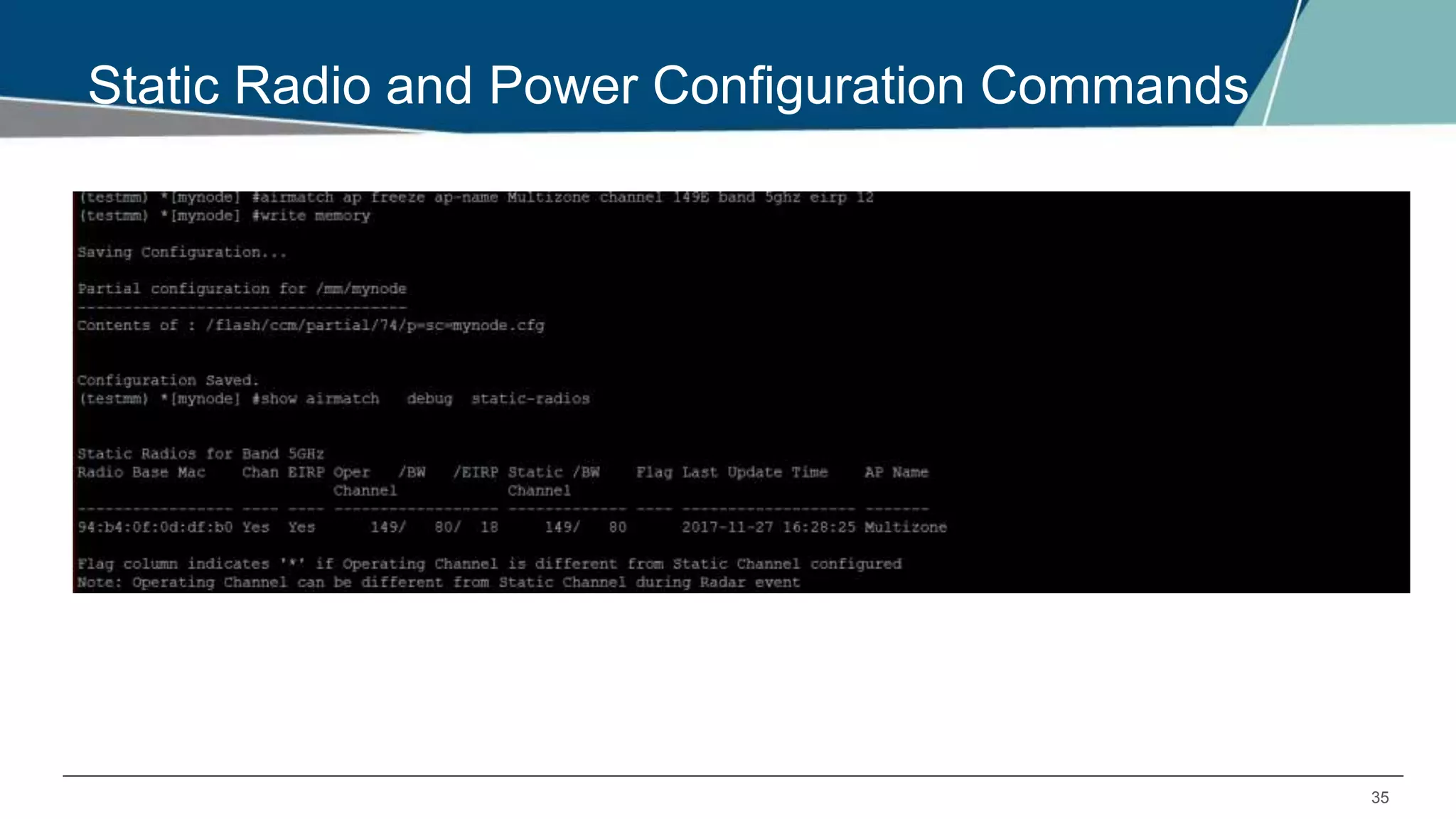
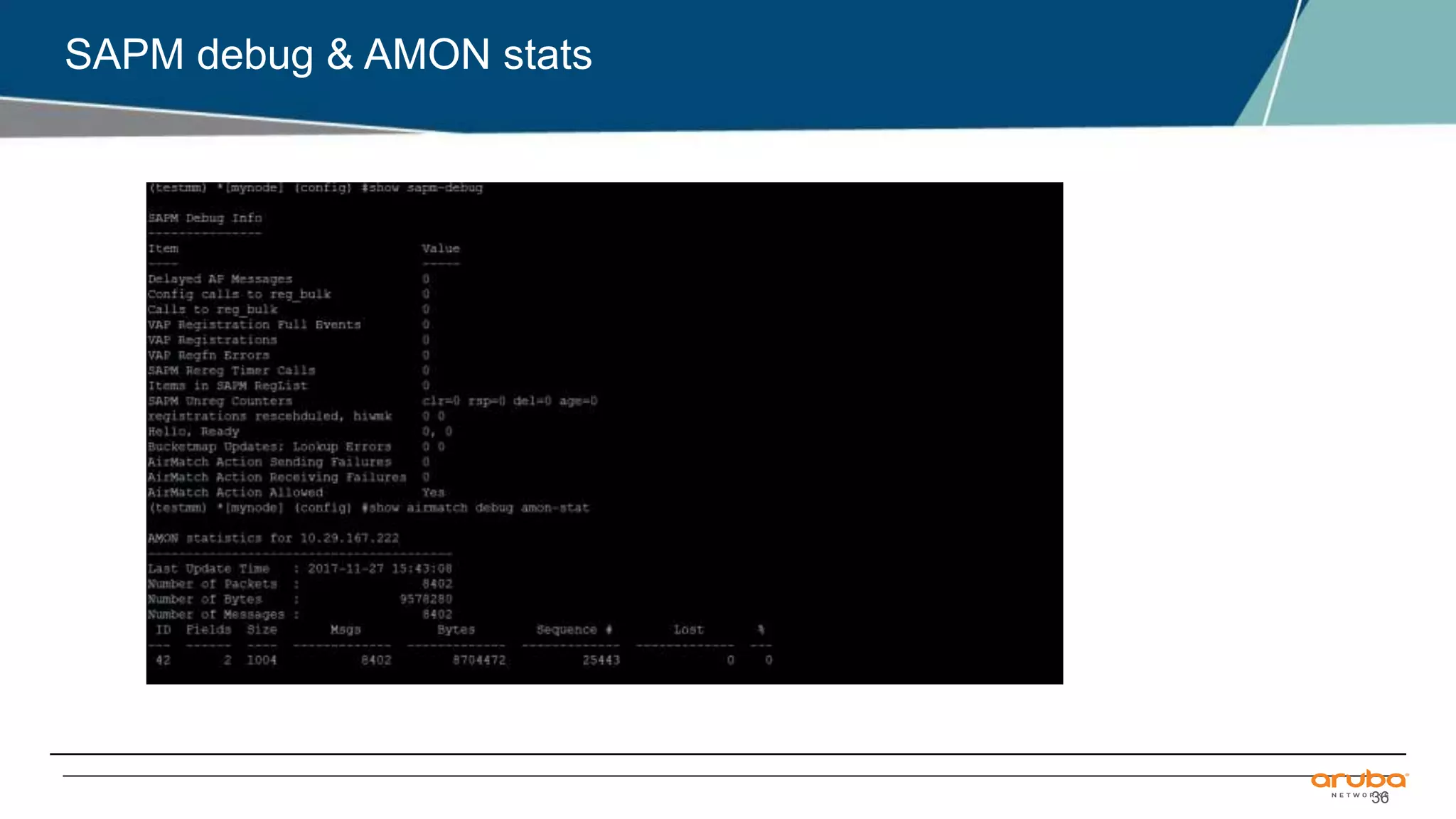
