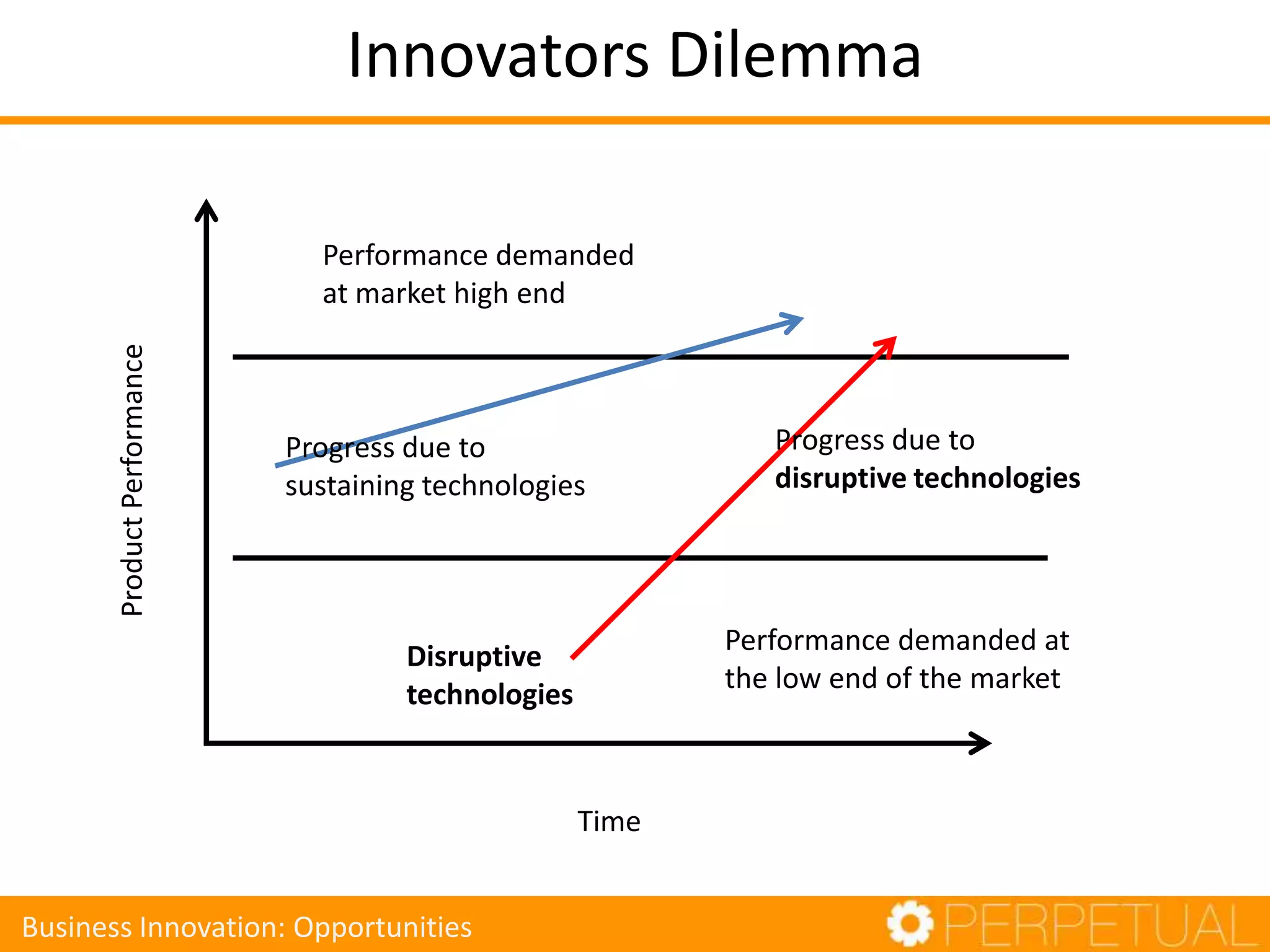
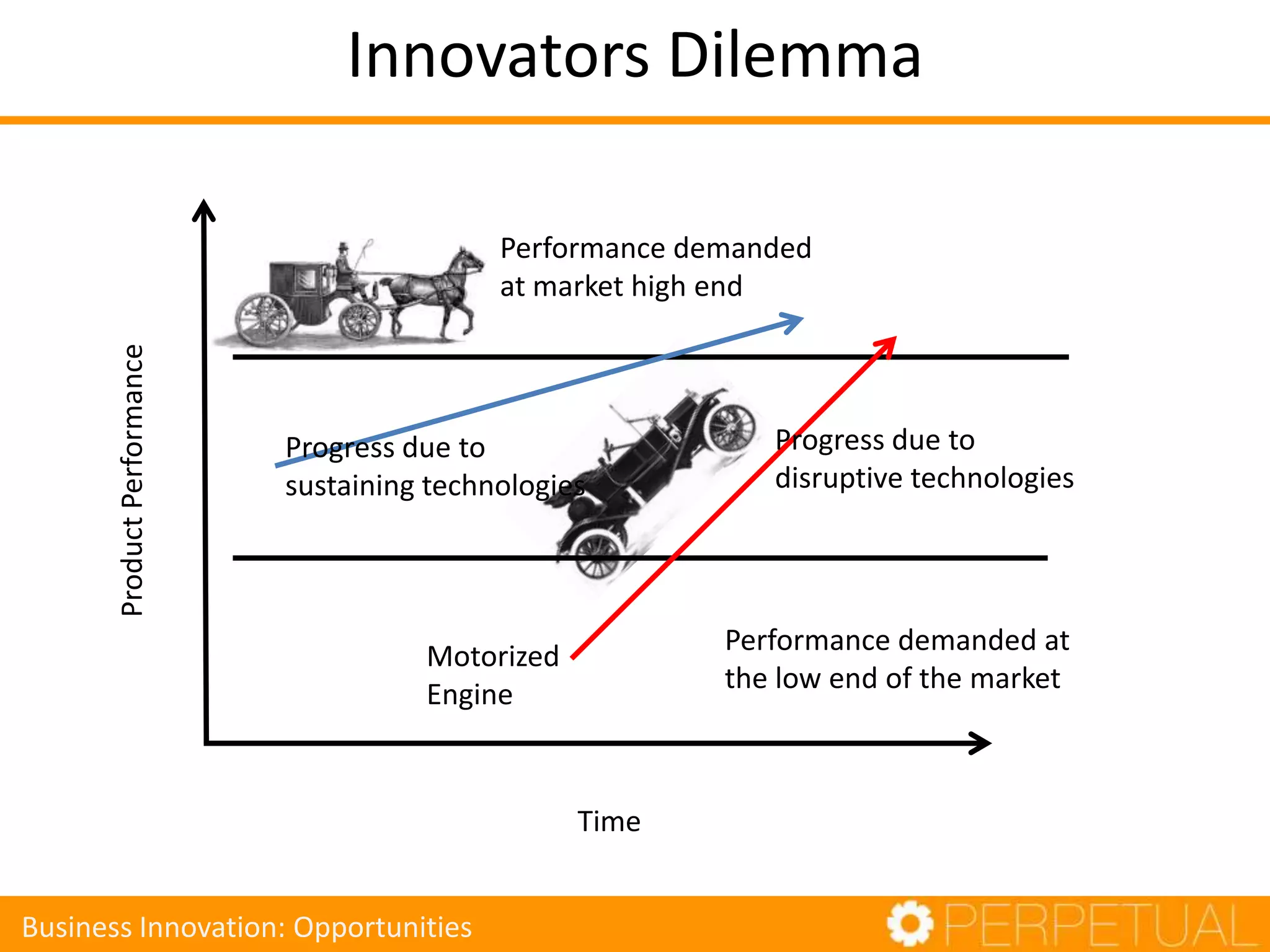
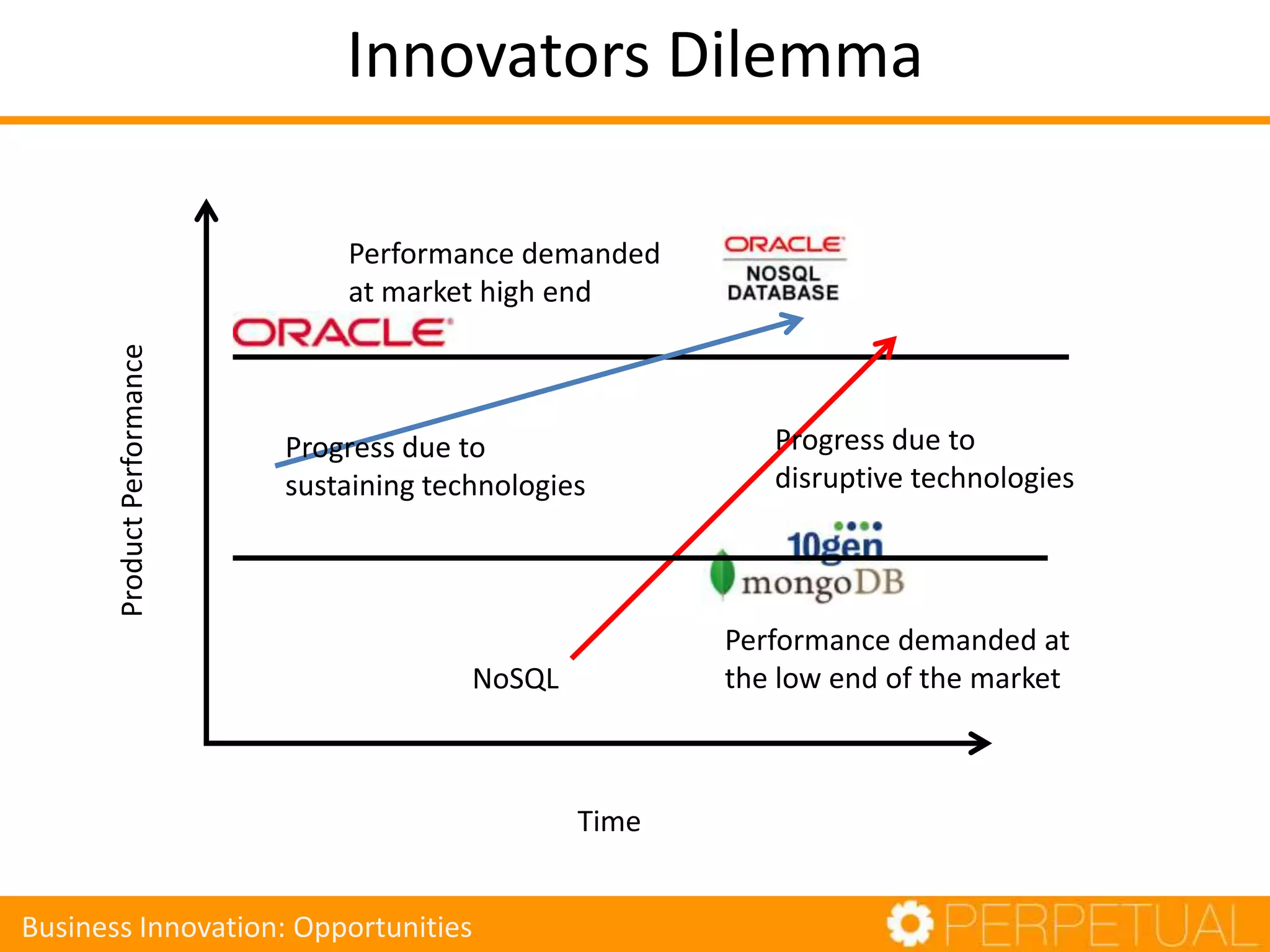
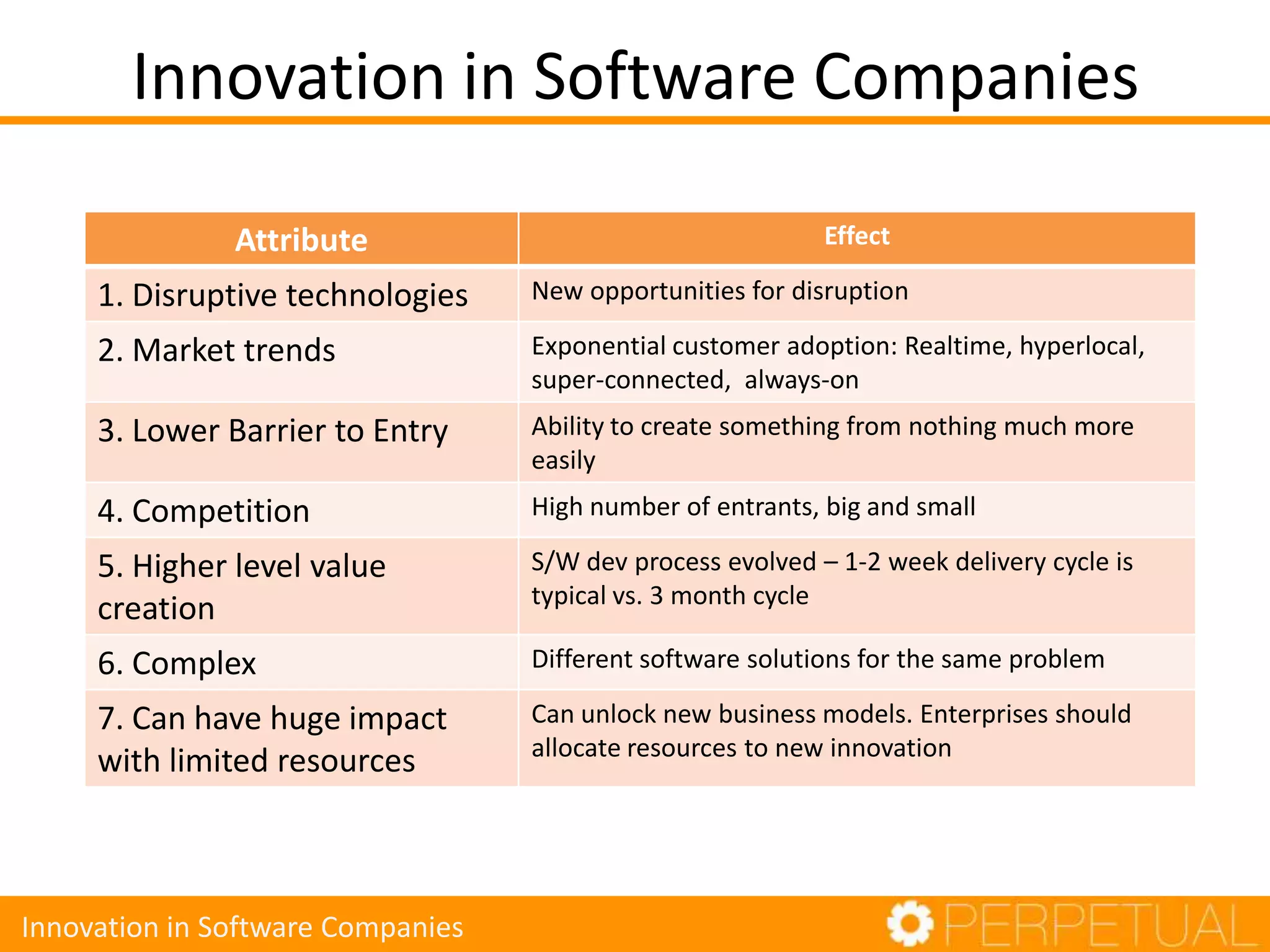
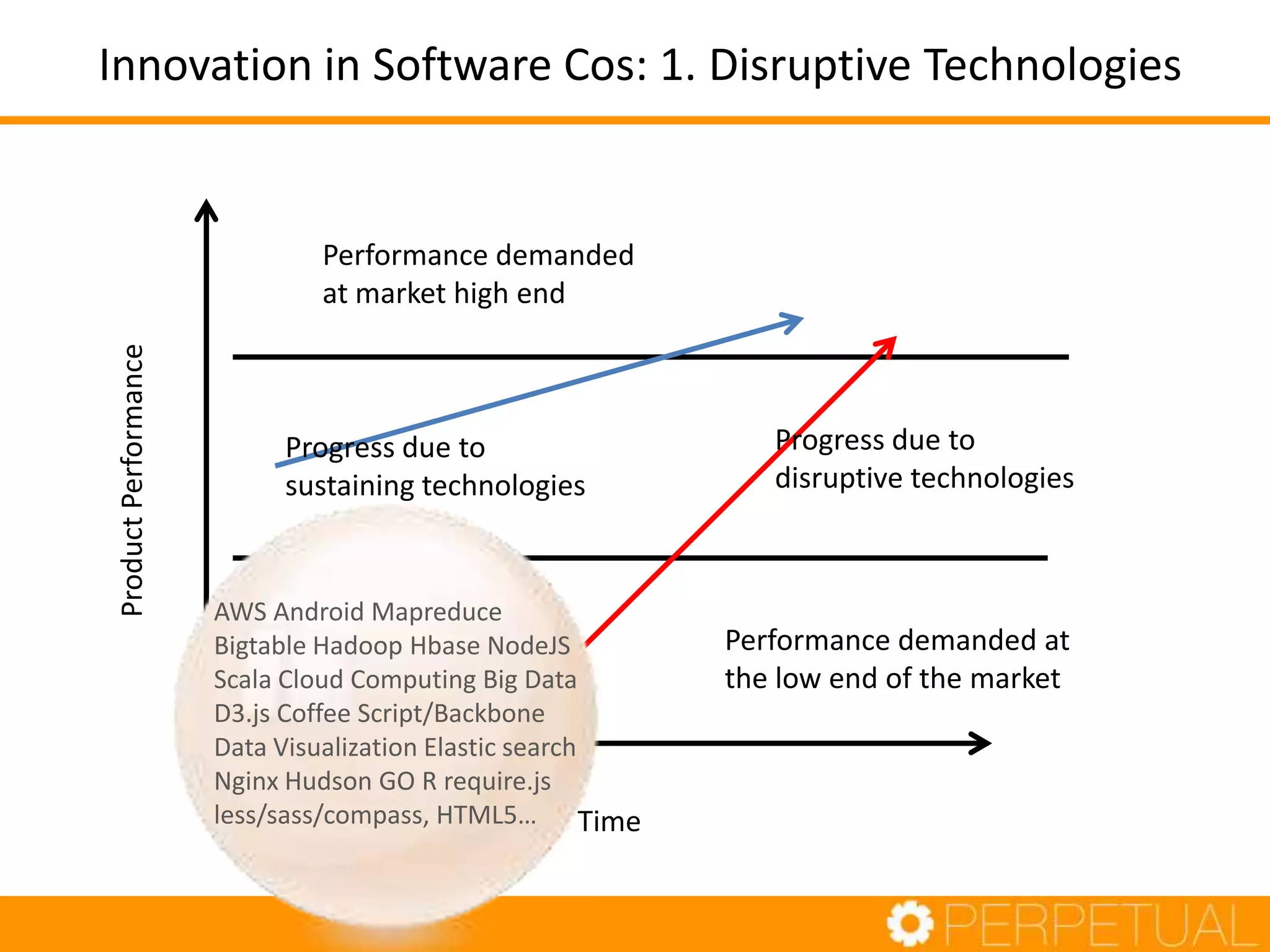
