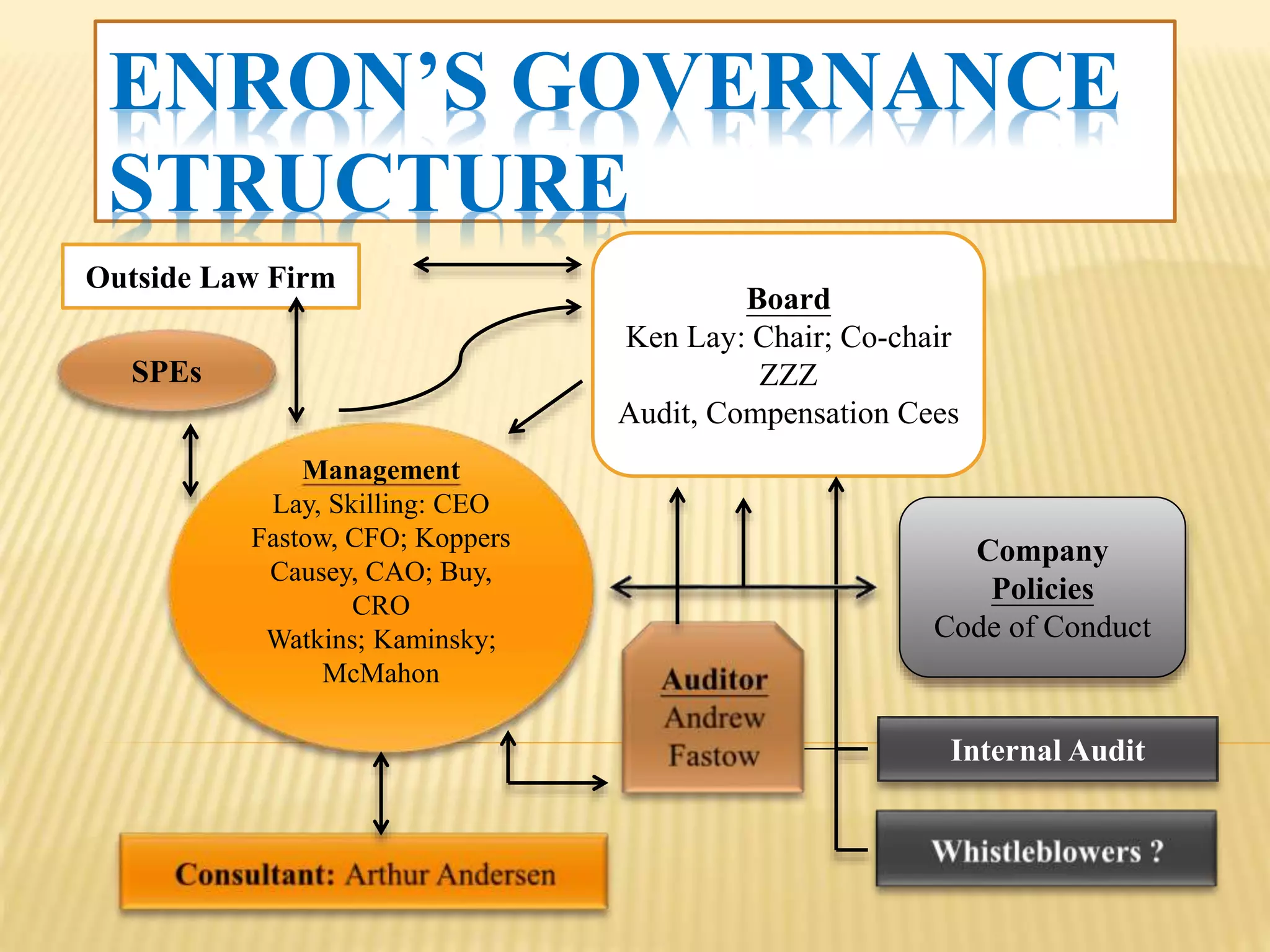
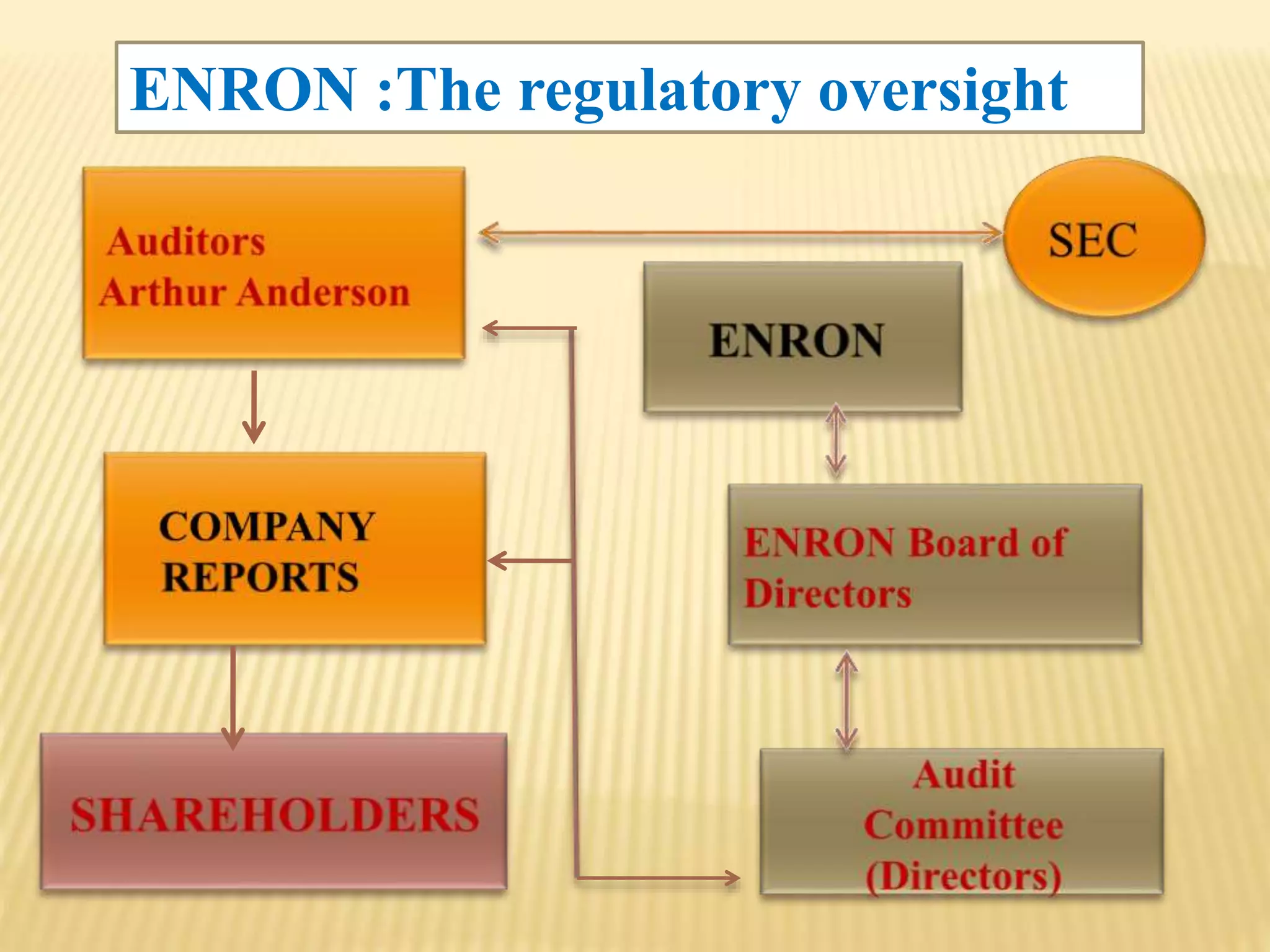
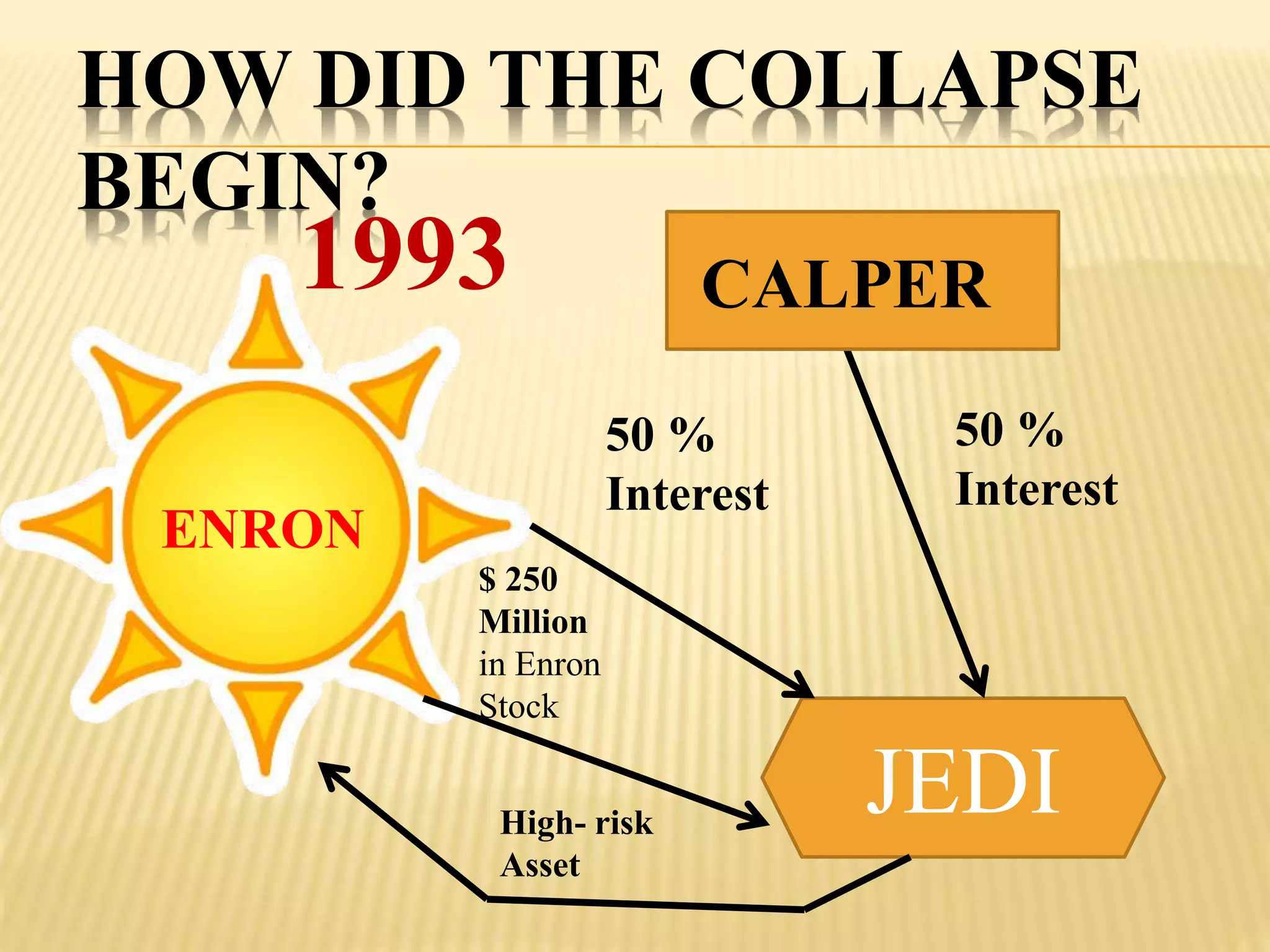