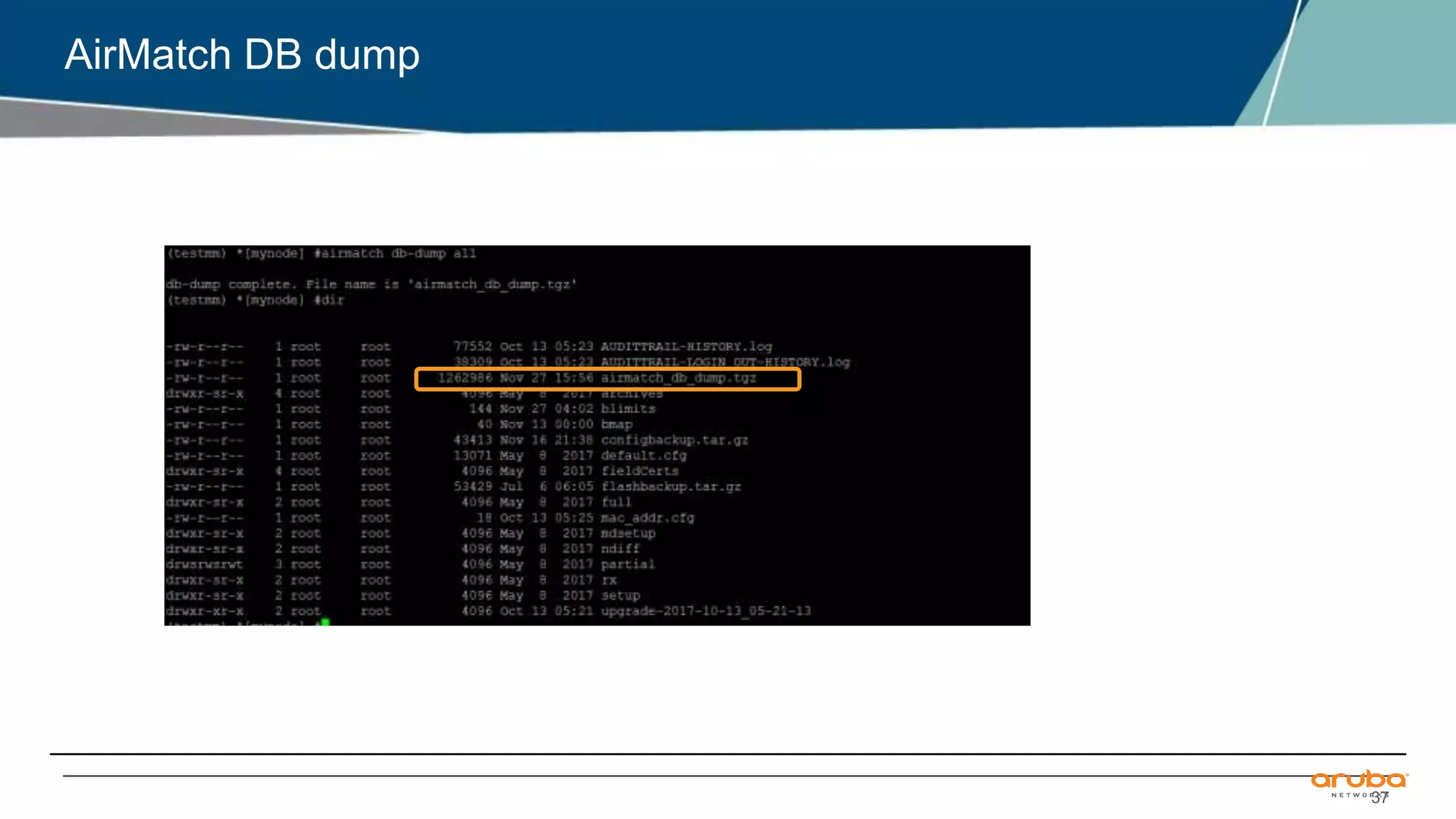