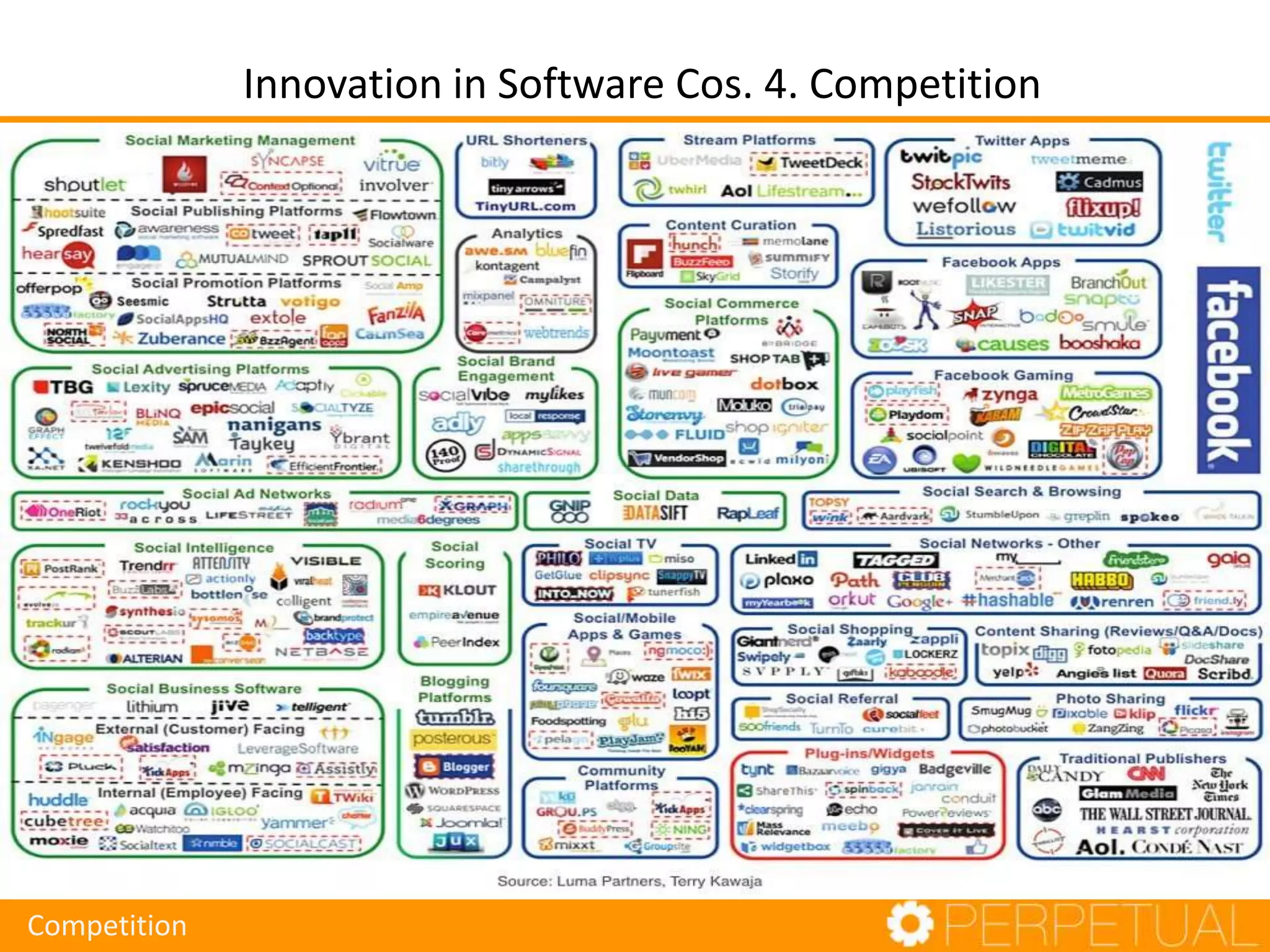
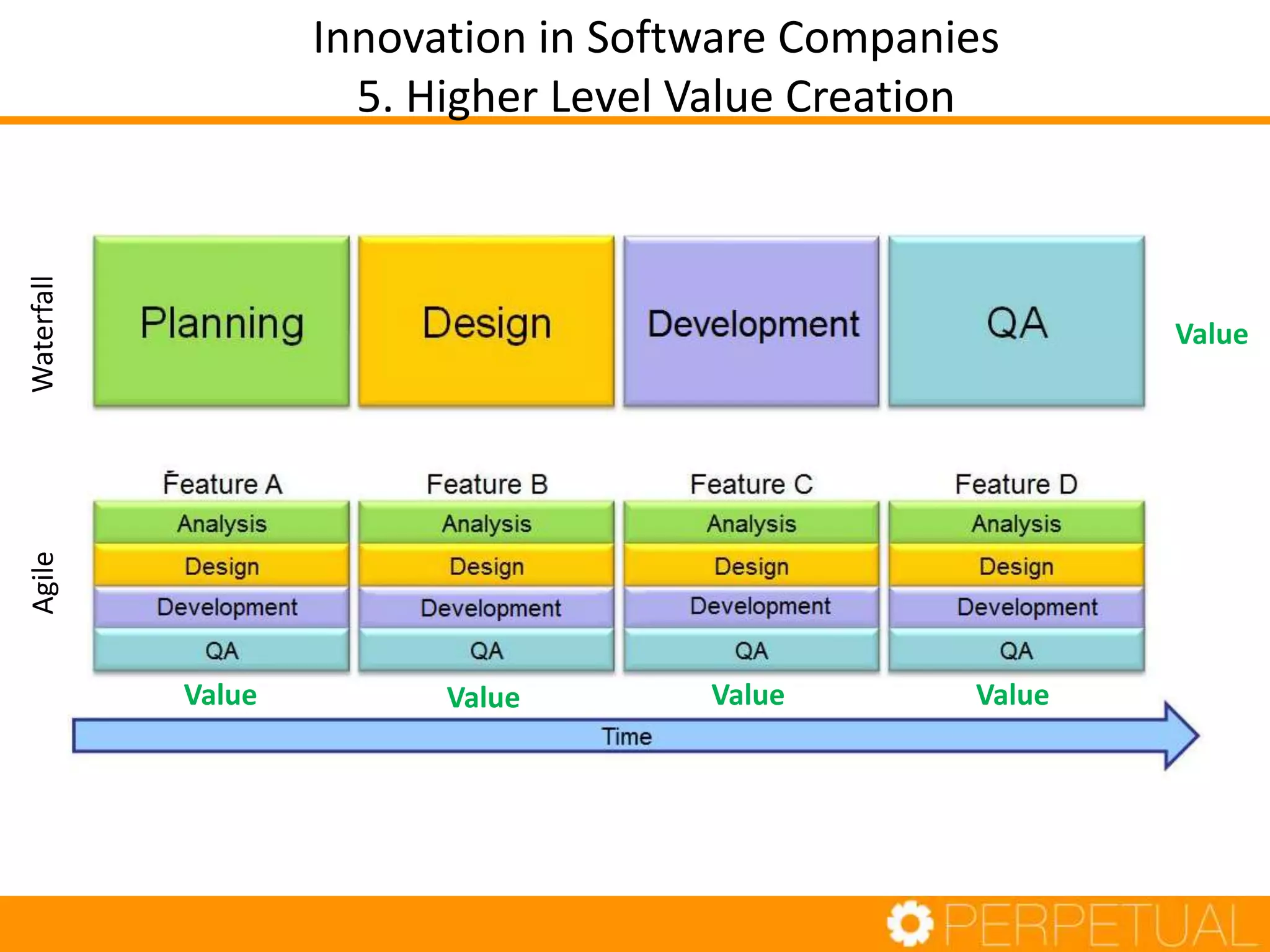
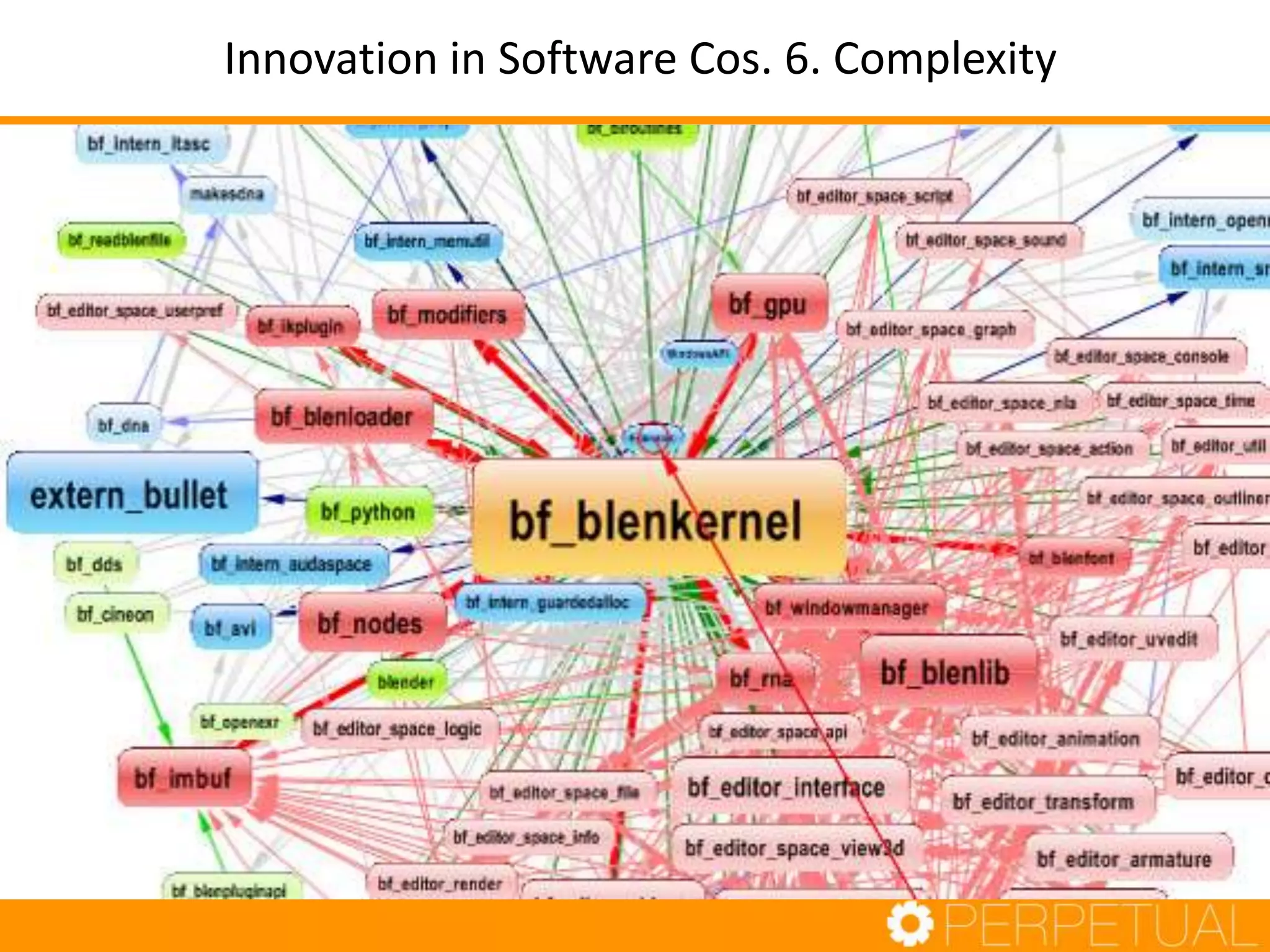
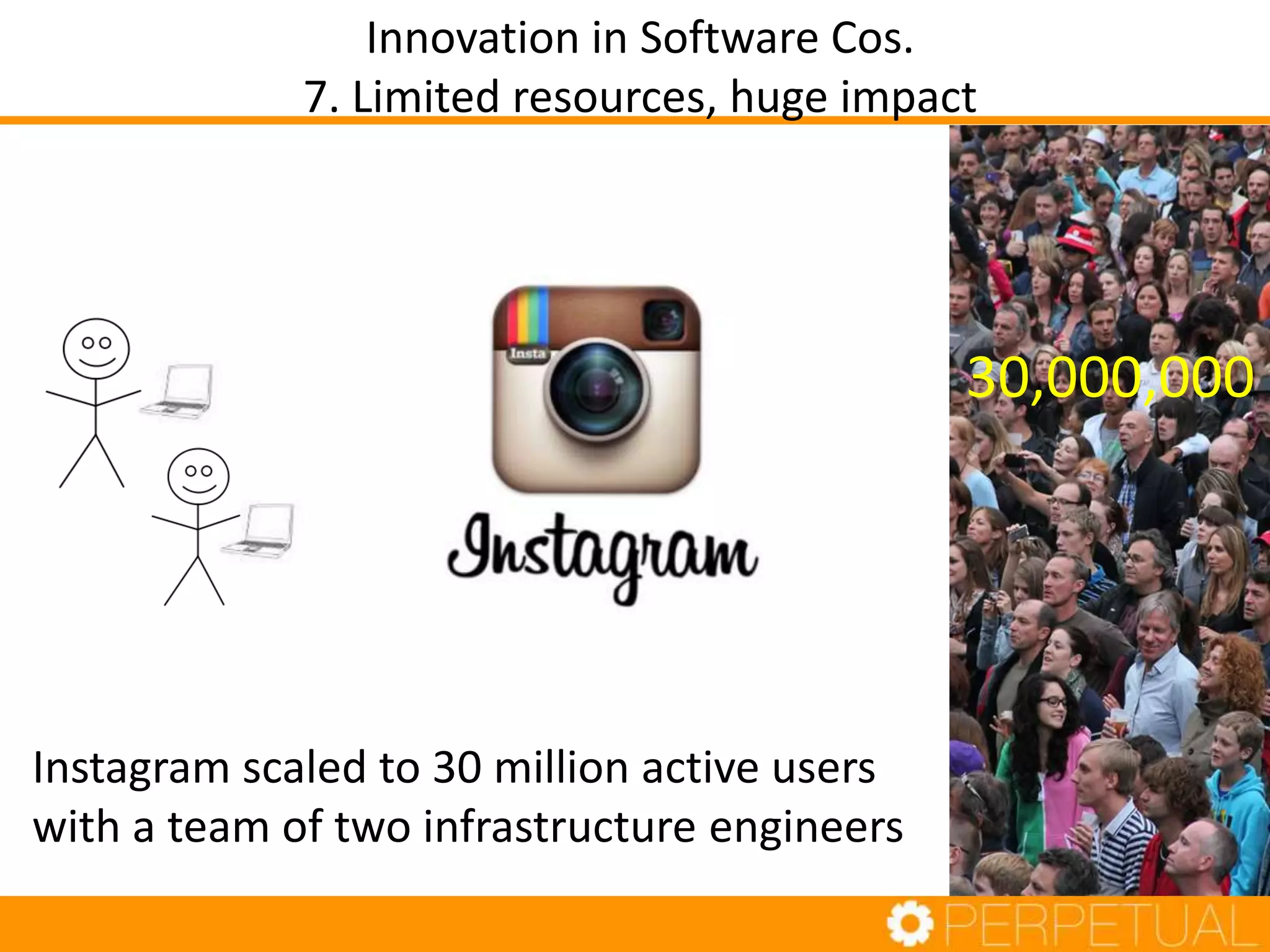
