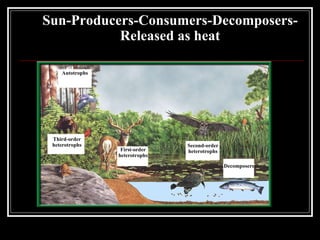
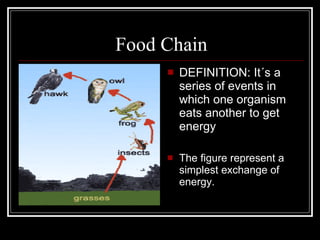
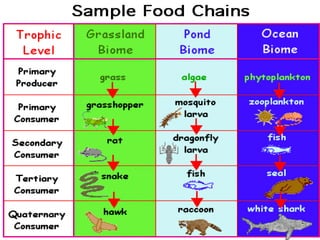
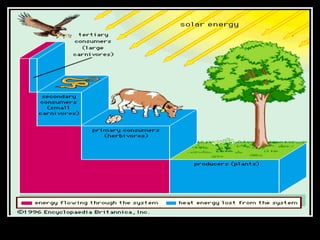
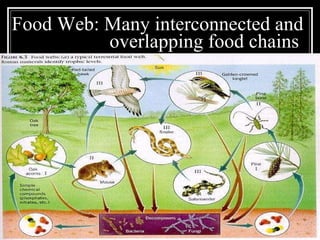
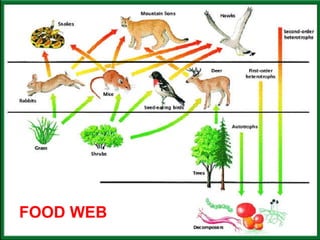
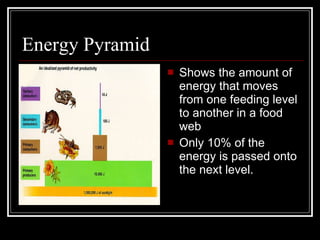
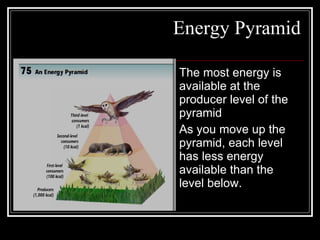
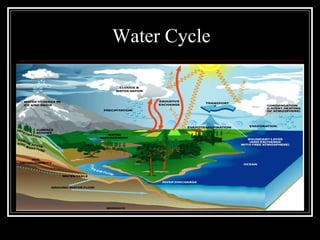
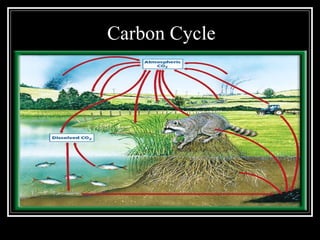
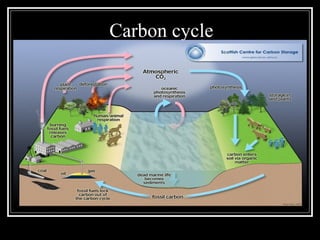
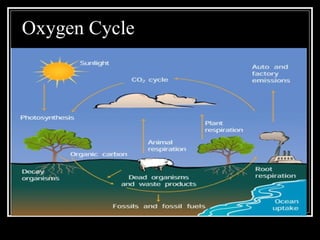
The document summarizes energy flow through ecosystems. It explains that all energy on Earth comes from the sun and is absorbed by producers like plants through photosynthesis. Producers are then eaten by primary consumers like herbivores and secondary consumers like carnivores. Decomposers break down waste and dead organisms, releasing energy and returning nutrients to the system. This flow of energy is depicted through food chains and food webs. Only 10% of energy is transferred between trophic levels, causing energy pyramids to narrow at higher levels. Key matter cycles like water, carbon, and oxygen are driven by the ecosystem and also flow in loops through producers, consumers, and decomposers.