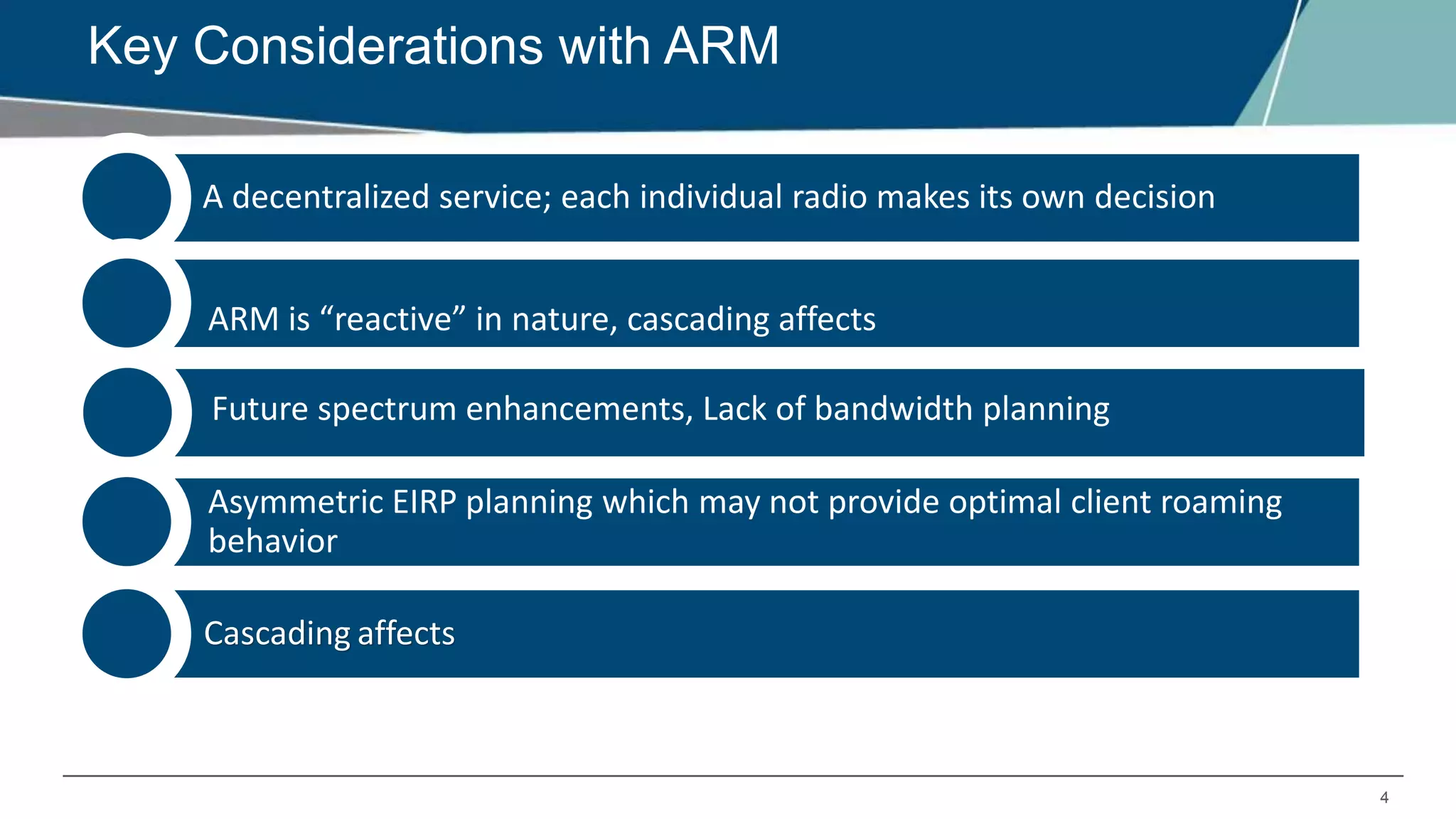
