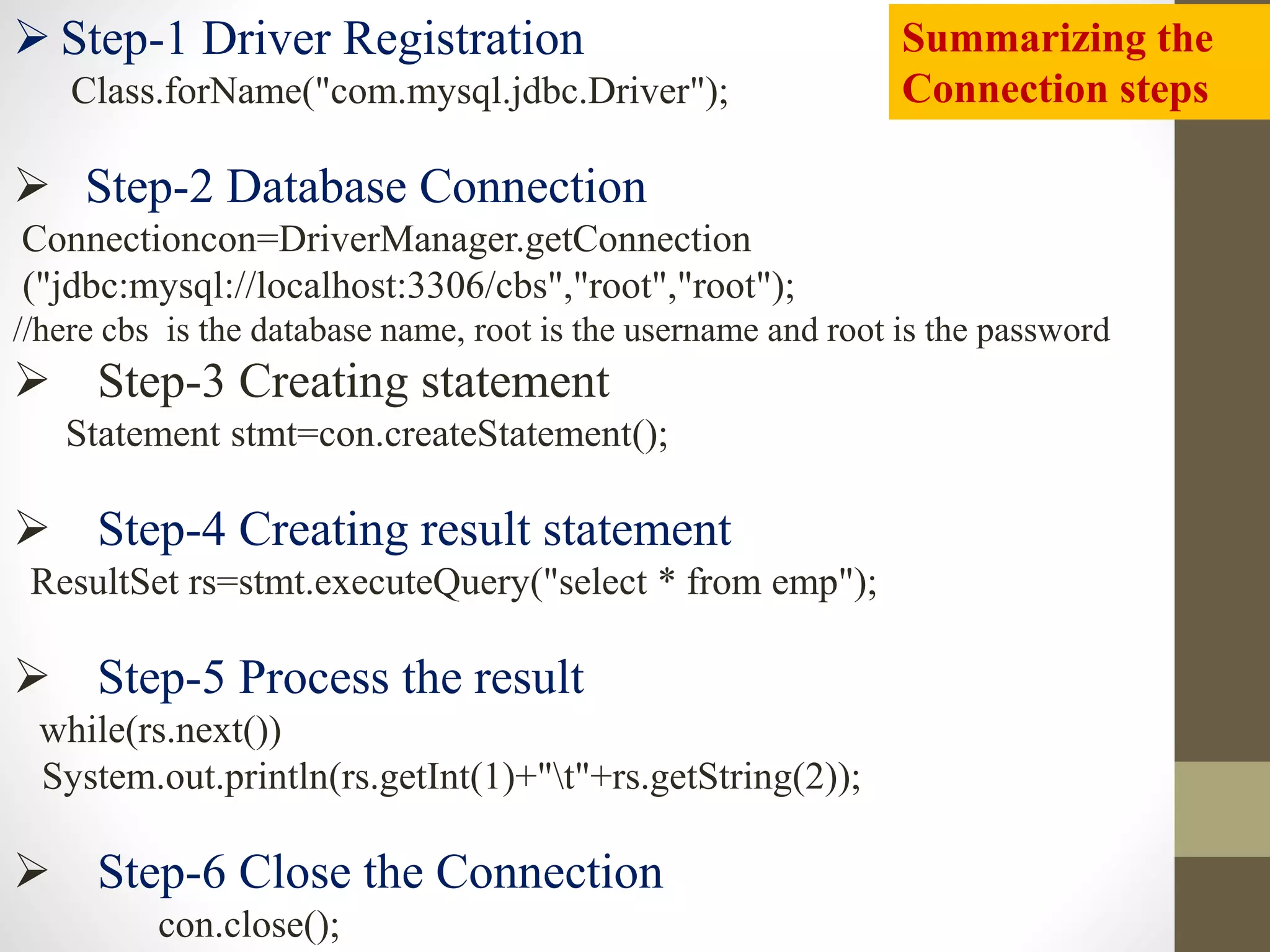
This document discusses Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) and the steps to connect to a database using JDBC. It provides an overview of JDBC architecture and its main components. It then outlines the key steps to connect to a database which include: 1) driver registration where the appropriate JDBC driver class is loaded, 2) defining the connection URL, 3) establishing a connection, 4) creating SQL statements, 5) executing queries and processing result sets, and 6) closing the connection. Examples are provided for connecting to MySQL and Derby databases using JDBC.