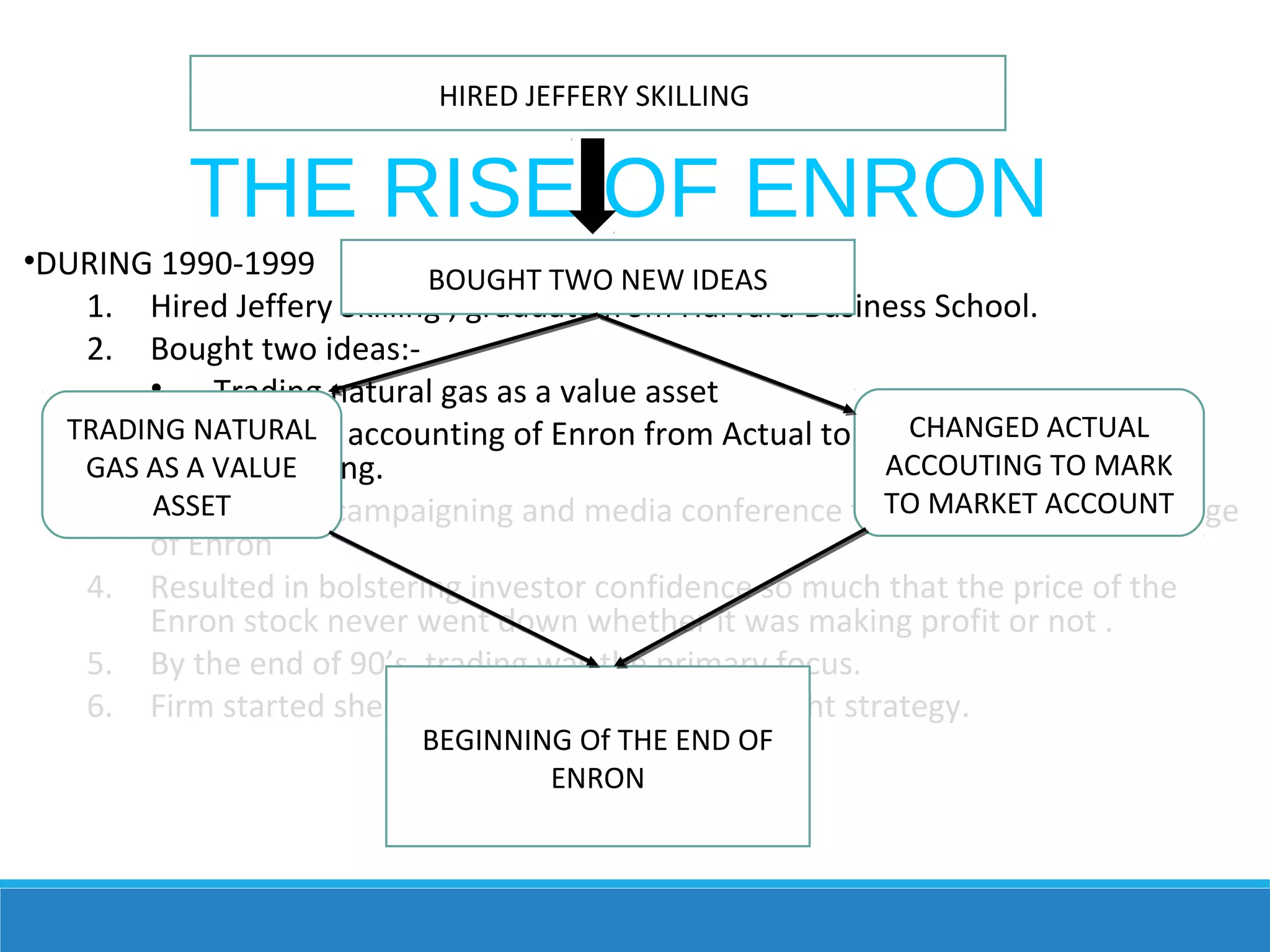
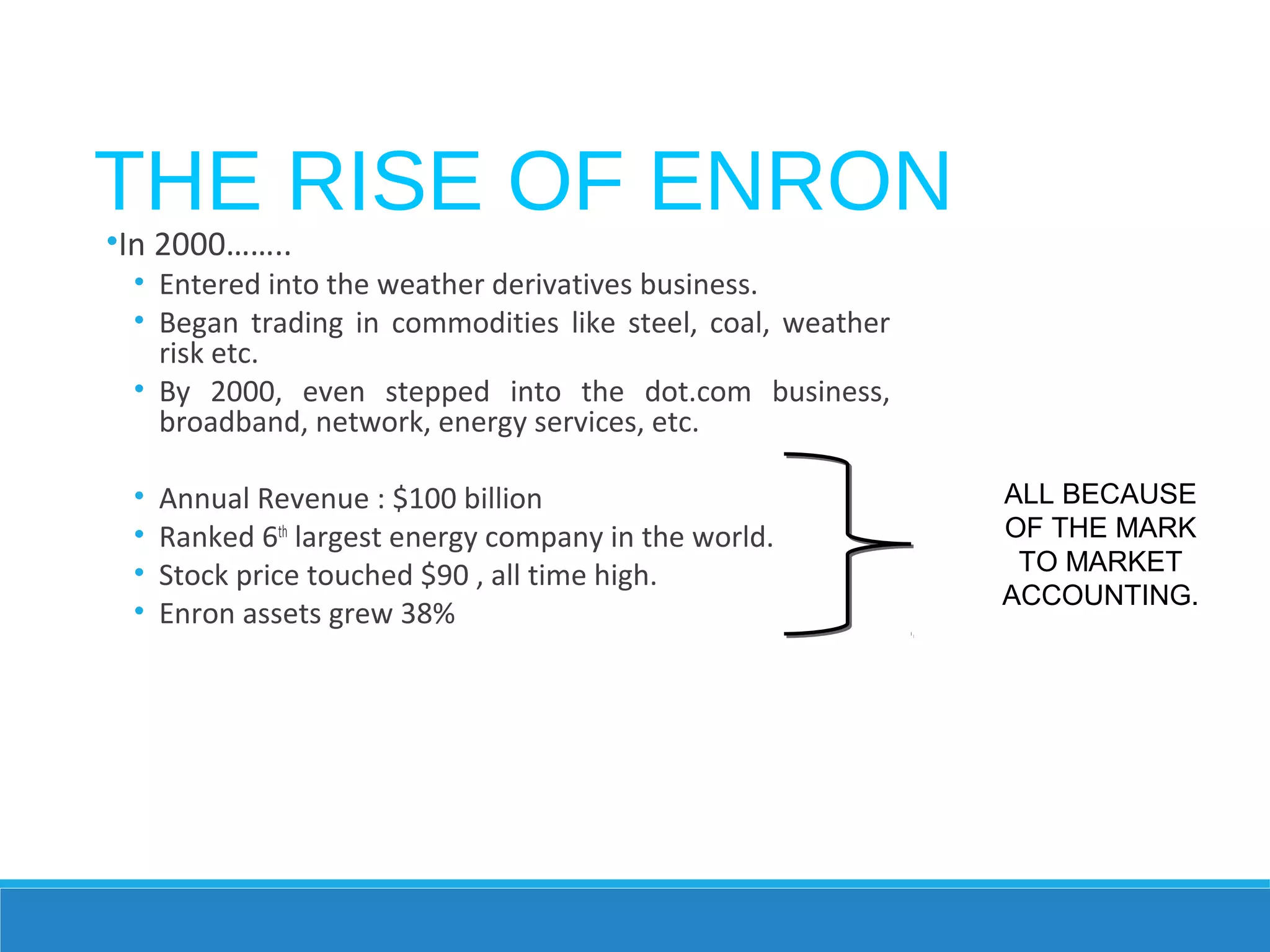
Enron rose rapidly in the 1980s and 1990s through aggressive accounting practices and trading of energy contracts. However, by 2001 it began collapsing under the weight of hidden debts and losses, revealed through the use of special purpose entities and misleading financial reports approved by its auditor, Arthur Andersen. The bankruptcy of Enron in late 2001 resulted in billions lost for investors and employees and led to reforms through the Sarbanes-Oxley Act to increase transparency in corporate accounting.








![ARTHUR ANDERSON AND
ENRON
[RISKY BUSINESS]
Arthur Andersn LLP and David B. Ducan , who
oversaw Enron’s account were the major players in
the scandal.
Arthur Anderson was one the largest accounting
firm in the US during that time.
Ignoring Enron’s malpractices, it offered its stamp of
approval, which was enough for investors and
regulators alike for a while.
Which included approval for many subsidiaries like
raptor and condor.
Received $52 million in 2001, mainly for non audit
related consulting services.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/auditingpresentation-170404043518/75/ENRON-SCANDAL-11-2048.jpg)

![Stock heading South
•Oct 22 – Enron announces , its facing SEC [Security and
Exchange Commission] probe. Shares fall further to around
$20.75 that day.
•8th
Nov, 2001 – Told investors that they were restating
earnings for past 4 and ¾ years and admits its inflated its
income by around $586 million since 1997.
•By end of Nov, 2001 stock reached $0.3 falling from its peak
price $90 in just 8 months.
•2nd
Dec, 2001 – Filed Bankruptcy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/auditingpresentation-170404043518/75/ENRON-SCANDAL-13-2048.jpg)