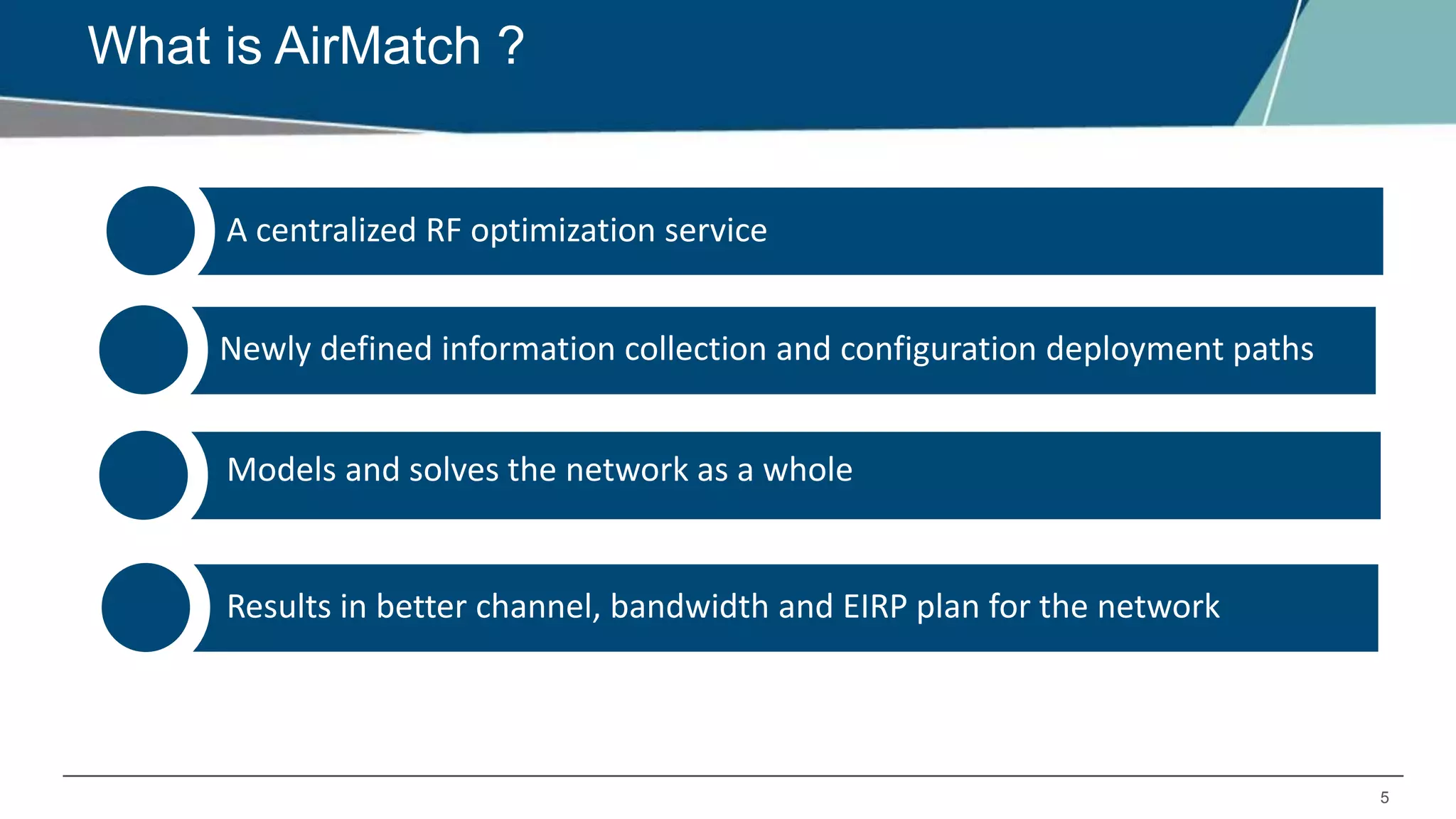
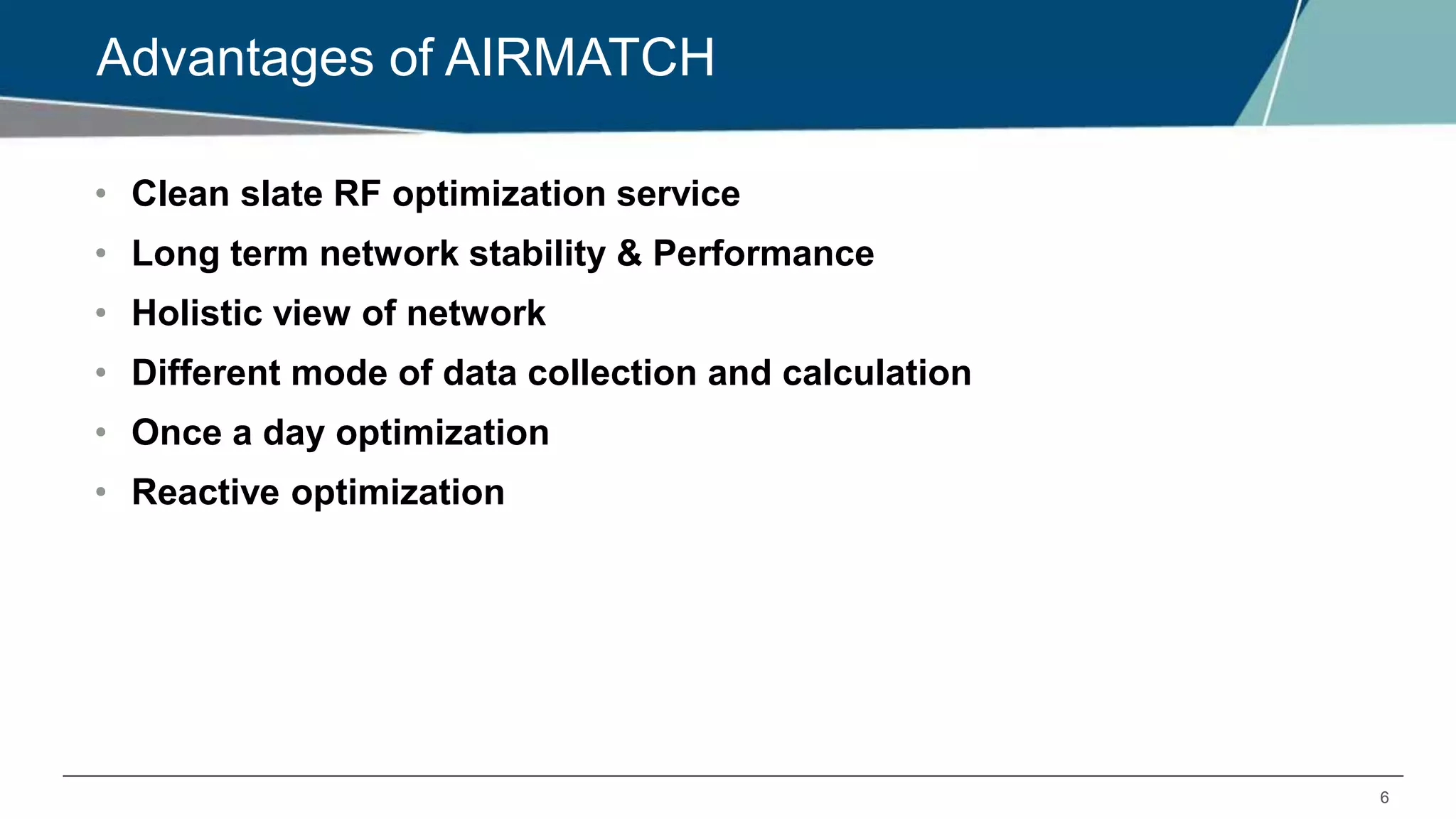