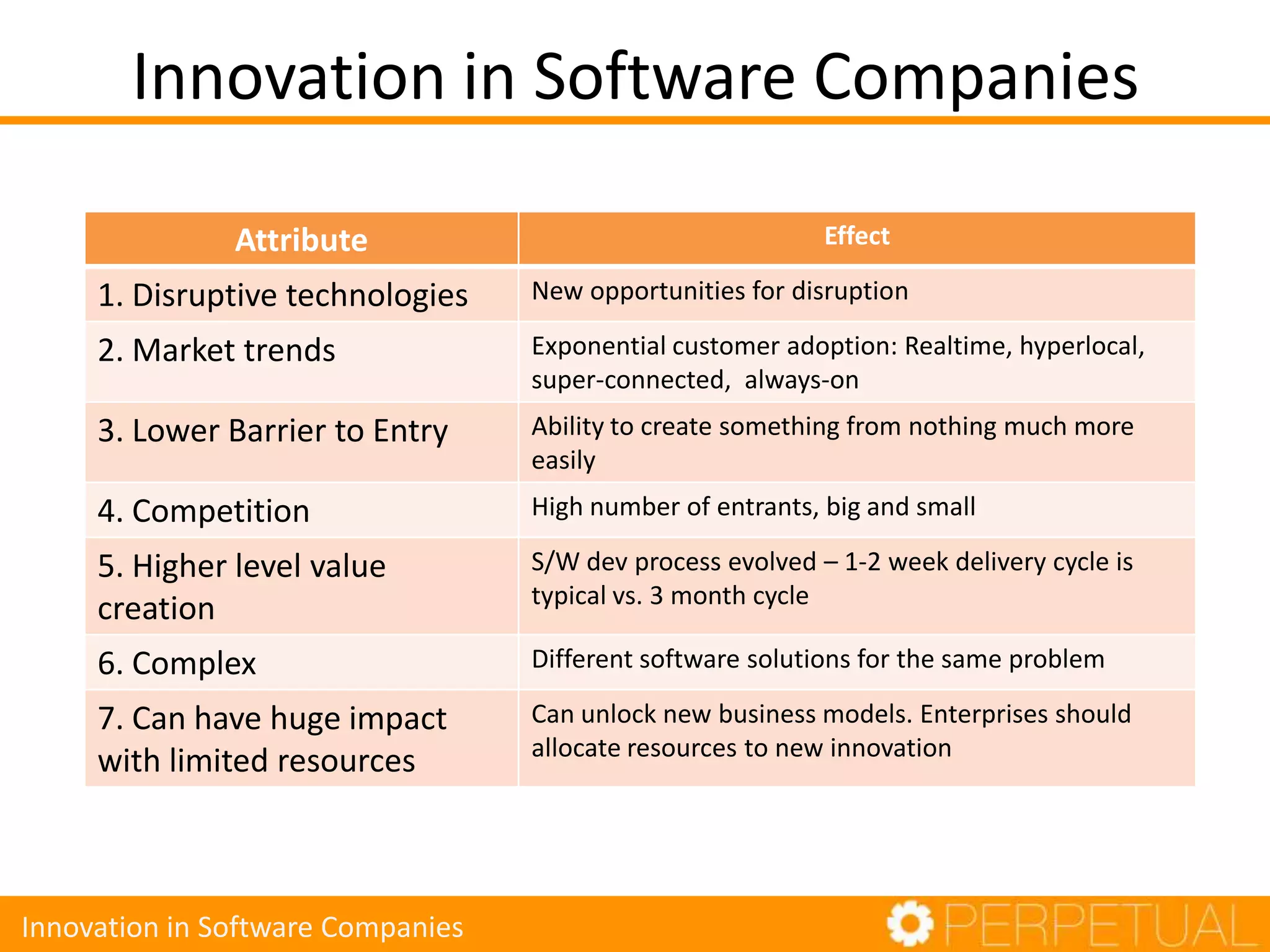
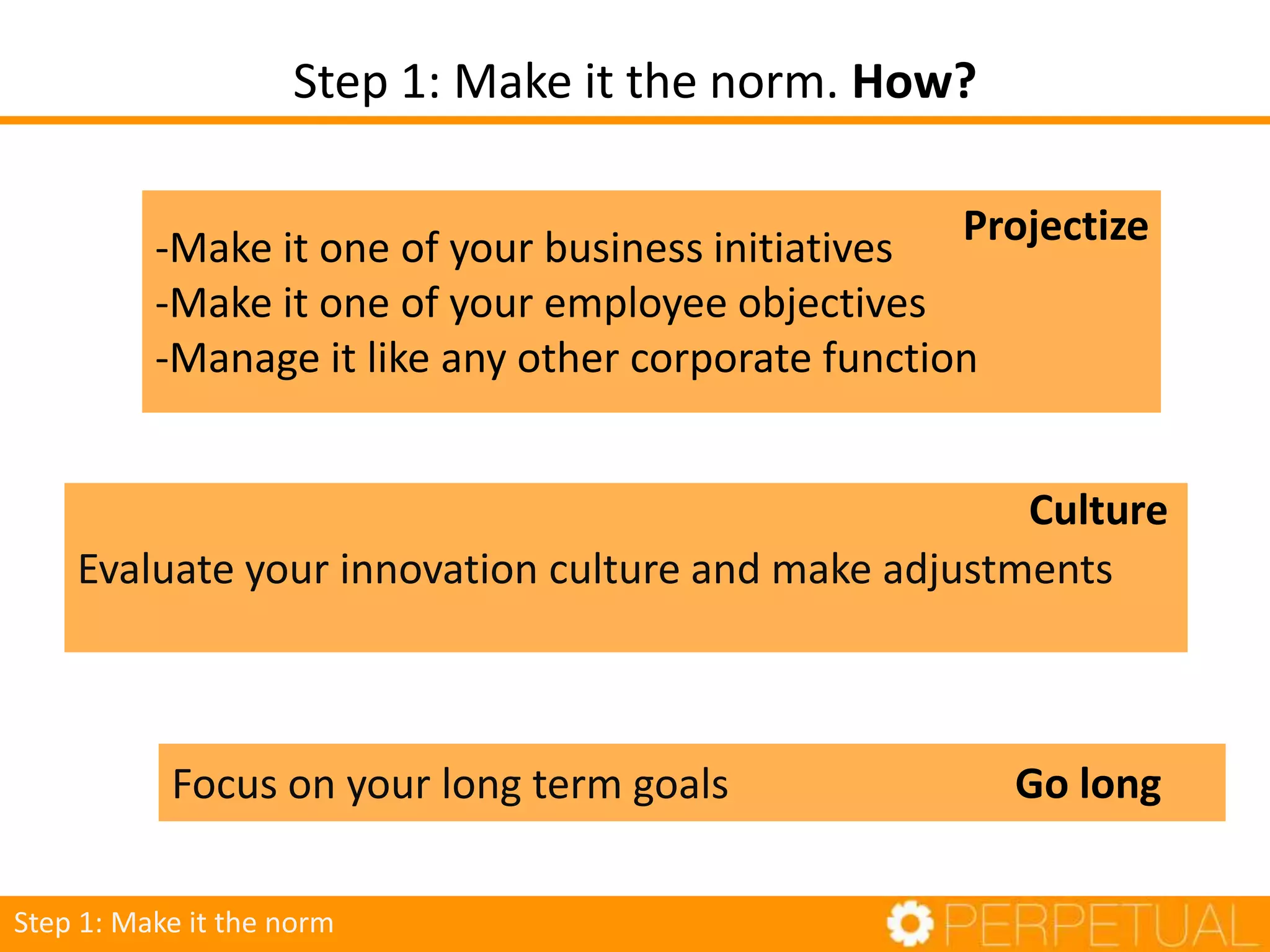
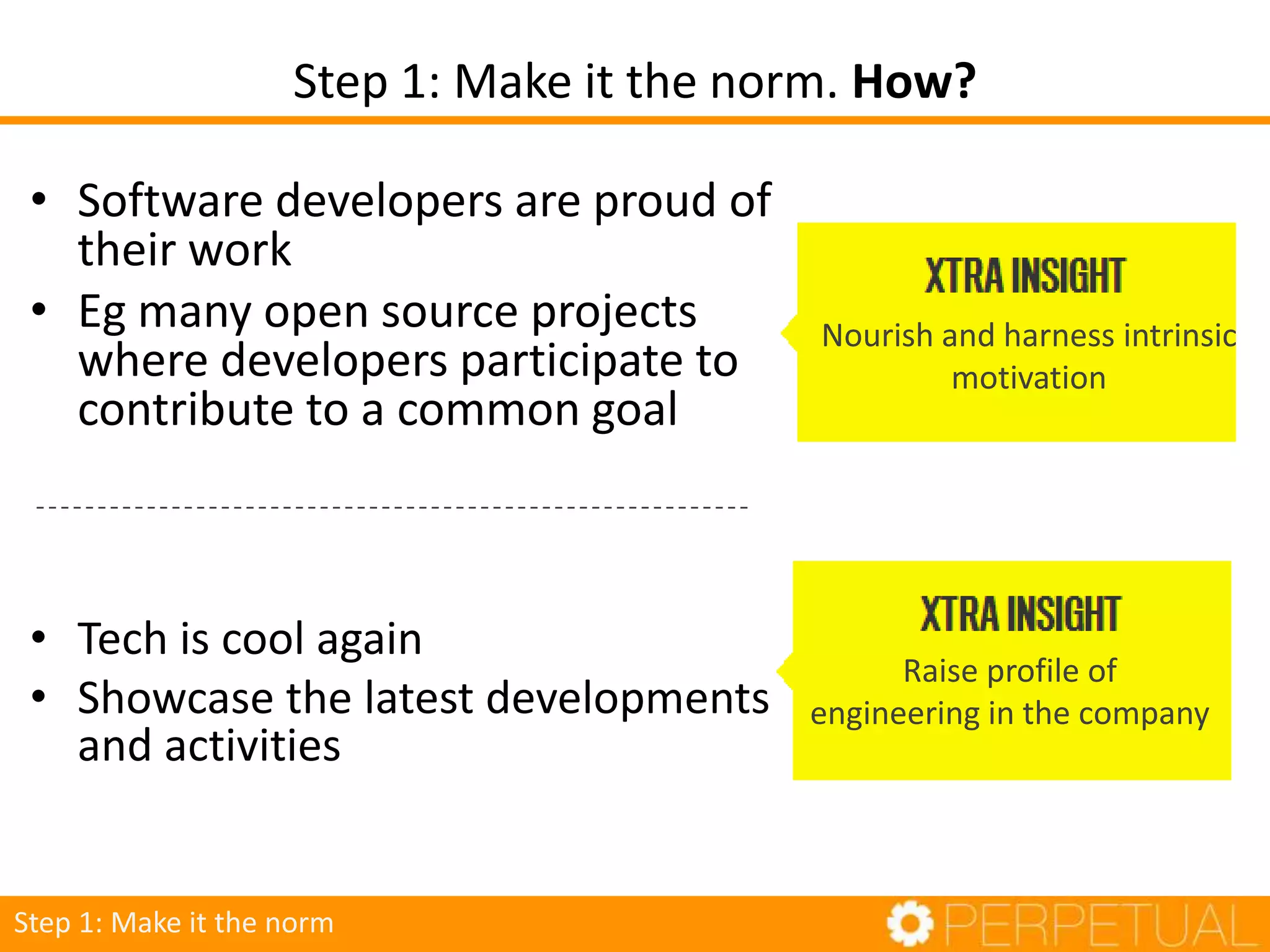
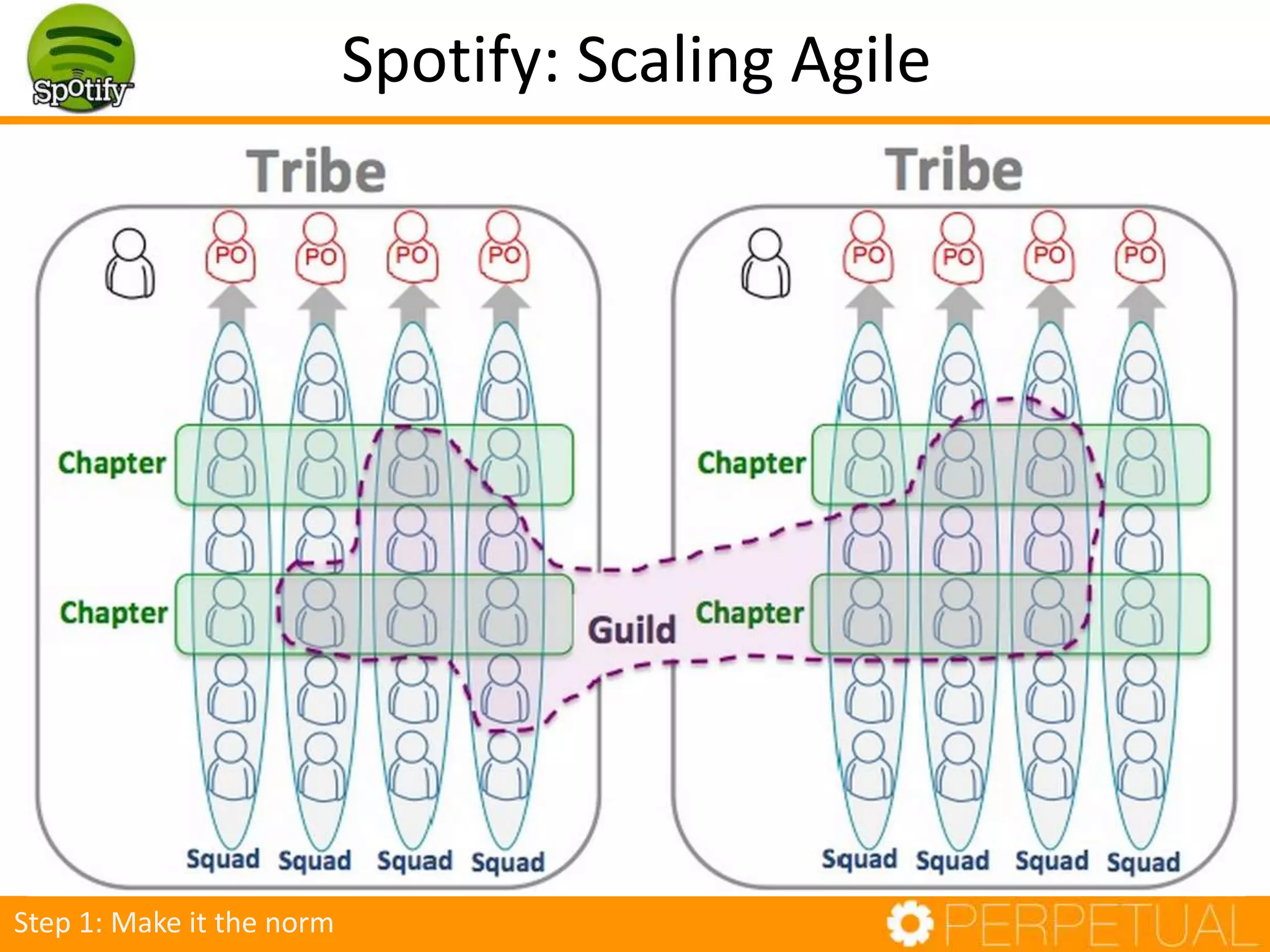
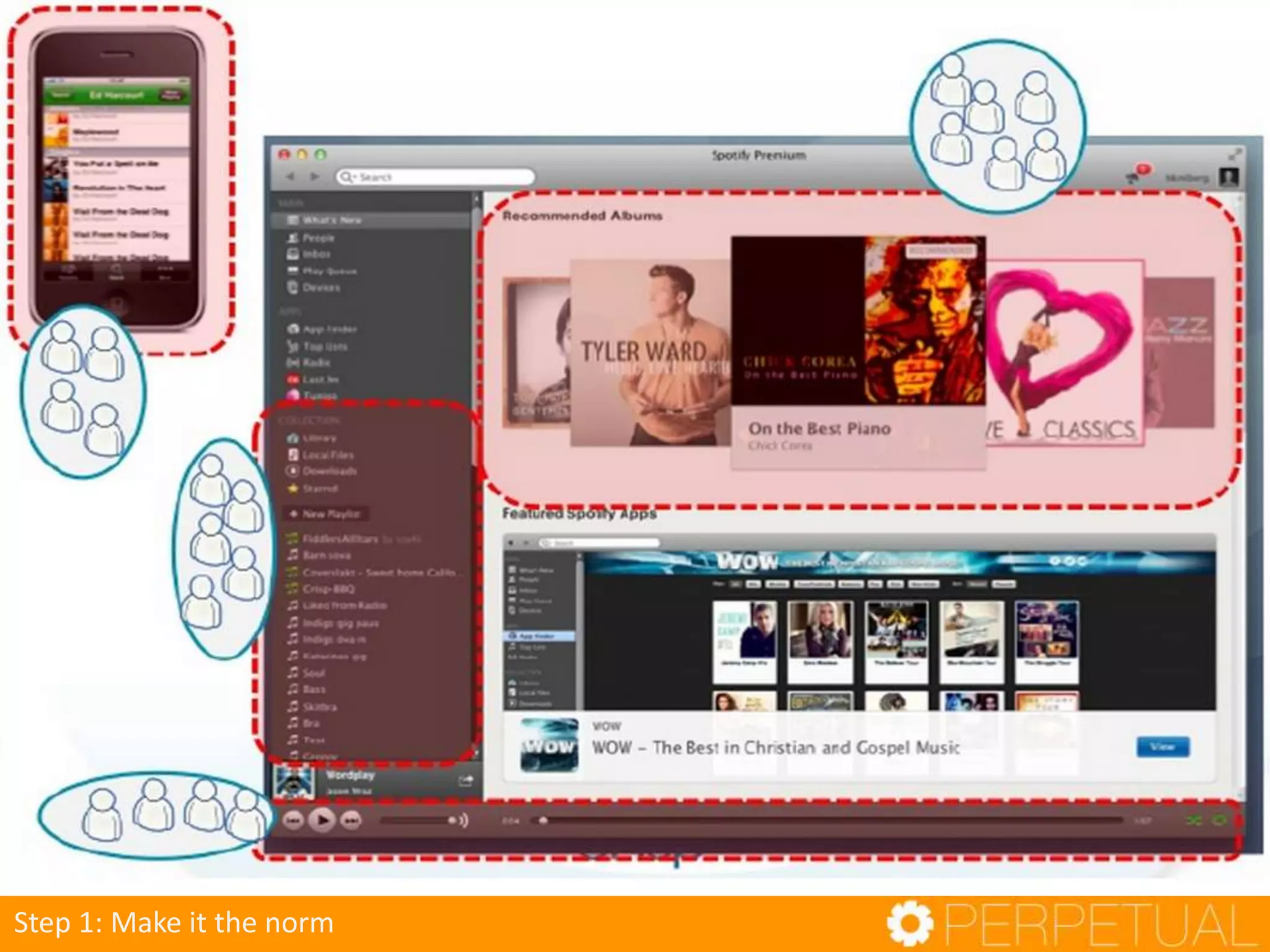
