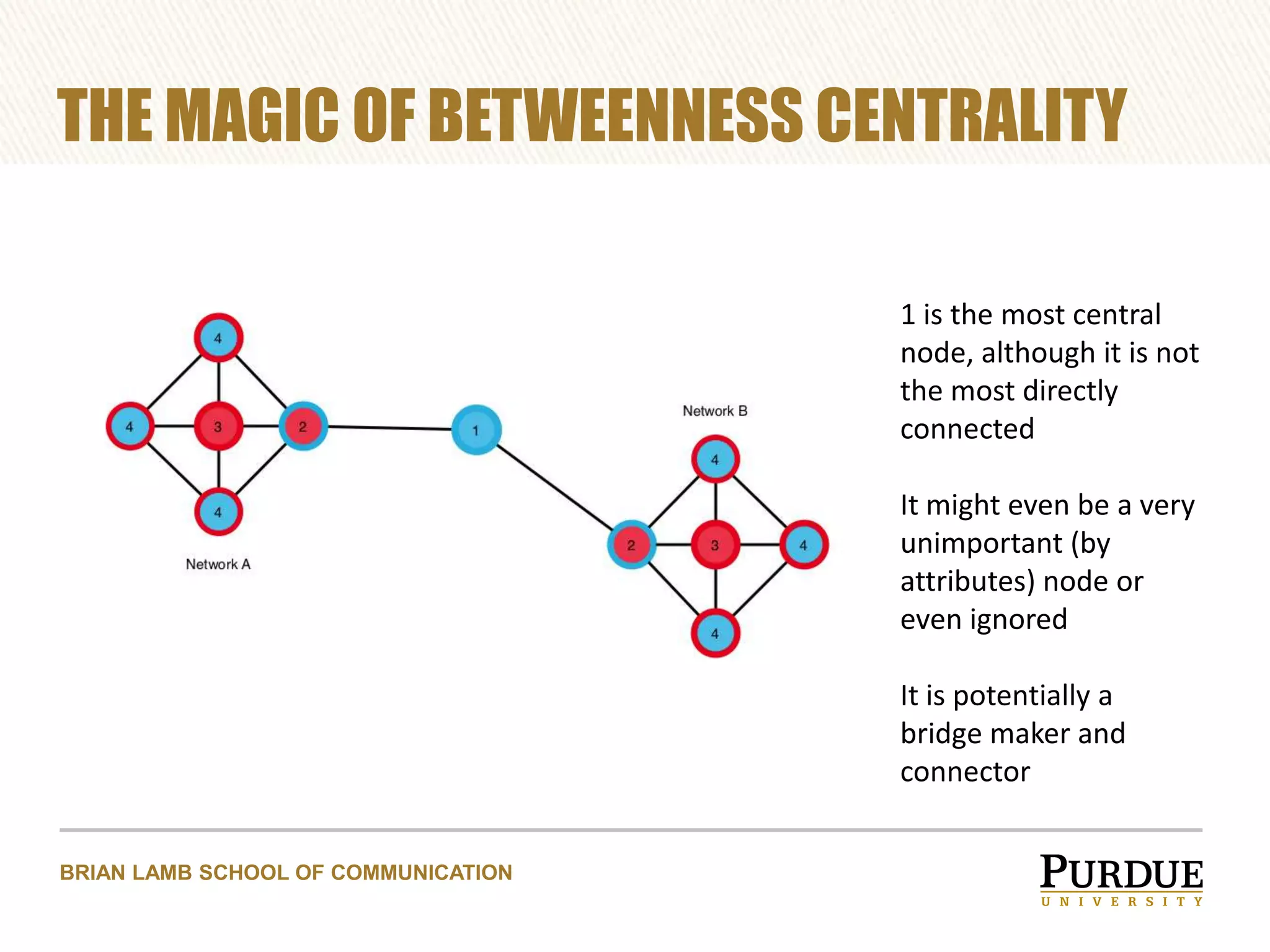
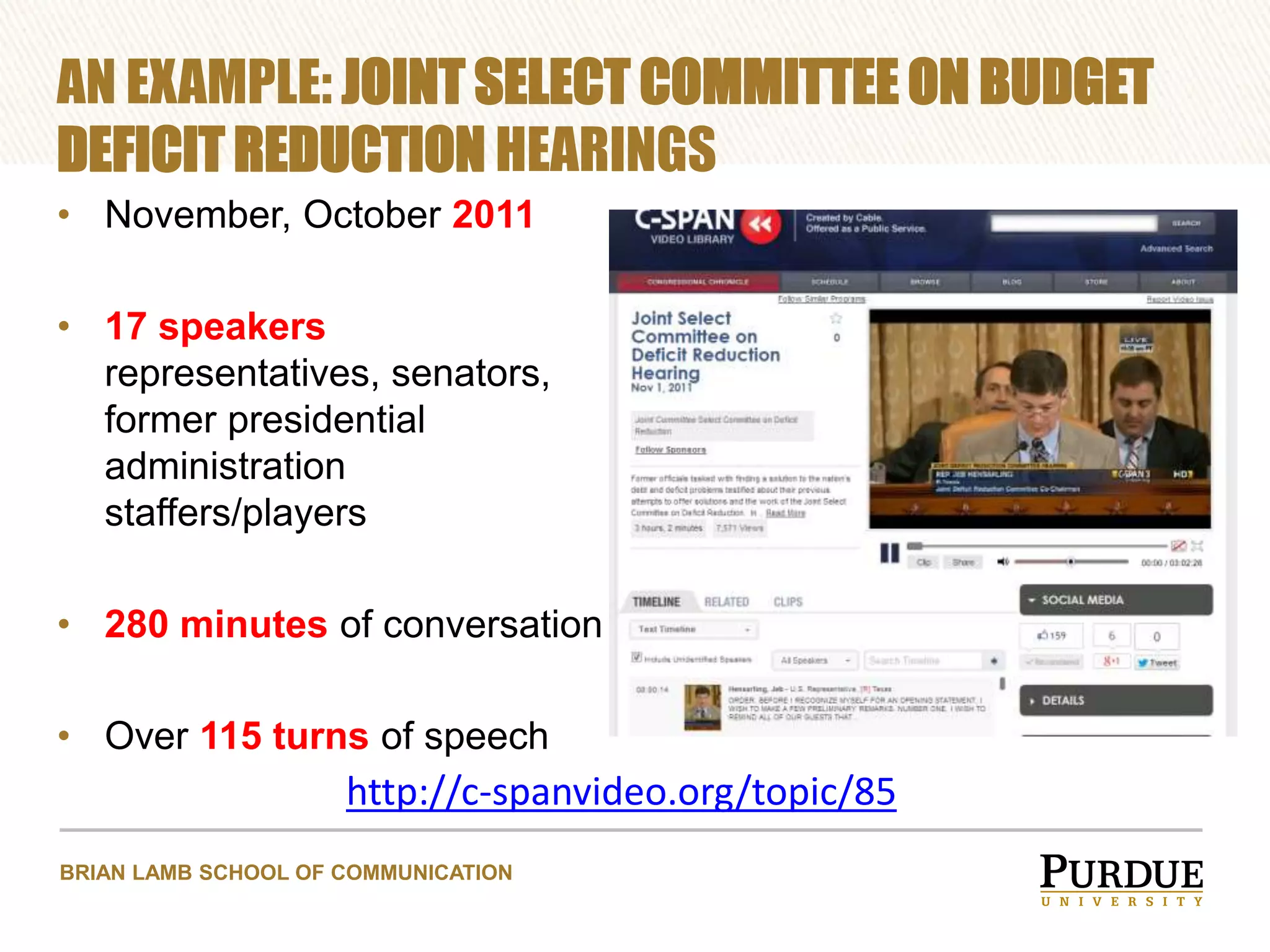
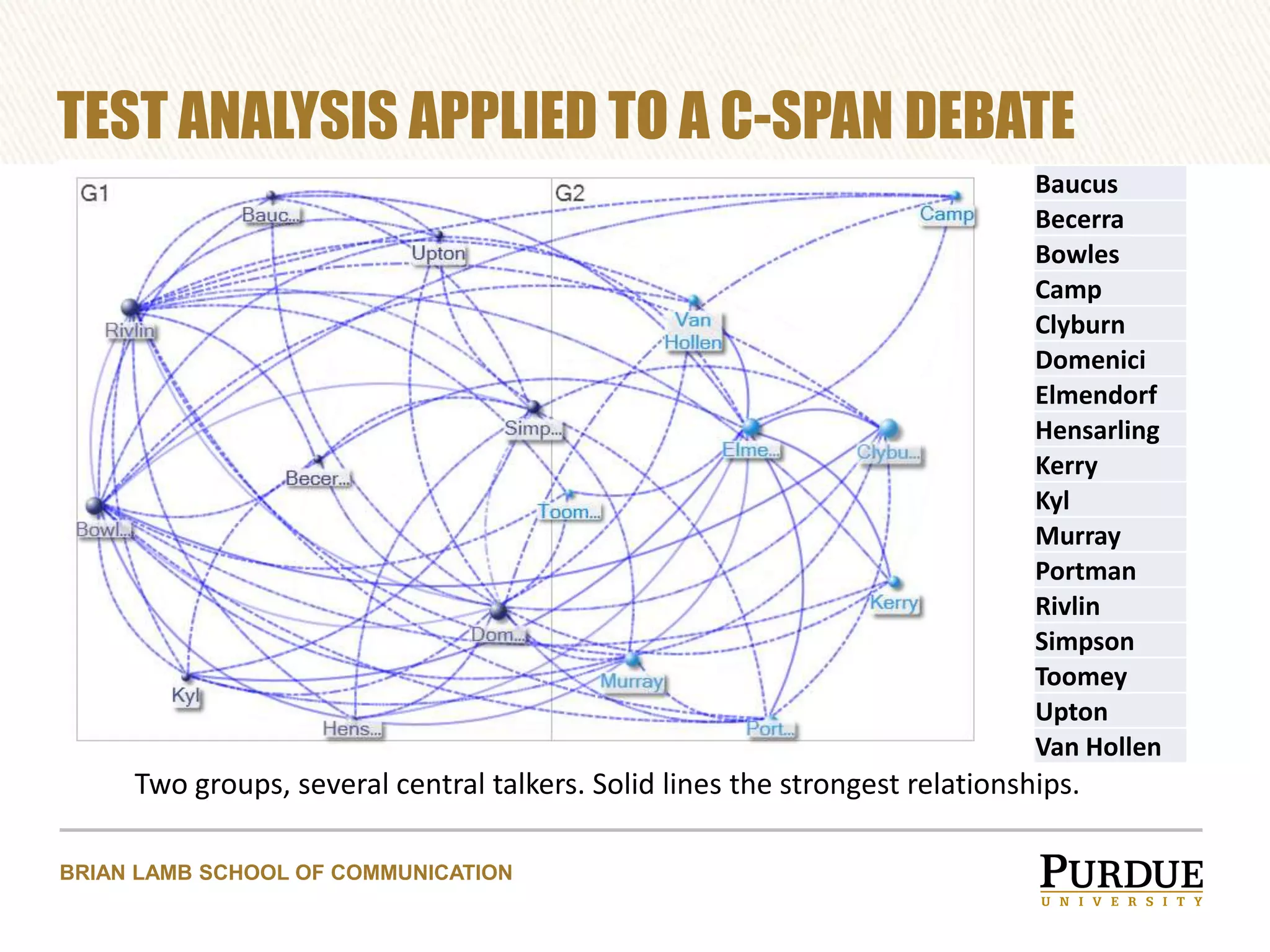
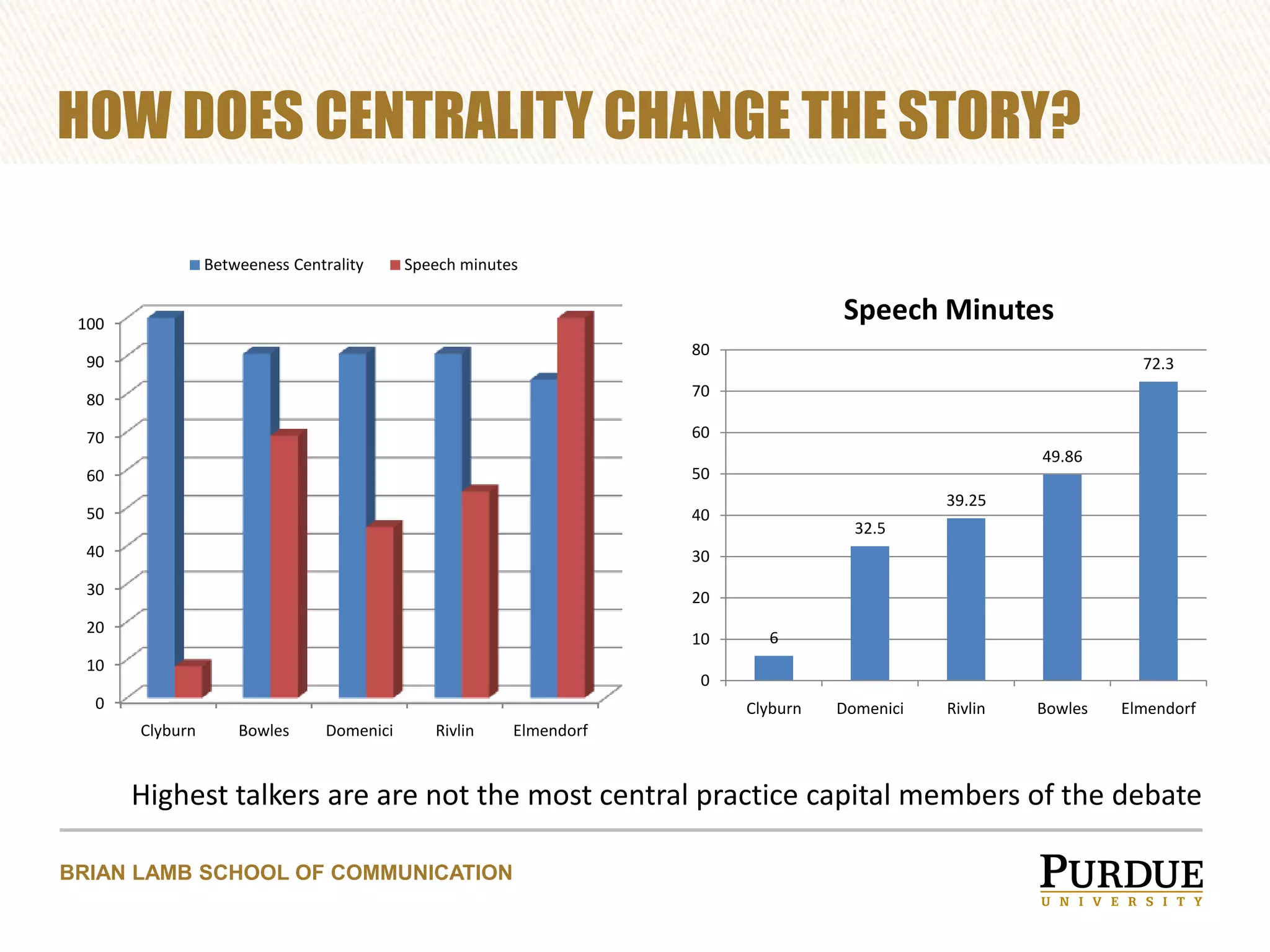