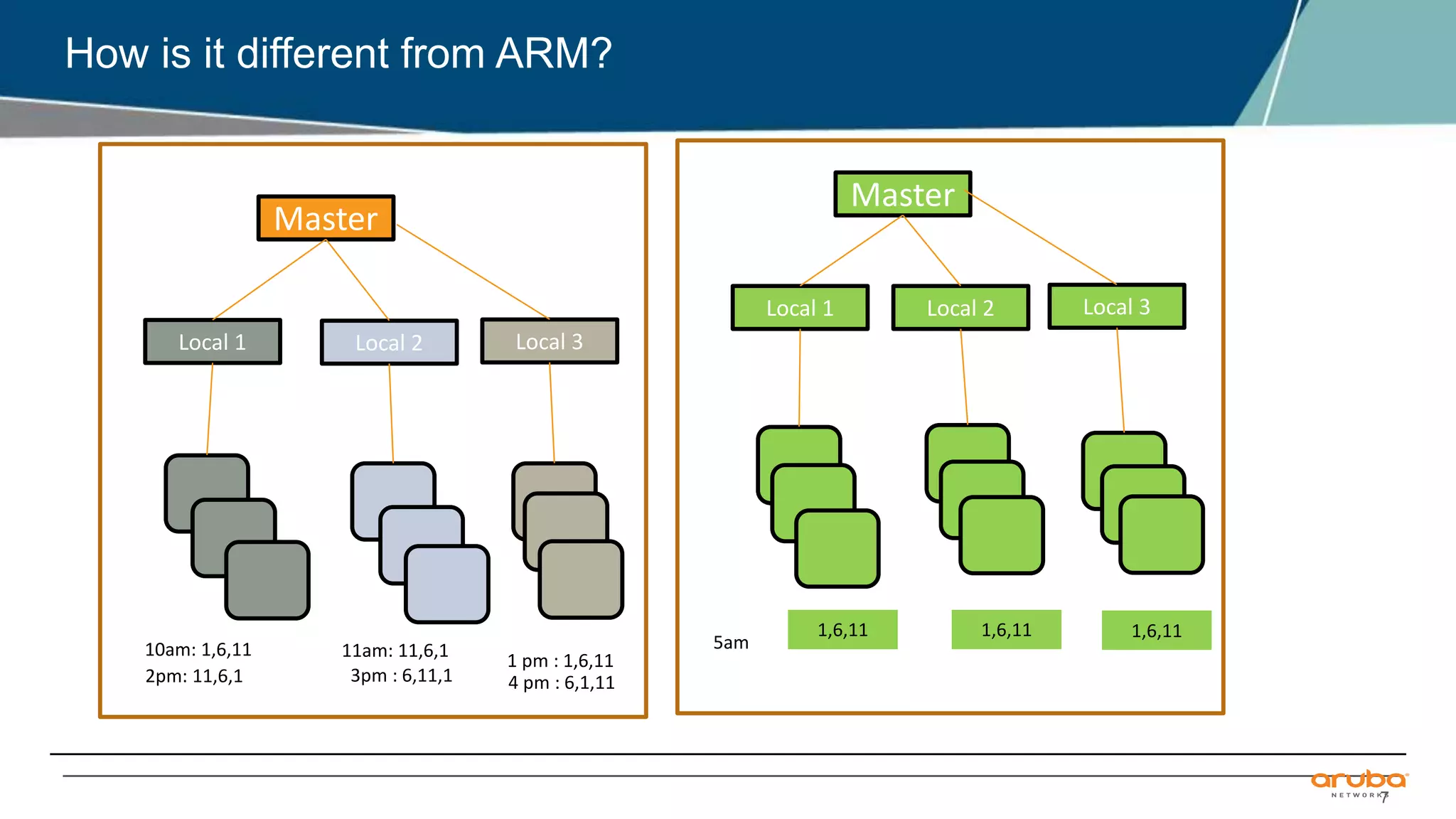
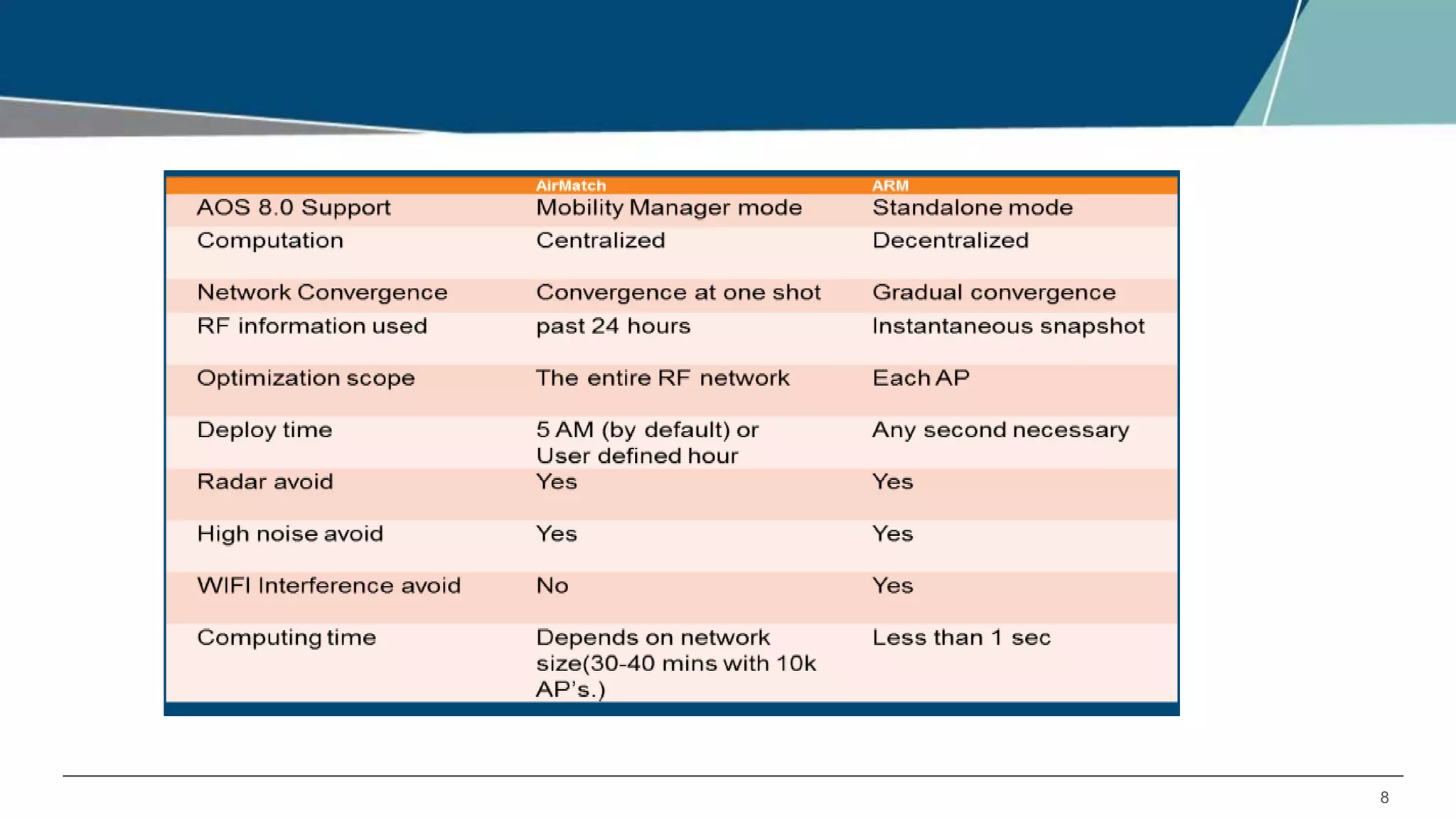