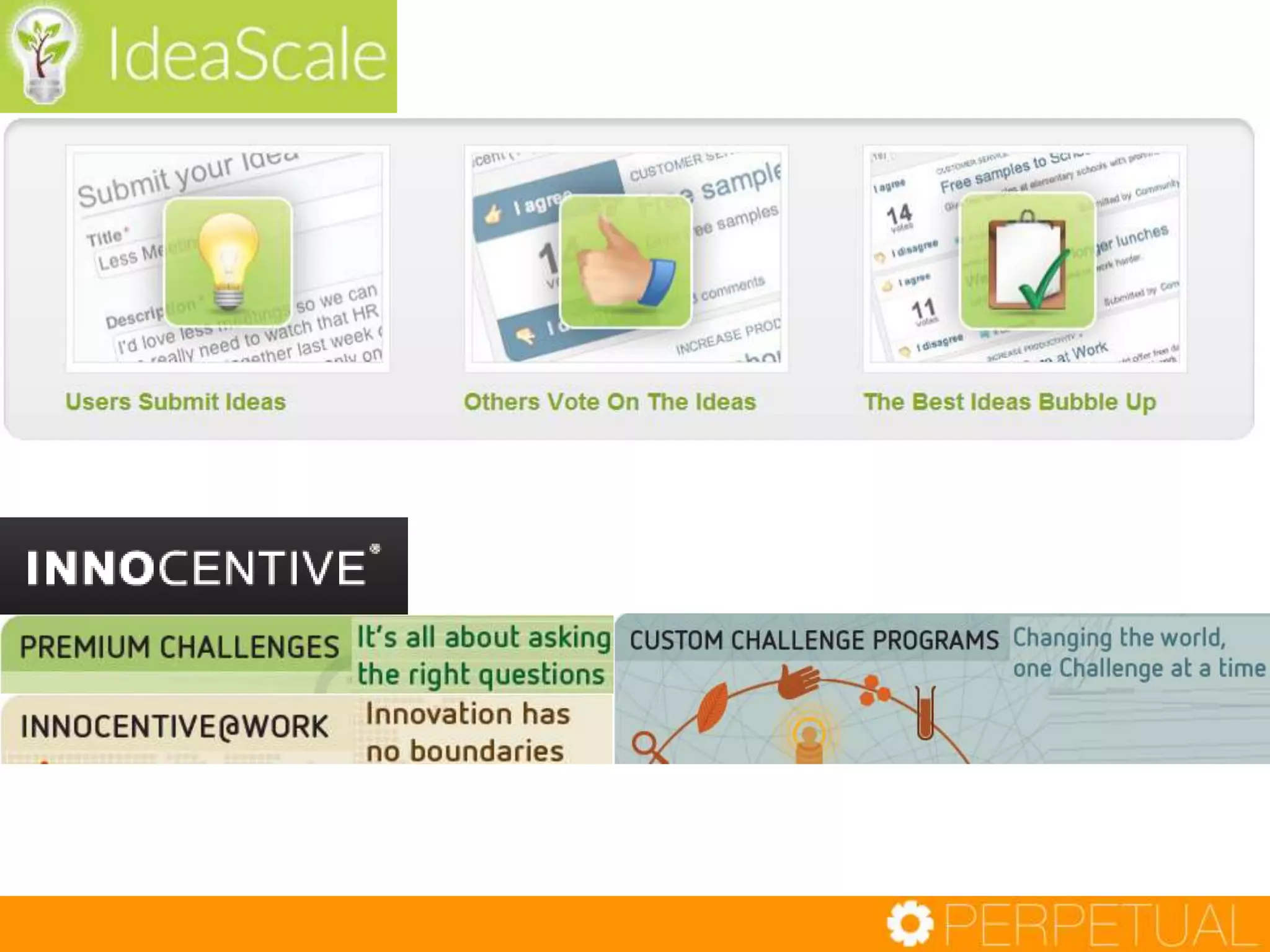
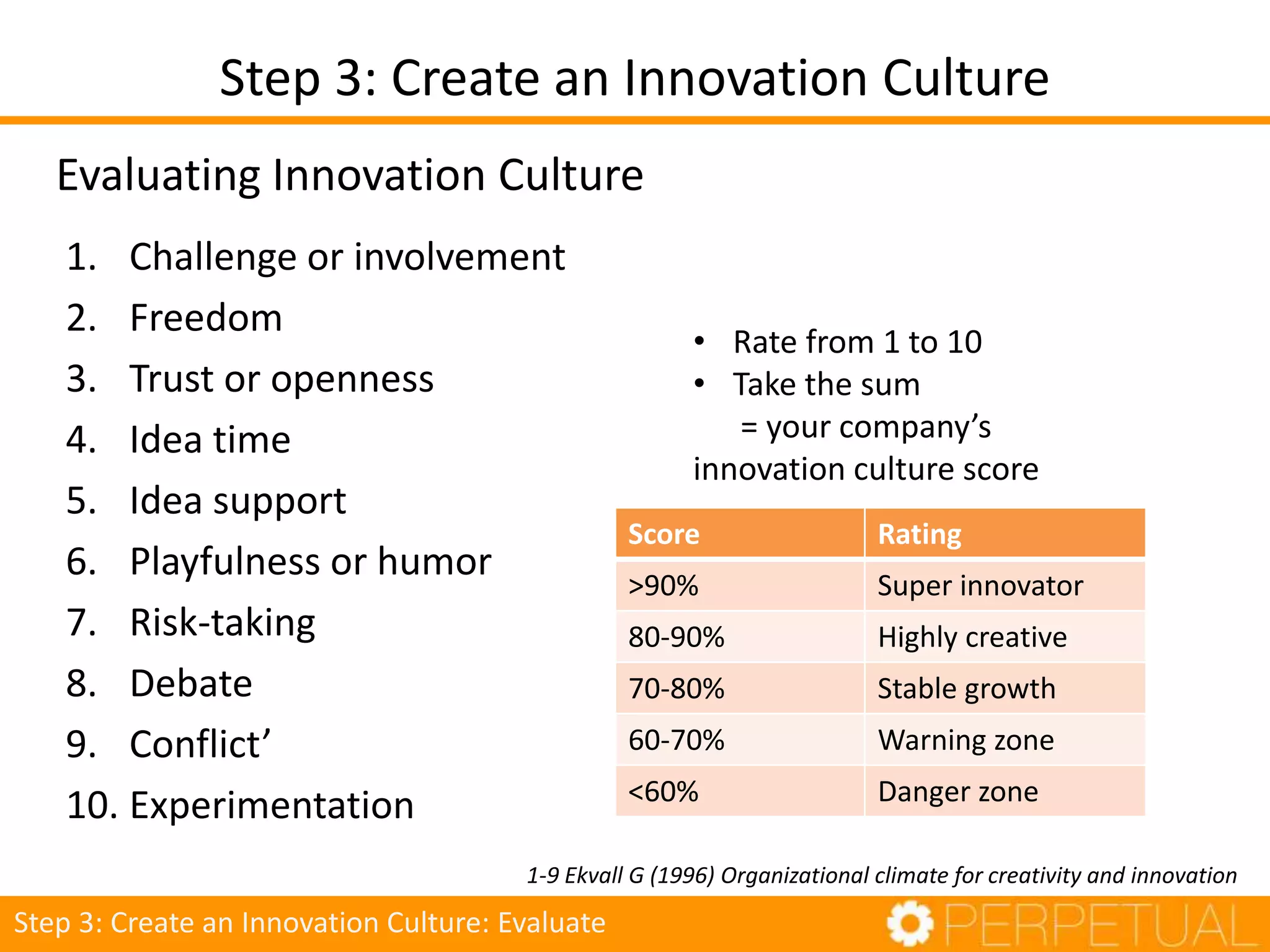
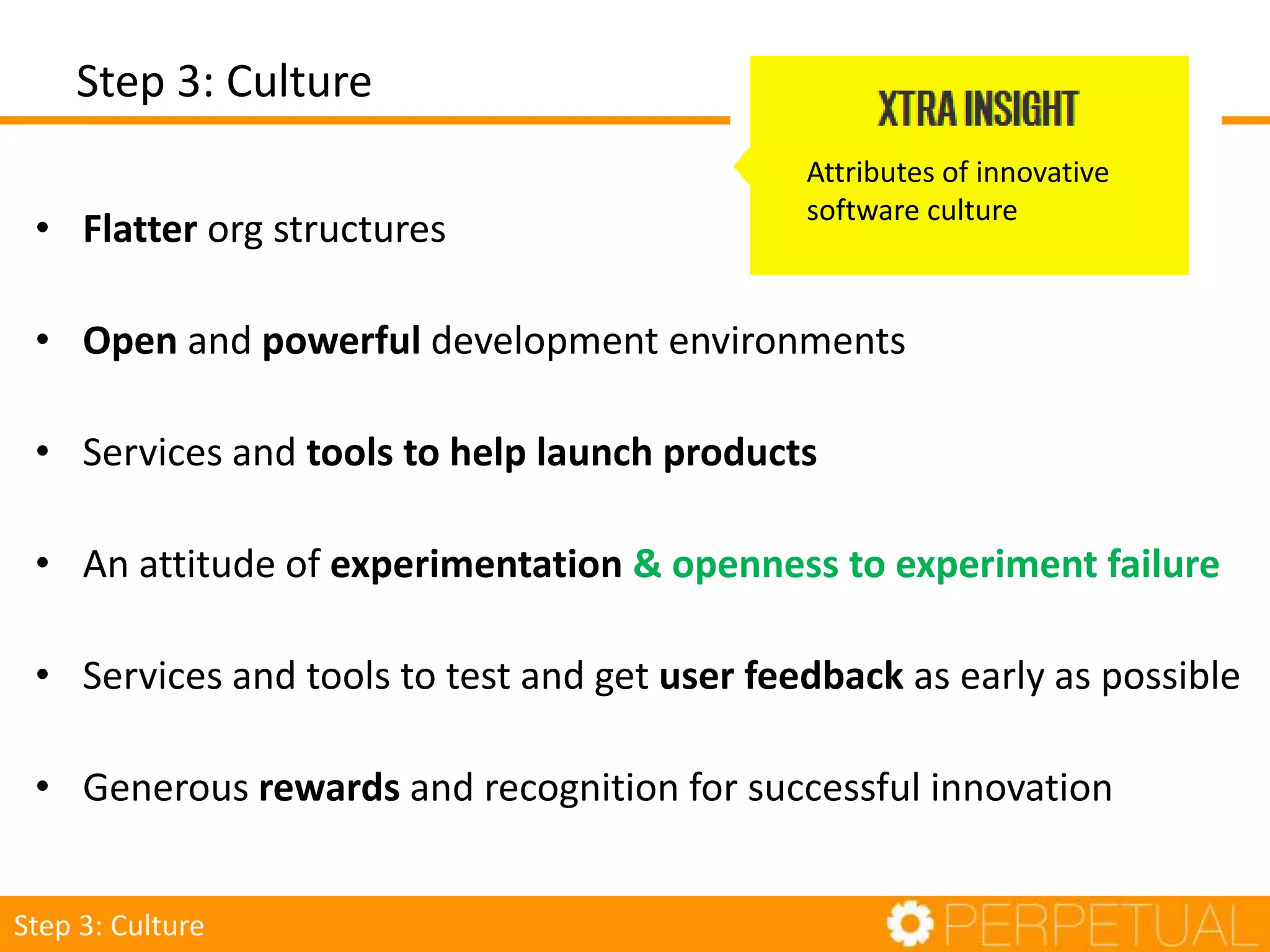
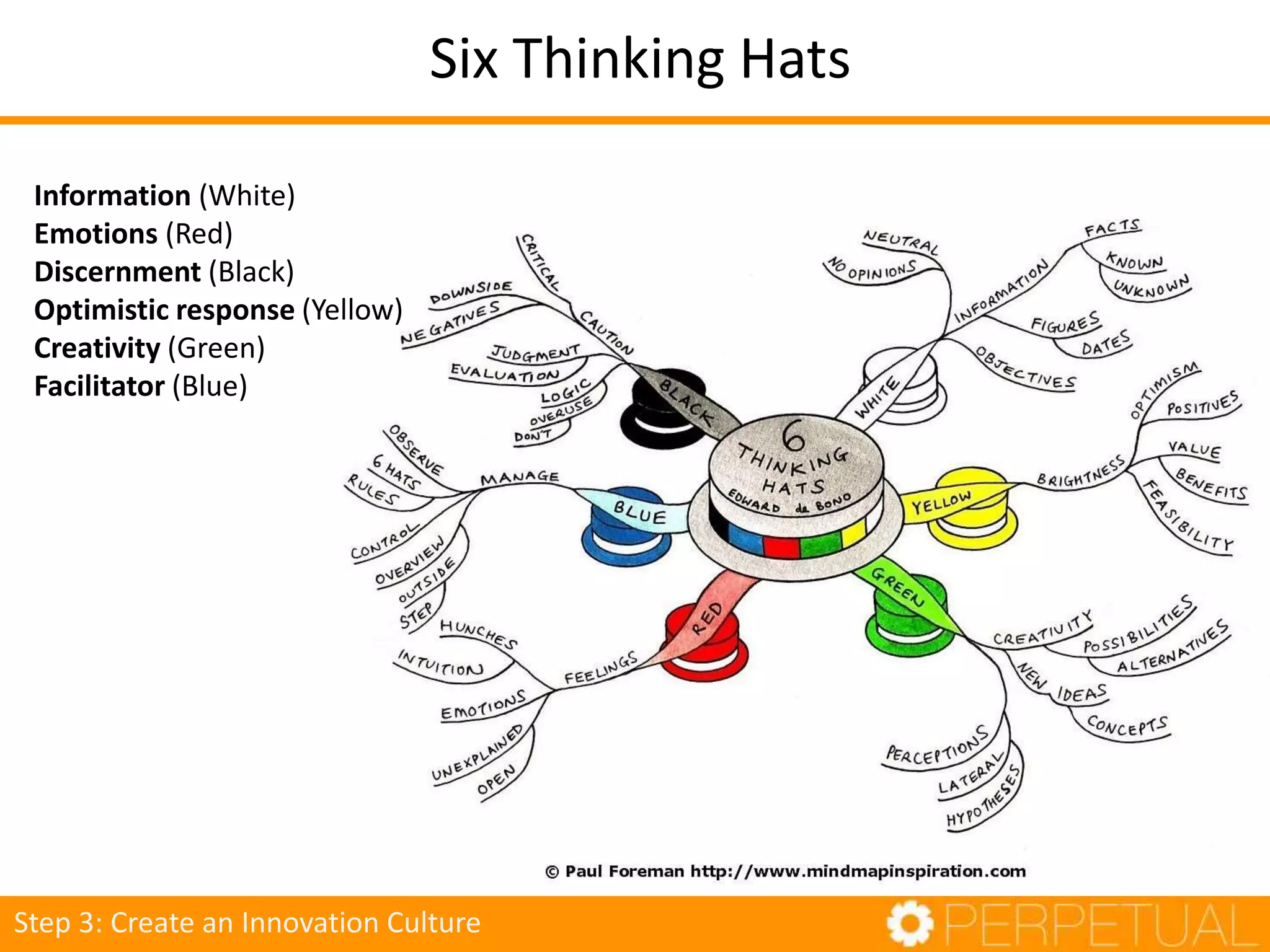
