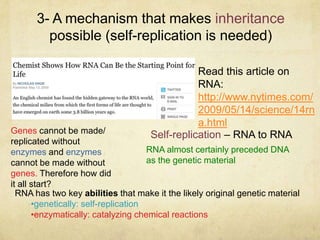
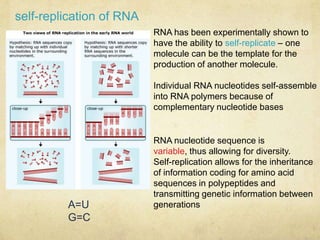
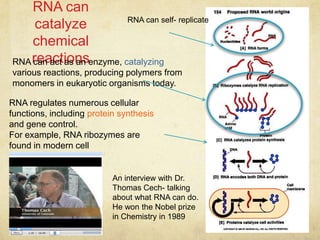
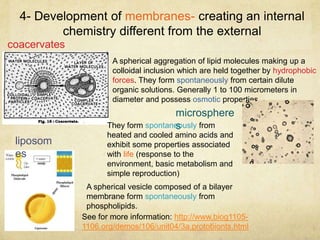
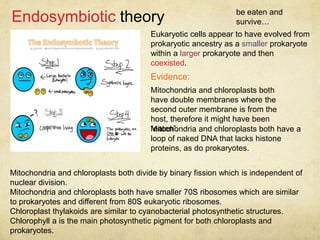
The document outlines the key processes thought to be necessary for the spontaneous origin of life on Earth: 1) The synthesis of simple organic molecules, as demonstrated by the Miller-Urey experiment; 2) The assembly of these molecules into polymers like polypeptides; 3) A mechanism for inheritance, proposed to be self-replicating RNA; 4) The development of membranes. These processes are hypothesized to have led to the formation of "protobionts", early cell-like structures surrounded by membranes. The endosymbiotic theory proposes that eukaryotic cells arose from engulfed prokaryotes that evolved to become organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts. Early prokaryotes also produced oxygen as




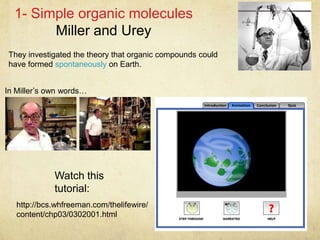


![Data
analysis
question
Read this paper for
more information:
http://www.lpi.usra.ed
u/publications/MSR/B
ada/BadaAbs.html
Amino Acid Murchison
meteorite
Miller-Urey
experiment
Glycine
Alanice
α-amino-N-butyric acid
α-aminoisobutyric acid
Valine
Norvaline
Isovaline
Proline
Popecolic acid
Aspartic acid
N-ethylglycine
Sarcosine
1. Compare the
amino acids found
in the meteorite
with those
produced in the
Miller-Urey
experiment. Refer
to named
examples [3]
2. Suggest a
conclusion based
on your
comparison. [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/d1originoflife-131007032838-phpapp01/85/D1-origin-of-life-8-320.jpg)