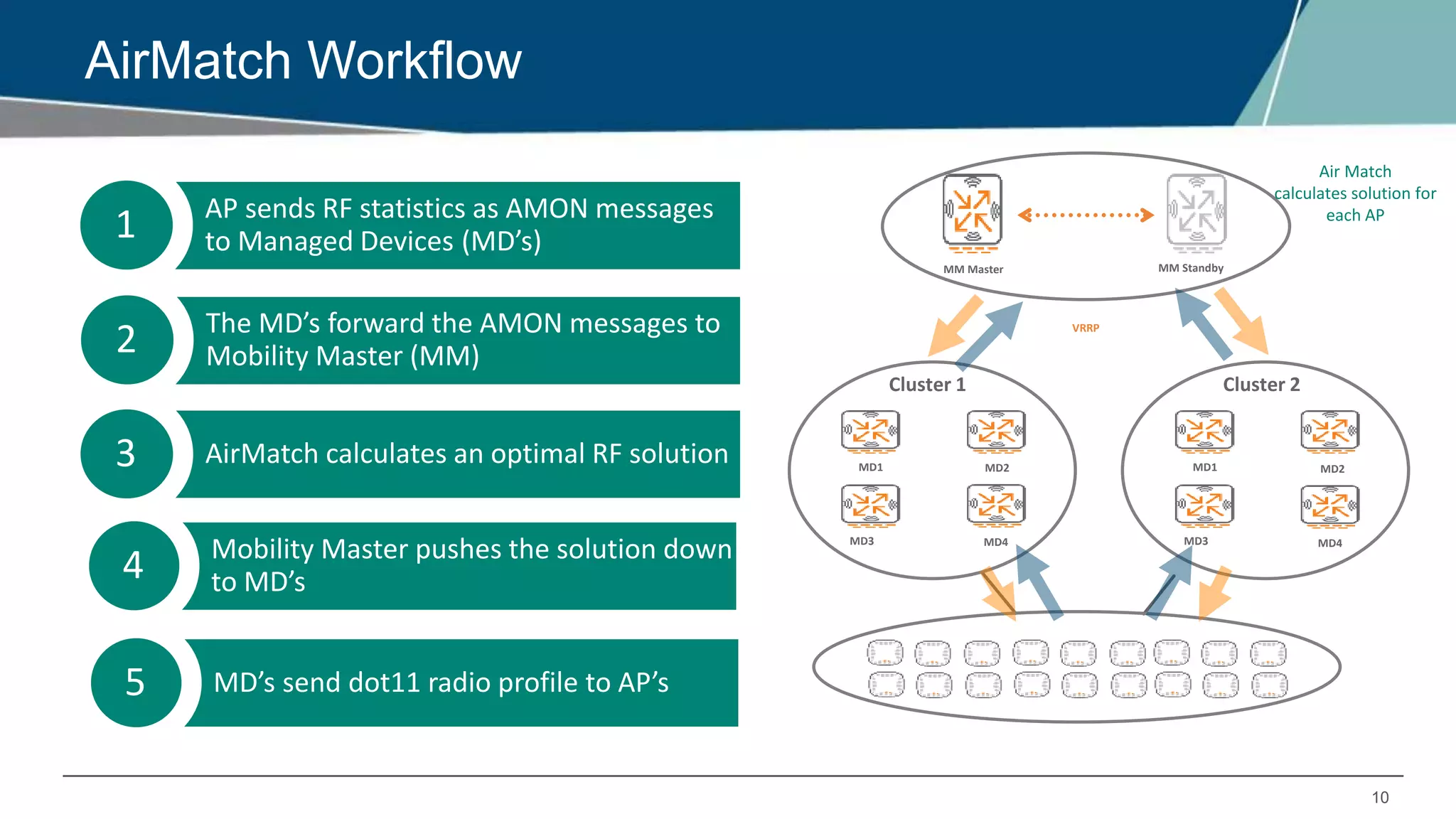