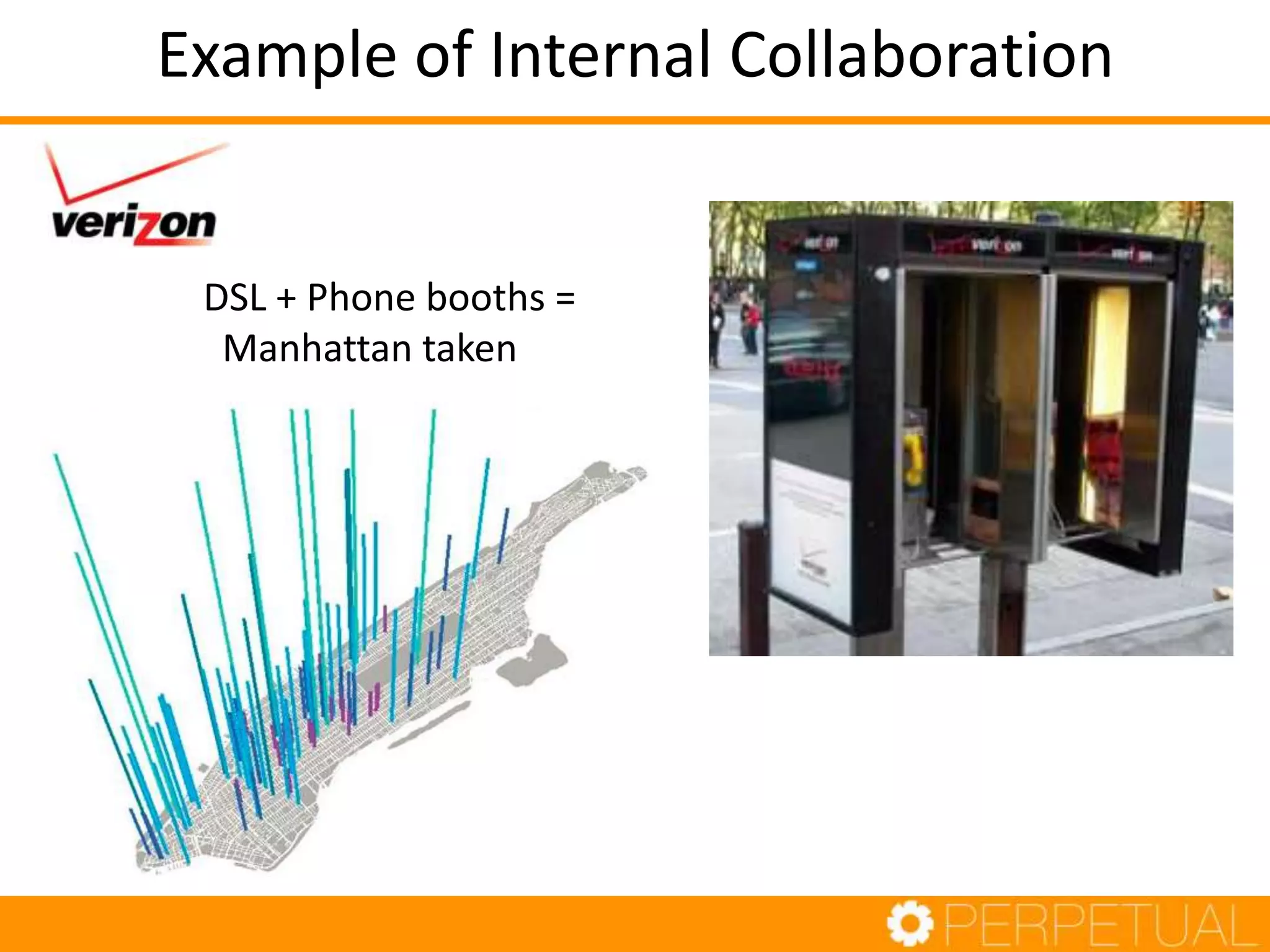
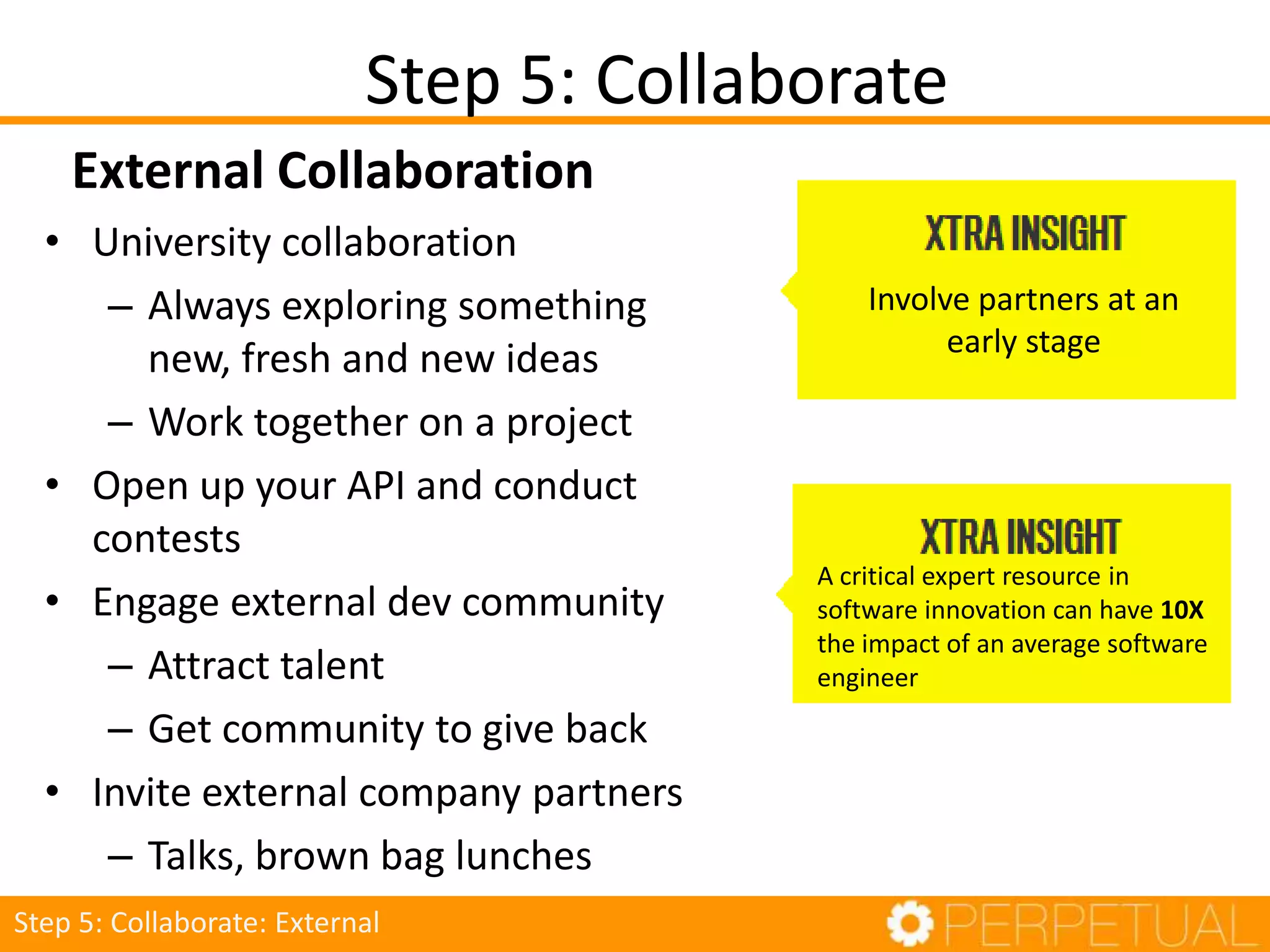
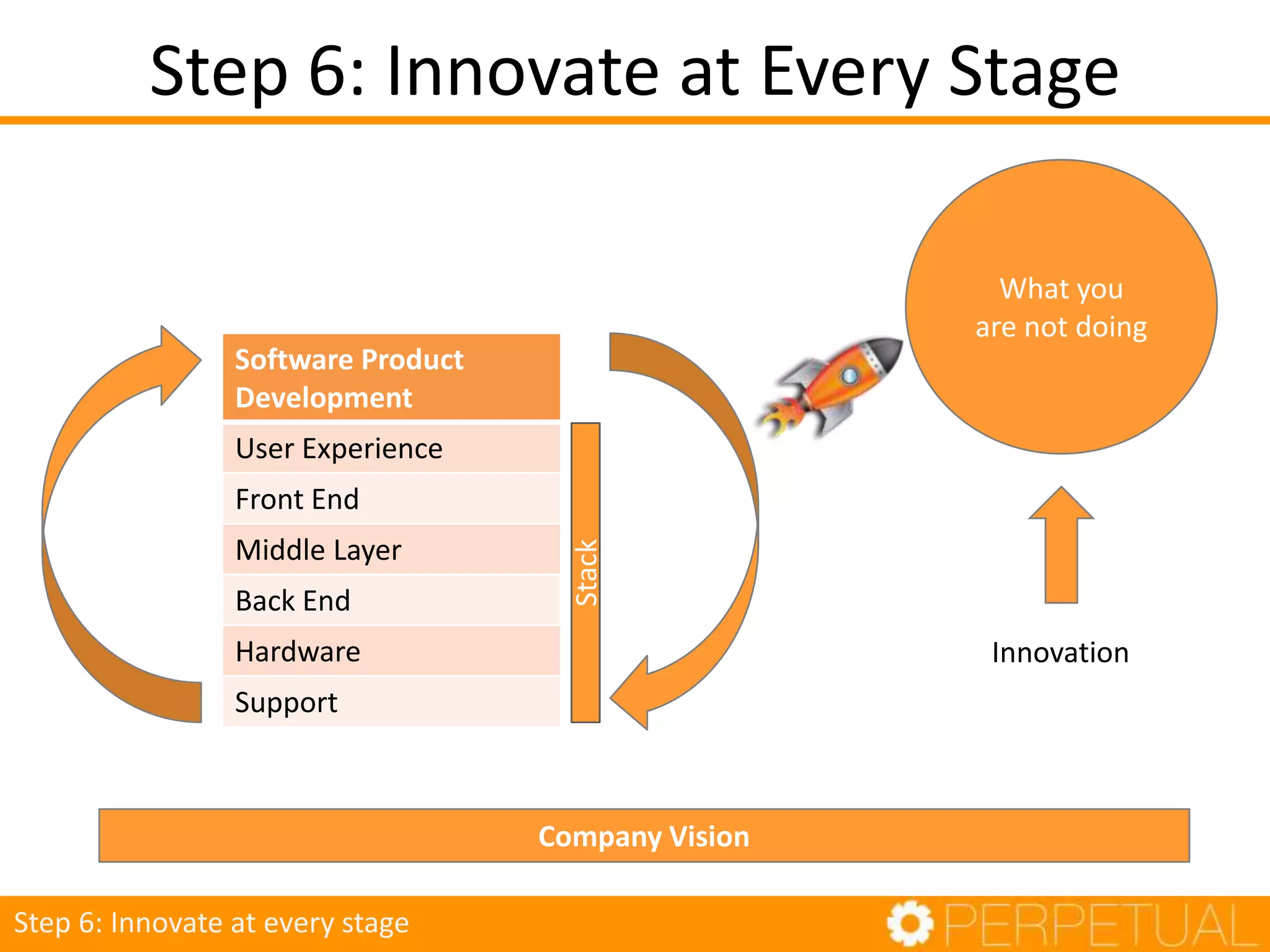
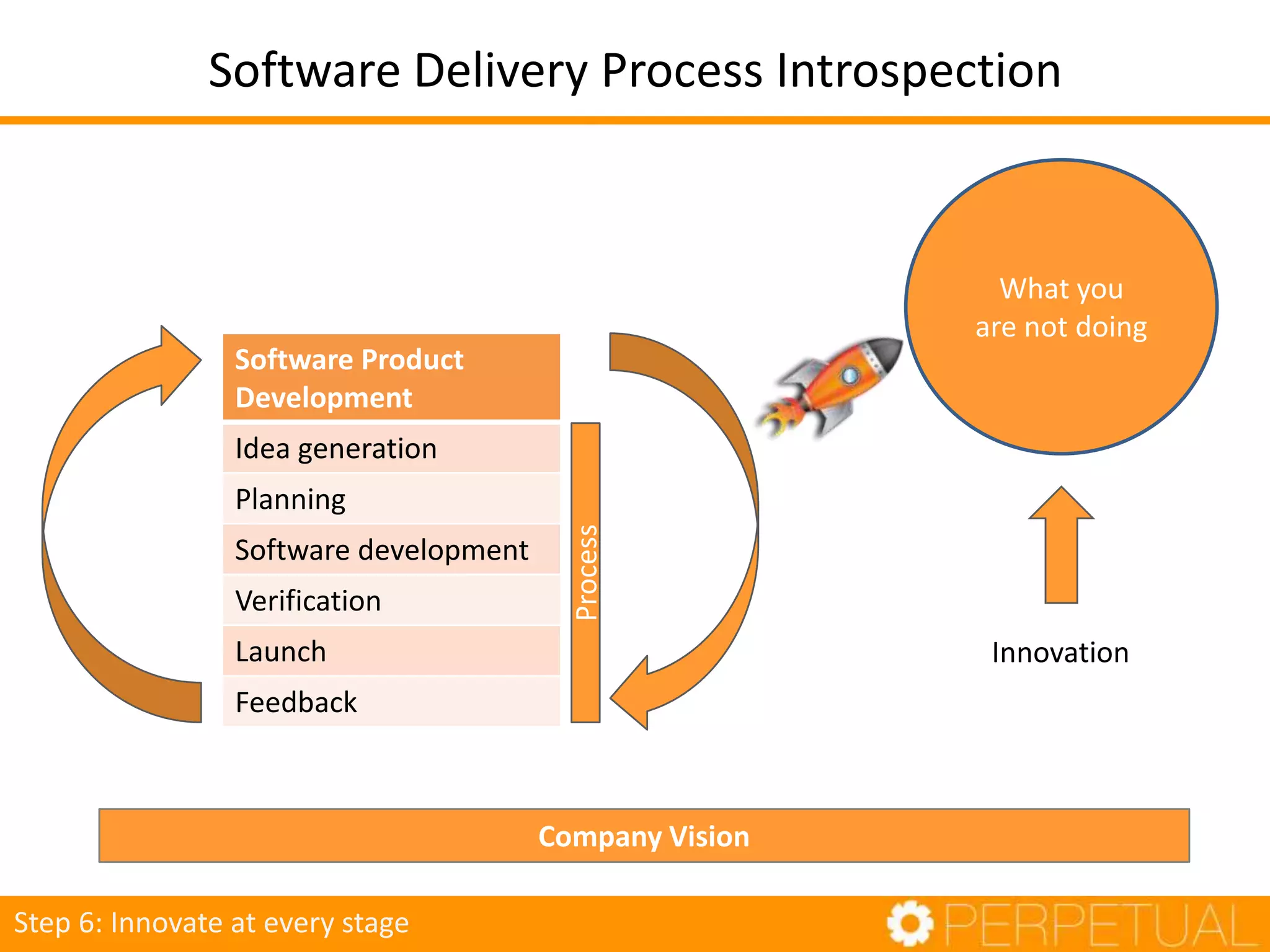
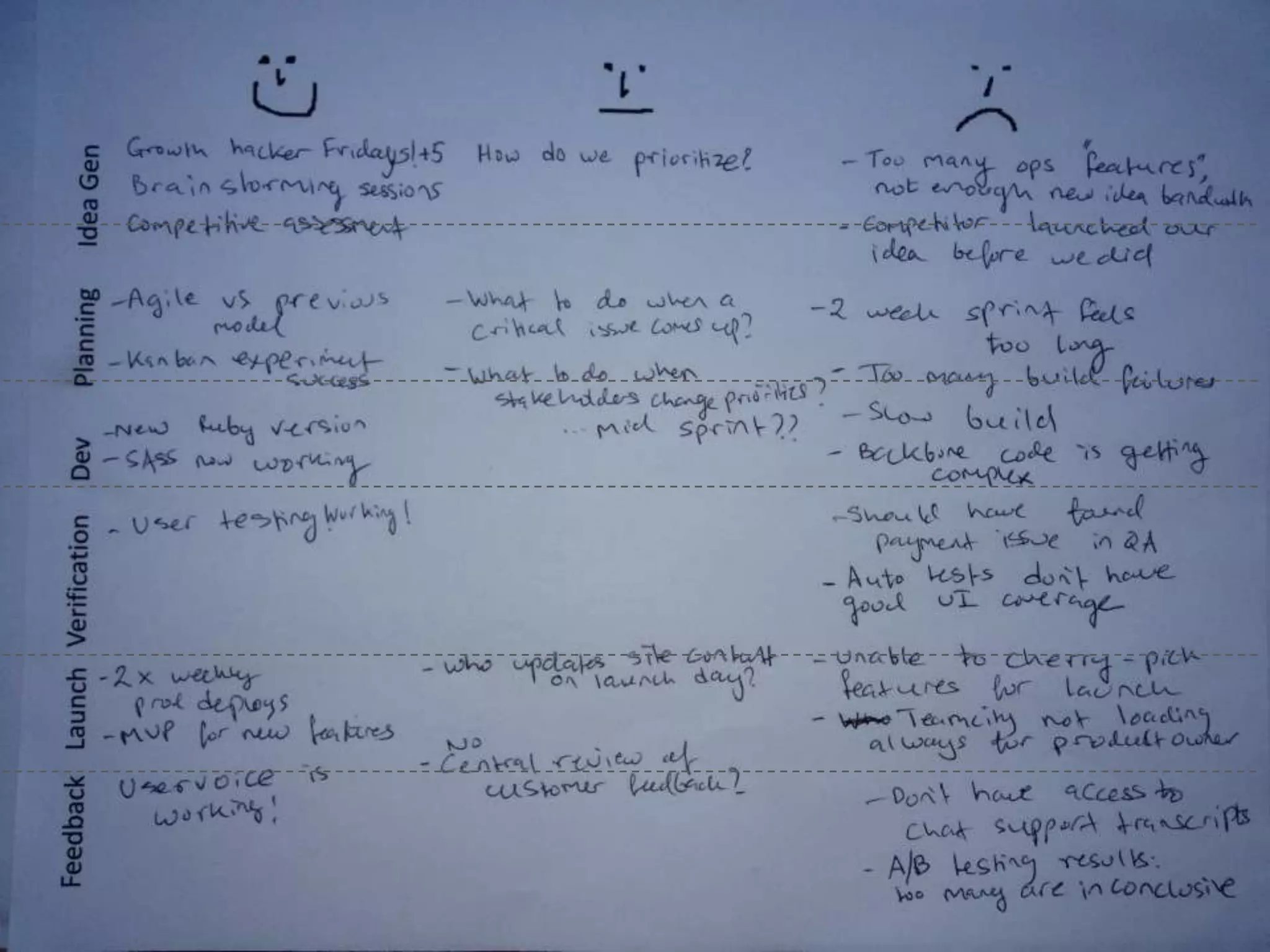
