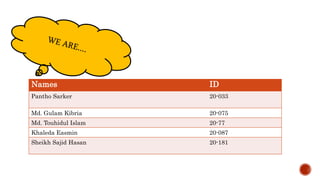
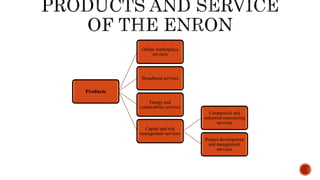
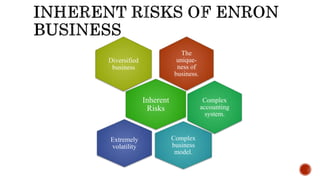
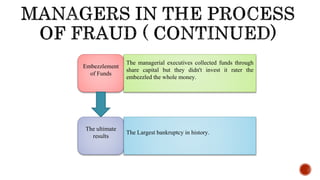
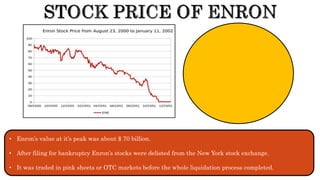
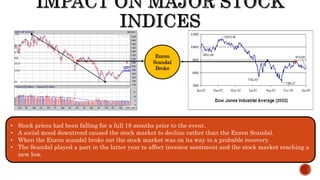
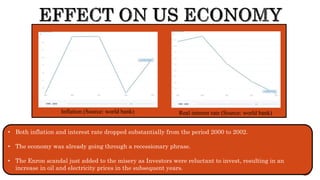
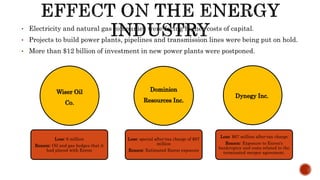
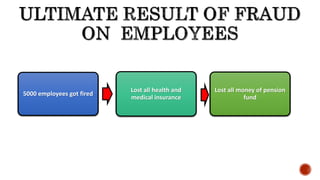
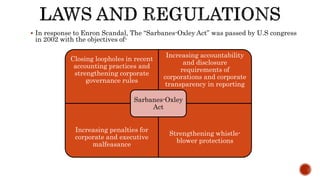
The document presents a detailed timeline of key events leading to the Enron scandal, including major management decisions, accounting manipulations, and the eventual bankruptcy filing in 2001. It discusses the roles of various stakeholders, including management's unethical practices, auditor complicity, and the broader financial impact on the market and employees. The scandal ultimately led to the conviction of Arthur Andersen and the introduction of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act to reform corporate governance and accounting practices.