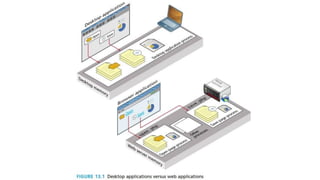
This document discusses different techniques for managing state in web applications:
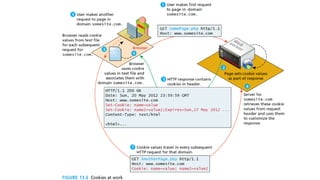
- Cookies store name-value pairs on the client-side and accompany HTTP requests/responses to persist user information across sessions. They can be session-based or persistent.
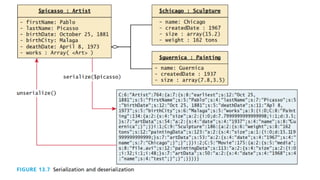
- Serialization converts objects to binary strings for storage or transmission. Classes need to implement the Serializable interface.
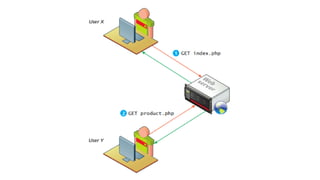
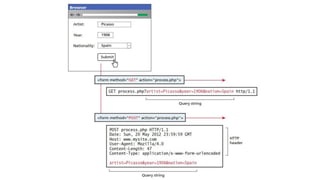
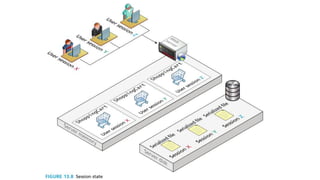
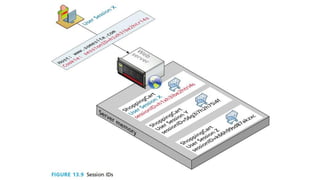
- Session state stores serialized objects on the server for each user session. It relies on session IDs transmitted via cookies or URLs.
- HTML5 Web storage APIs like localStorage and sessionStorage store data client-side instead of transmitting with each request. localStorage persists across sessions while sessionStorage lasts one session.
- Caching locally stores files







![Accessing session state
<?php
session_start();
if ( isset($_SESSION['user']) ) {
// User is logged in
}
else {
// No one is logged in (guest)
}
?>
• Session state relies on session IDs that are
transmitted via cookies or via embedding in the URL
path.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5jquery-191220054404/85/Module-5_WTA_Managing-State-jQuery-15-320.jpg)