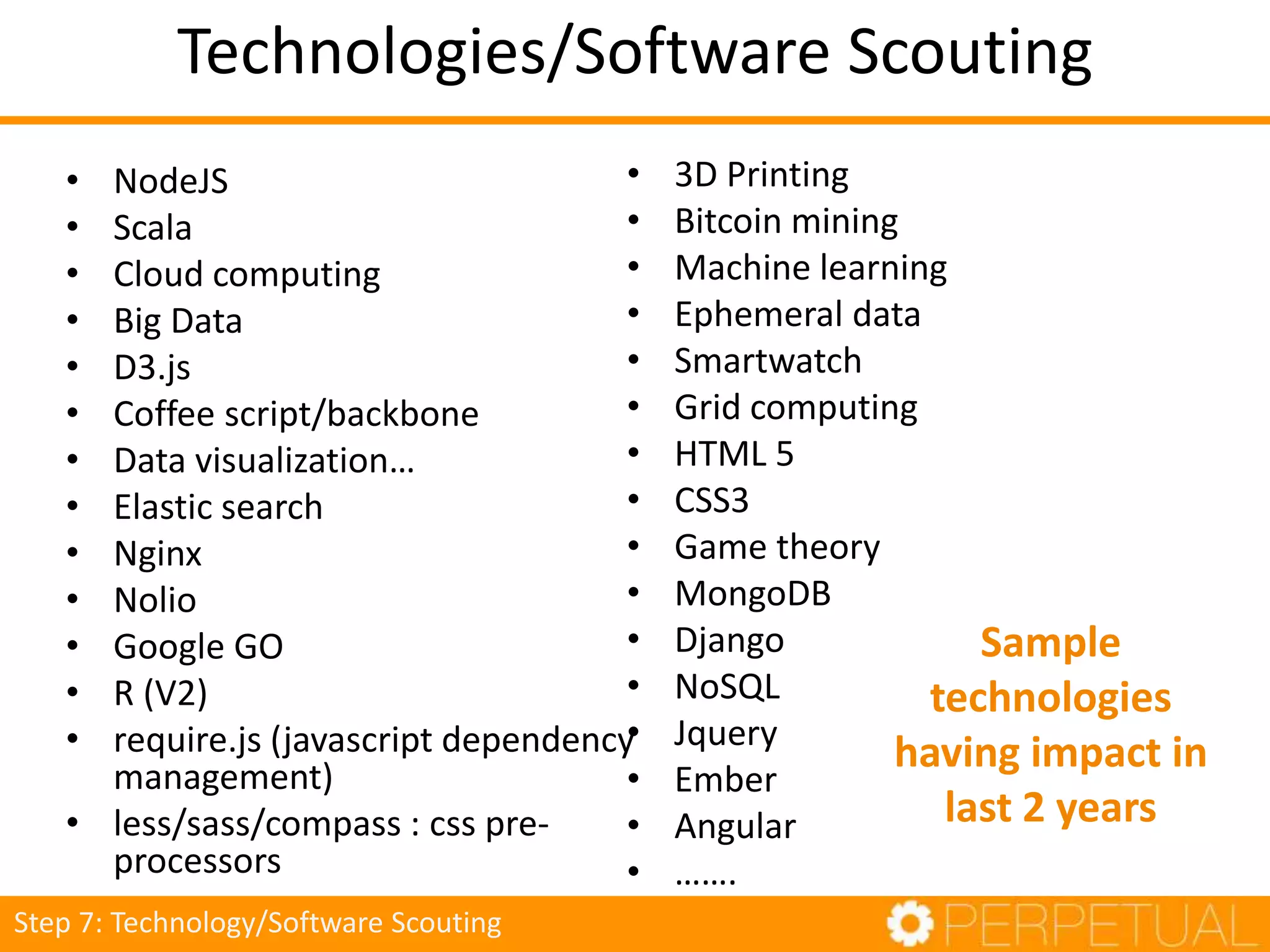
The document discusses innovation in software development, outlining its importance and distinct process involving opportunity discovery, idea implementation, and significant impact. It emphasizes that true innovation is not mere improvement or invention, but rather substantial change that can unlock new business models. The document also provides a seven-step framework for fostering innovation within software companies, highlighting aspects such as culture, collaboration, and the adoption of new technologies.