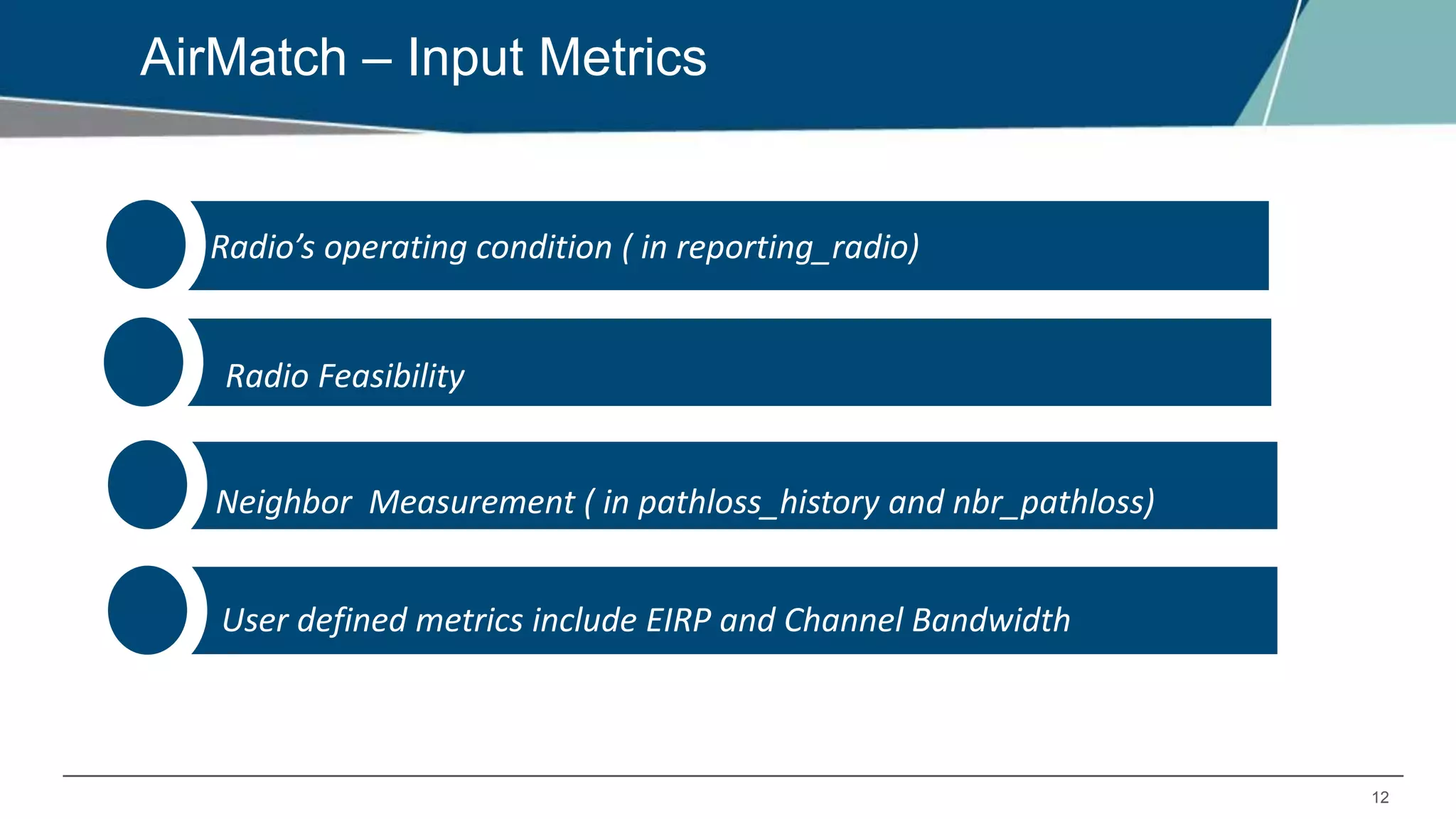
