This document summarizes a presentation by Michael de Paauw of Gartner on how to get innovation started in an organization. It discusses establishing an innovation culture with executive support, generating ideas, evaluating ideas, and developing the most promising ideas into innovations. It also covers organizing for innovation through teams and offices, and using tools to support the innovation process and track metrics. The key challenges addressed are setting the stage for innovation, organizing innovation in an existing business, and tools to support the process.







![Where does innovation come from?Onder druk wordt alles vloeibaar “Necessity is the mother of invention” [Plato]“Invention arises from idleness” [Agatha Christie]Crisis forces you to make choices that you probably wouldn't have made otherwise.Extreme StressEmployees are expected to spend 20% of their time on innovation.Creativity features strongly in the recruiting process](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lectureoninnovationhowtogettheballrolling-100630040859-phpapp01/85/Innovation-how-to-get-the-ball-rolling-9-320.jpg)









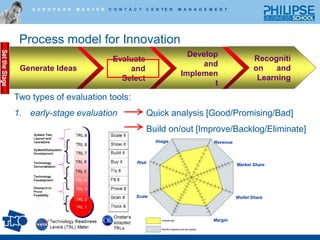
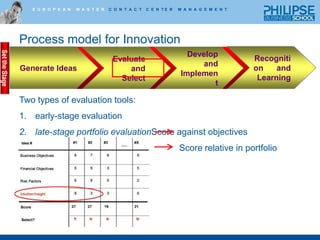
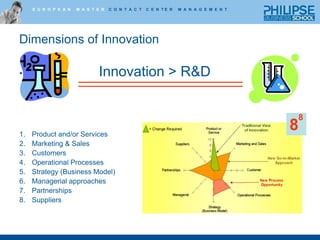
![Process model for InnovationRecognition and LearningGenerate IdeasEvaluate and SelectDevelop and ImplementTwo types of evaluation tools:early-stage evaluation Quick analysis [Good/Promising/Bad] Build on/out [Improve/Backlog/Eliminate]ImageRevenueRiskMarket ShareScaleWallet ShareMarginSet the Stage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lectureoninnovationhowtogettheballrolling-100630040859-phpapp01/85/Innovation-how-to-get-the-ball-rolling-21-320.jpg)