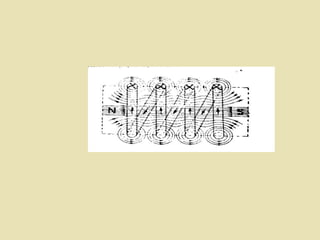
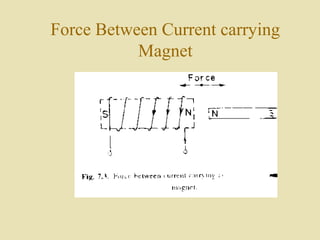
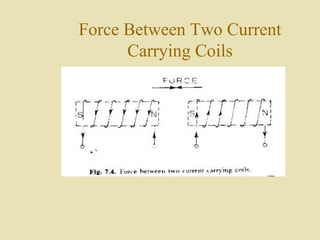
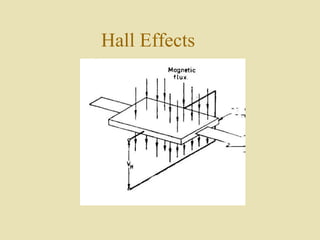
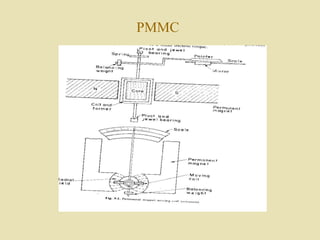
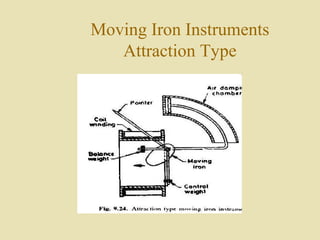
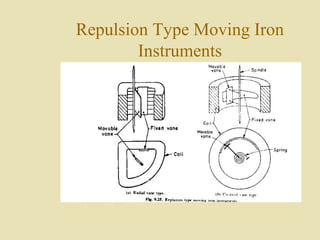
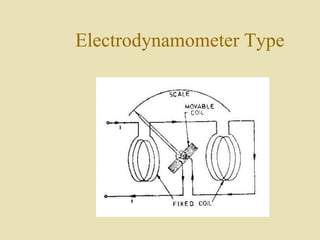
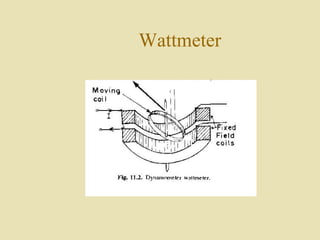
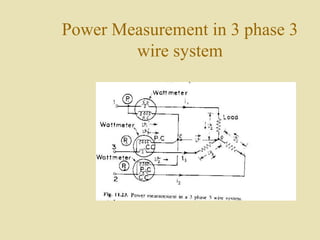
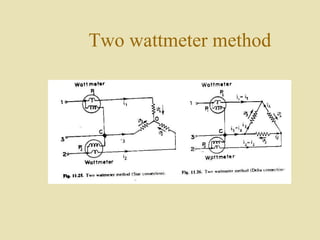
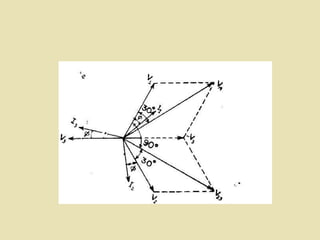
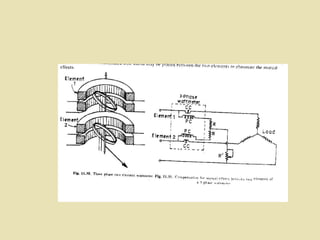
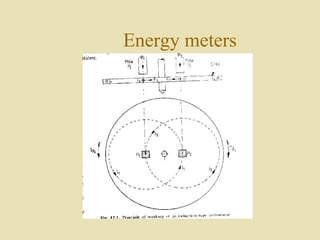
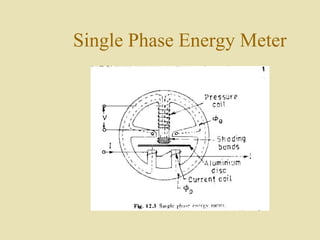
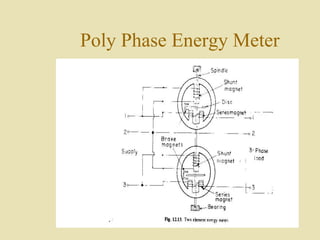
The document outlines a call for research projects aimed at final year B.E and M.E students in electrical and electronics disciplines, providing hardware assembly support in research labs under expert guidance. It includes details about various electrical instruments, their principles of operation, classifications, and types including analog voltmeters and ammeters. Additionally, it discusses measurement techniques and the principles behind different types of measuring instruments used in the field.