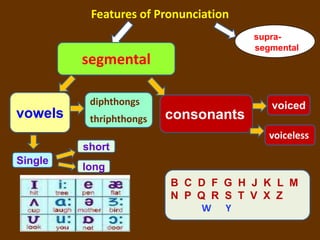
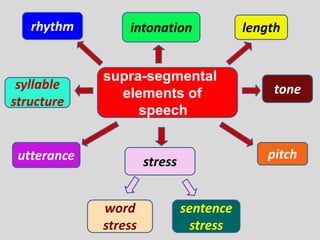
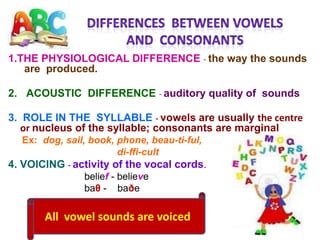
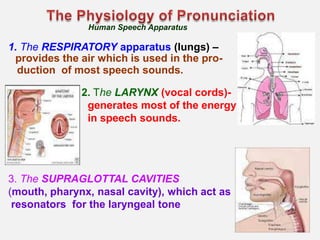
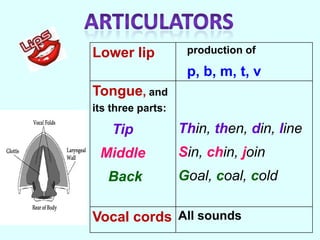
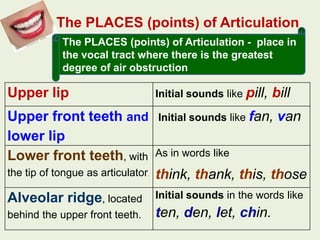
Phonemes are the basic units of phonology that signal differences in meaning. They are the perceived speech sounds that make up words. This document discusses phonemes and pronunciation, describing phonemes, features of pronunciation including segmental features like vowels and consonants, and suprasegmental features. It also outlines the human speech apparatus and articulators involved in sound production.