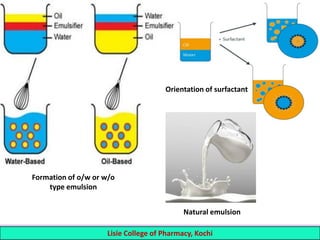
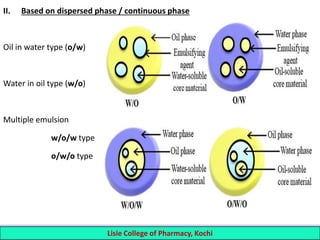
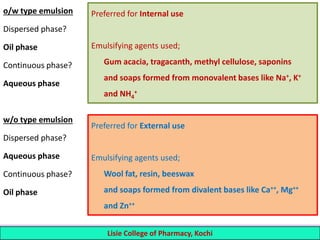
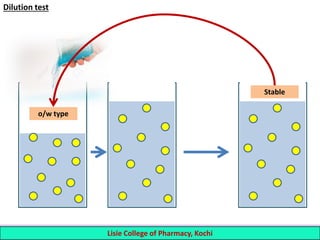
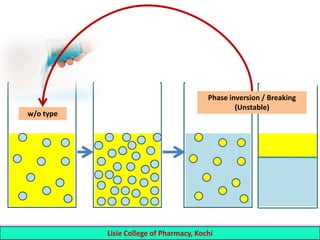
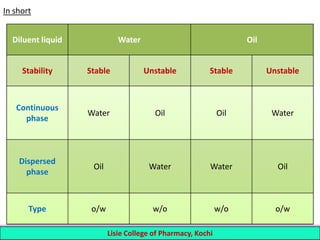
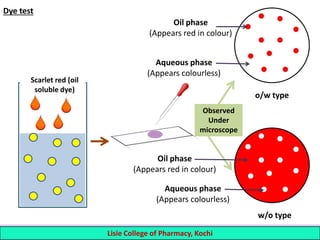
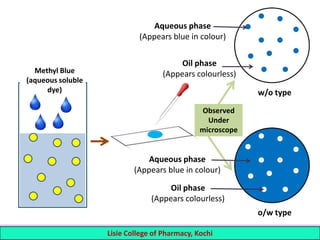
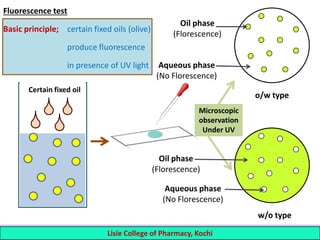
This document defines and describes emulsions. An emulsion is a biphasic liquid preparation containing two immiscible liquids, one dispersed as minute globules into the other. The liquid dispersed is called the dispersed phase while the liquid it is dispersed in is the continuous phase. Emulsions are stabilized by emulsifying agents which form films around the globules. Emulsions can be classified based on globule size, dispersed and continuous phases, and the emulsifying agent used. Identification tests include dilution, dye, conductivity, and fluorescence tests to determine the emulsion type. Emulsions offer advantages like masking unpleasant tastes, protecting drugs, and facilitating absorption of oils.