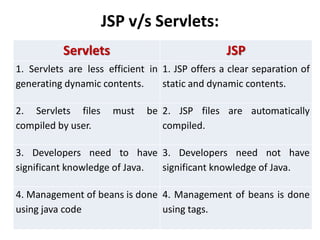
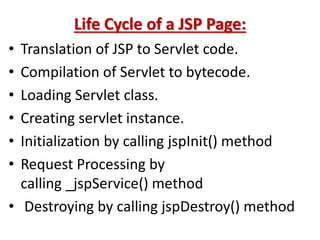
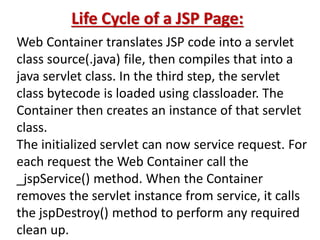
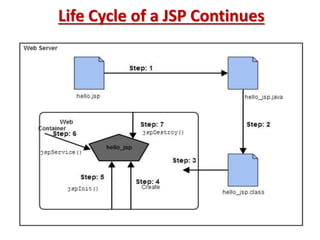
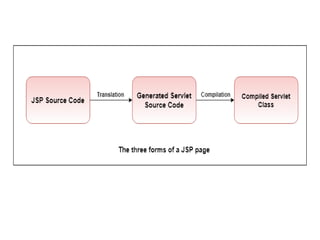
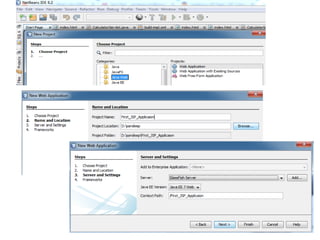
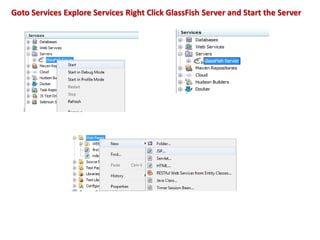
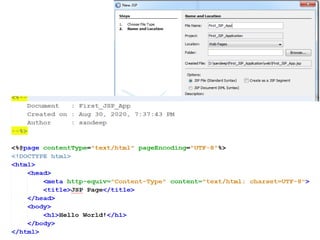
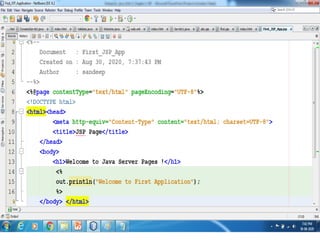
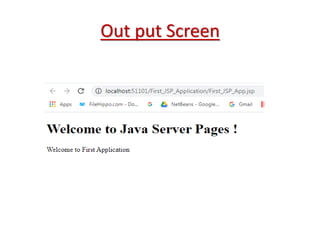
This document provides an introduction and overview of Java Server Pages (JSP) technology. It discusses what JSP is, its advantages over other technologies like CGI and servlets, its life cycle, and how to create basic JSP applications. Key points include: JSP allows embedding dynamic Java code in HTML pages, separates presentation and business logic, offers performance benefits over CGI, and supports features like tag libraries. The JSP life cycle mirrors that of servlets, with an initial translation of JSP to servlet code before compilation and execution.