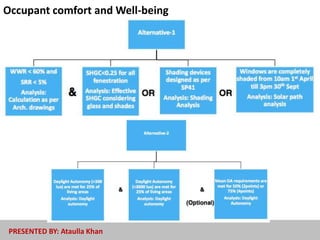
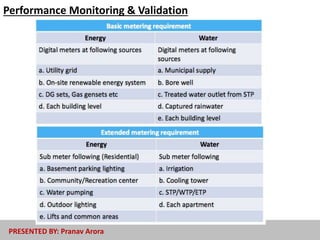
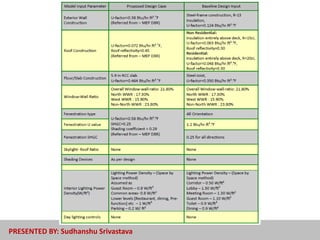
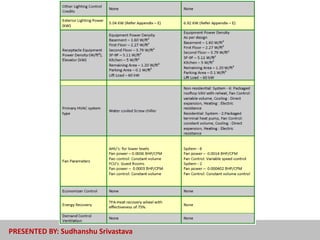
The document discusses energy-efficient practices in the hotel industry, emphasizing the importance of sustainable growth through reduced electricity and water consumption. It highlights the benefits of becoming a 'green star hotel', which include marketing advantages, reduced operating costs, and increased customer satisfaction among environmentally conscious tourists. Various strategies for energy savings, water management, and sustainable building materials are detailed, alongside case studies of specific hotels demonstrating successful implementation of these initiatives.