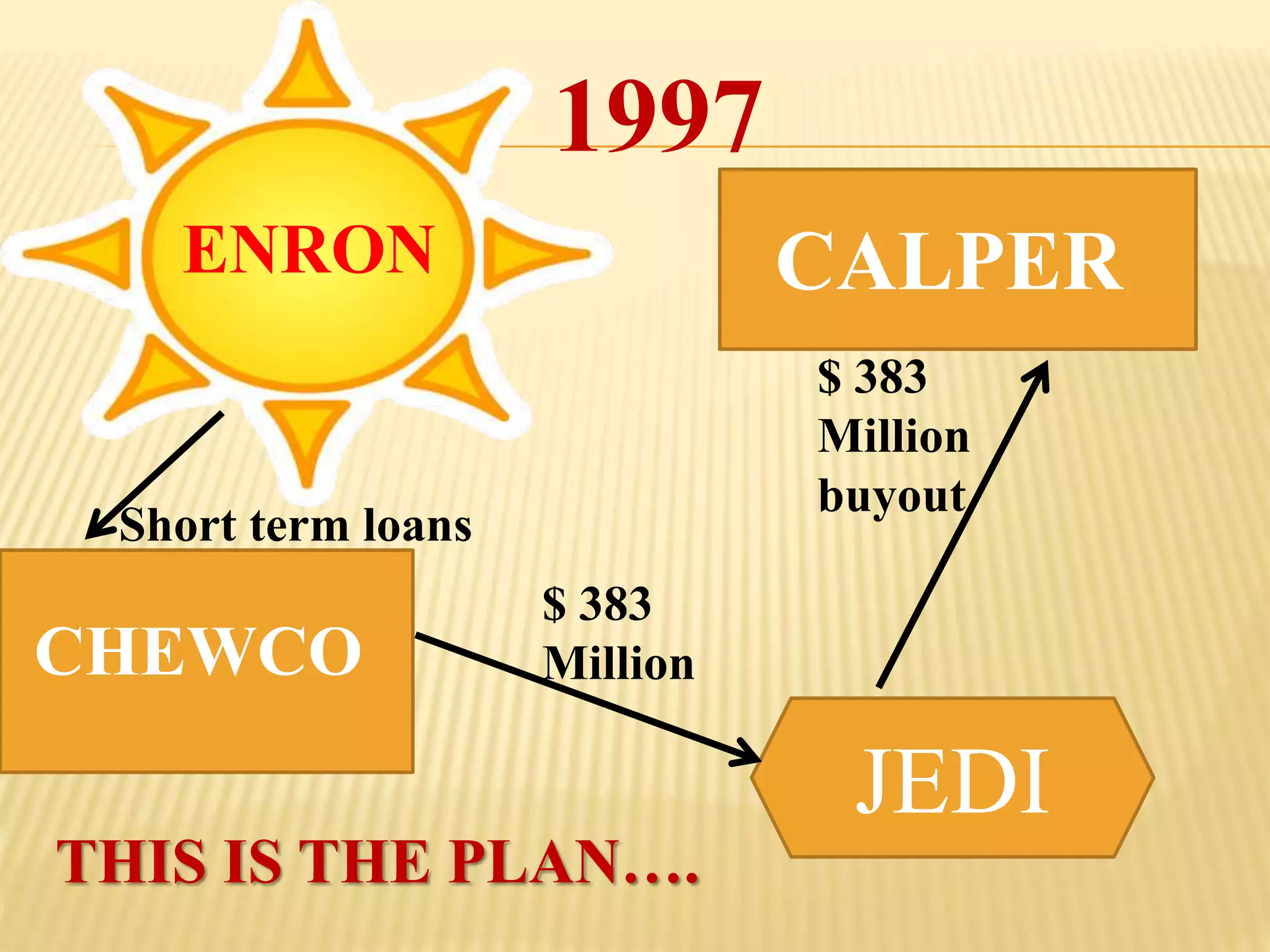
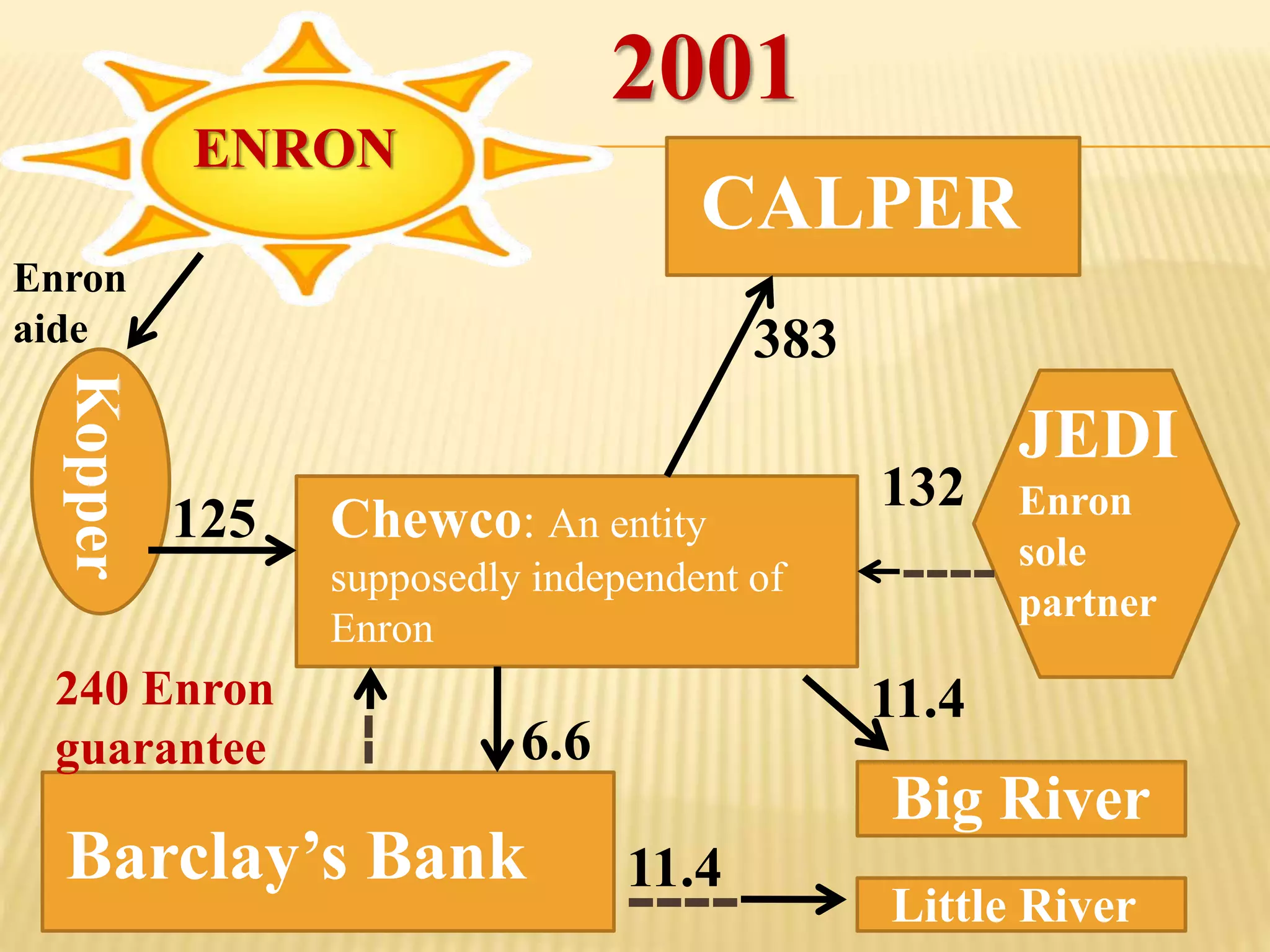
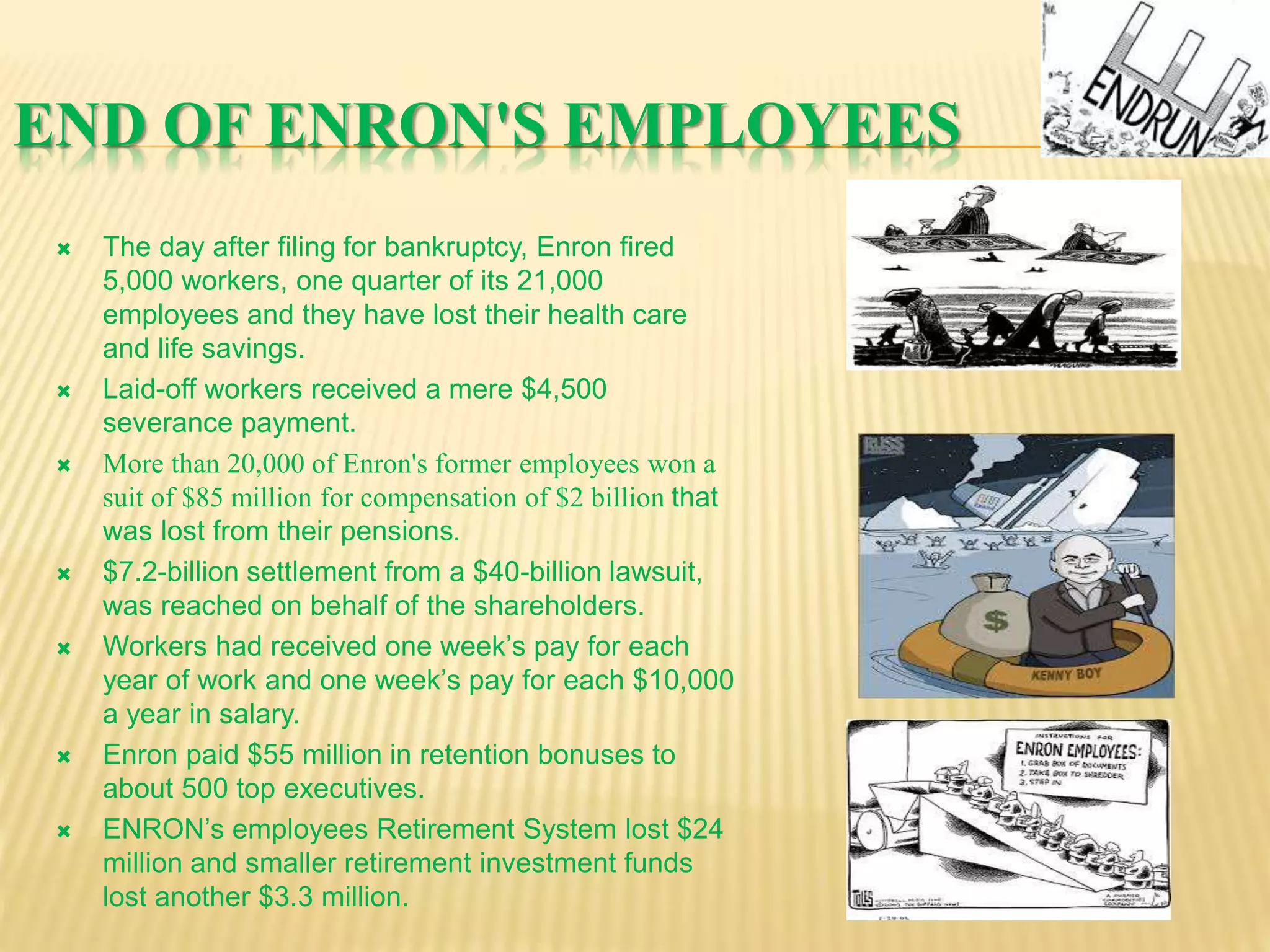
The document provides an overview of the rise and fall of Enron, beginning with its founding in 1932 and growth into one of the largest companies in the US by 2000. Key events discussed include Enron's use of mark-to-market accounting and special purpose entities to hide debts and inflate profits, the revelation of accounting irregularities in late 2001, Enron filing for bankruptcy in December 2001, and the criminal investigations and prosecutions that followed the company's collapse.