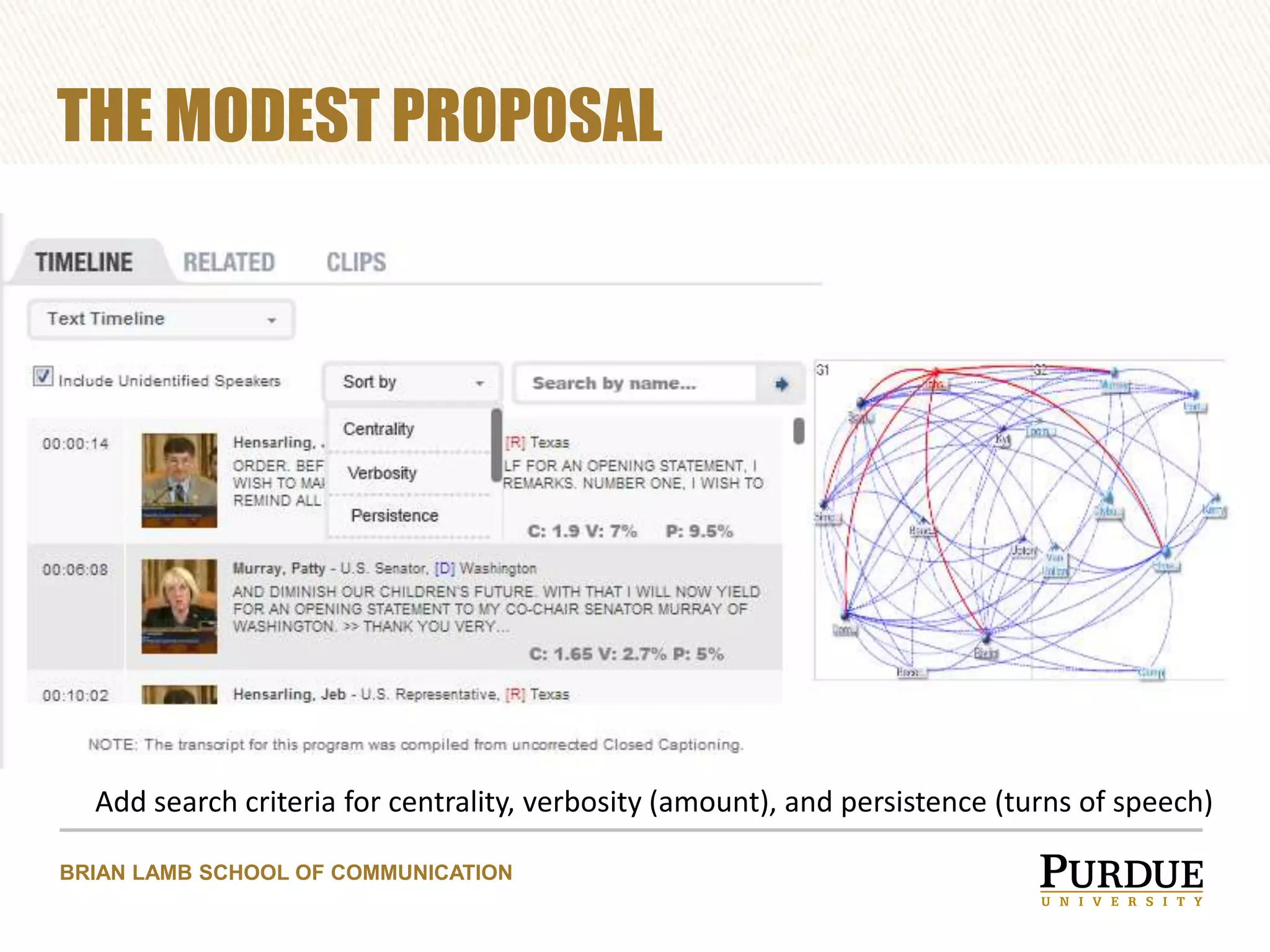
The document proposes enhancing the C-SPAN archive with communicative metadata to capture and analyze social networks of debate, focusing on the roles and impacts of speakers through centrality metrics. It highlights the significance of mapping interactions to reveal influential figures and improve video search capabilities. Additionally, it outlines a plan to apply network analysis methodologies to the entire C-SPAN video corpus, aiming to facilitate new data journalism tools for visualization of conversation dynamics.