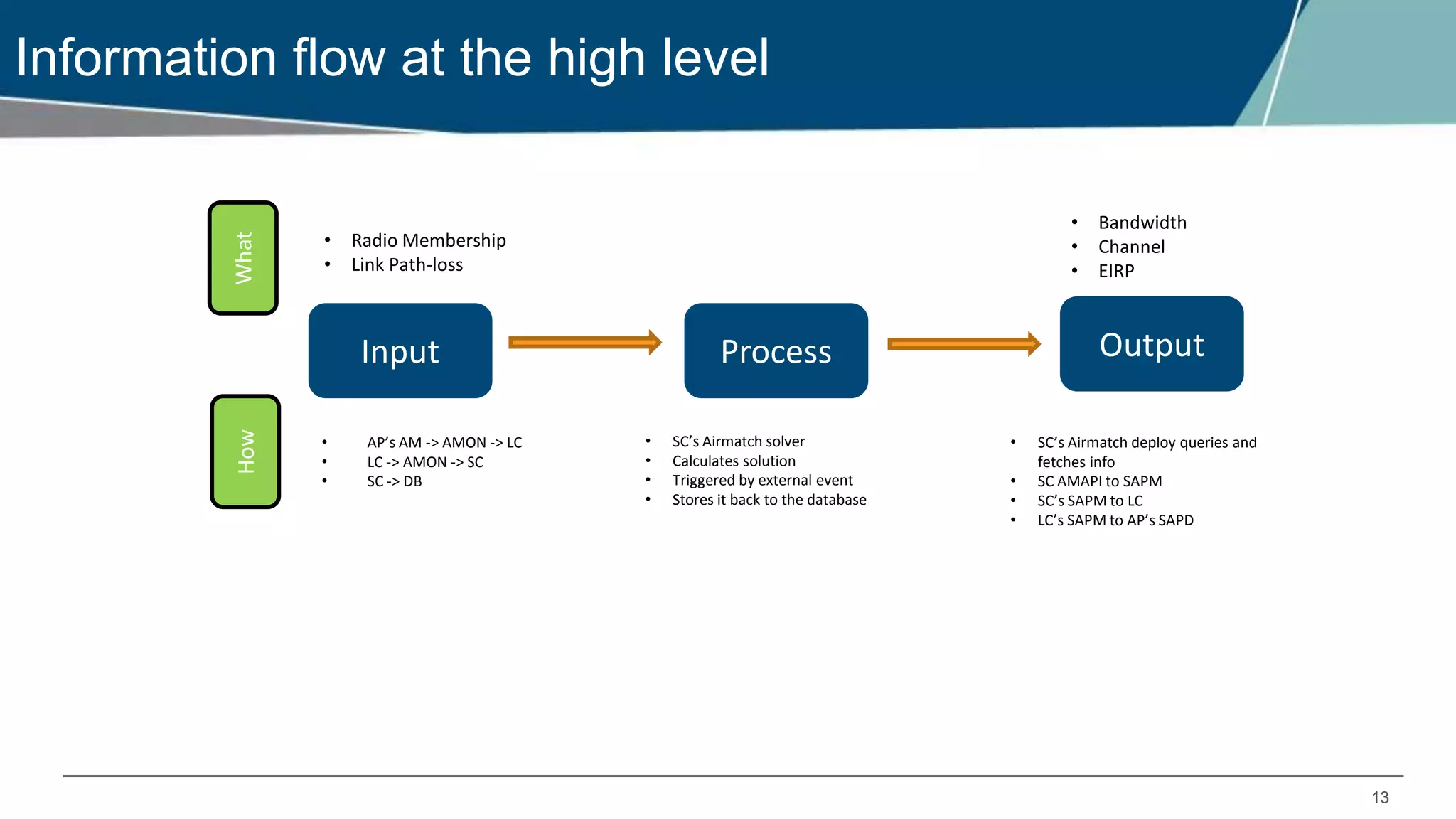
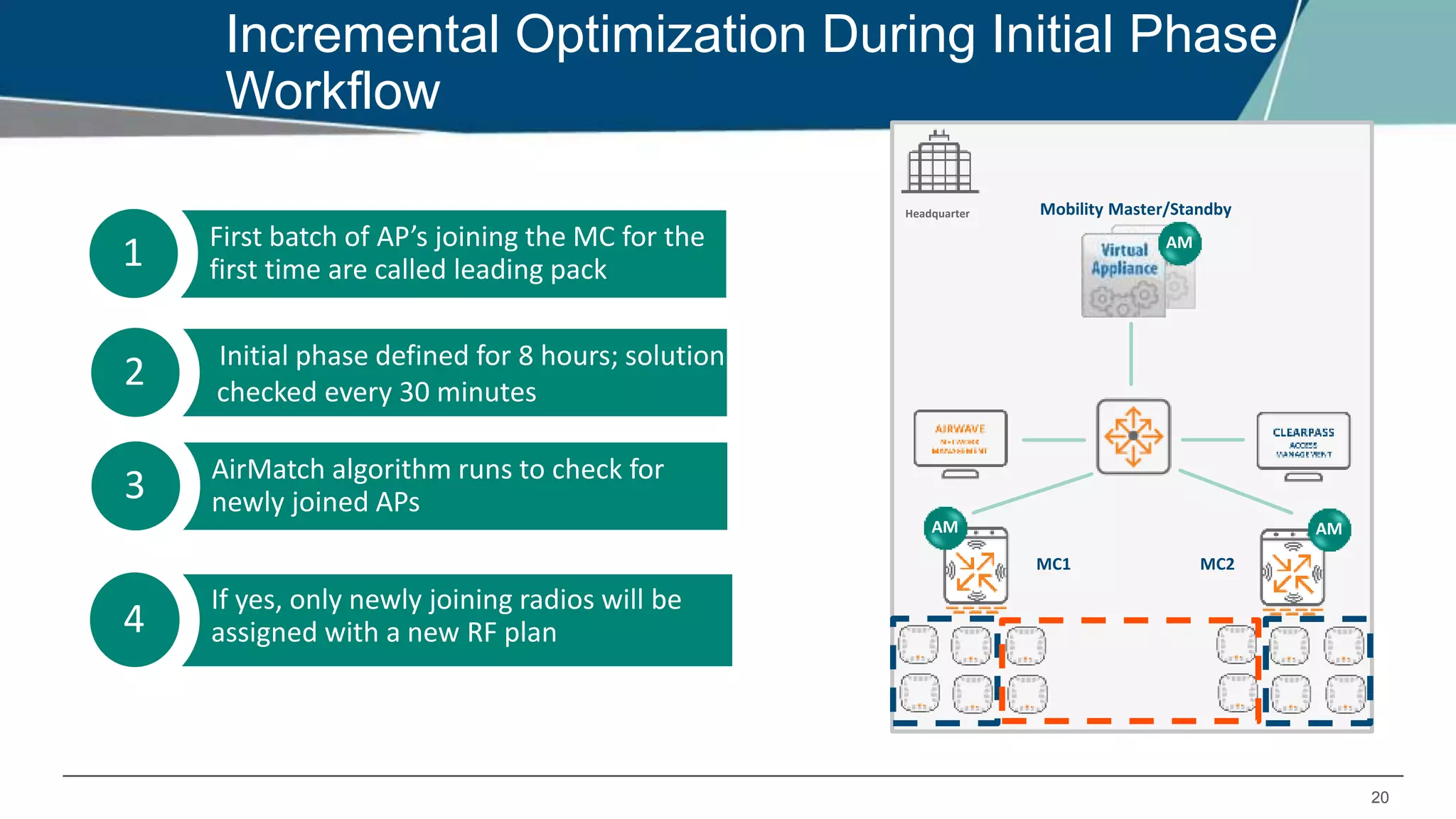
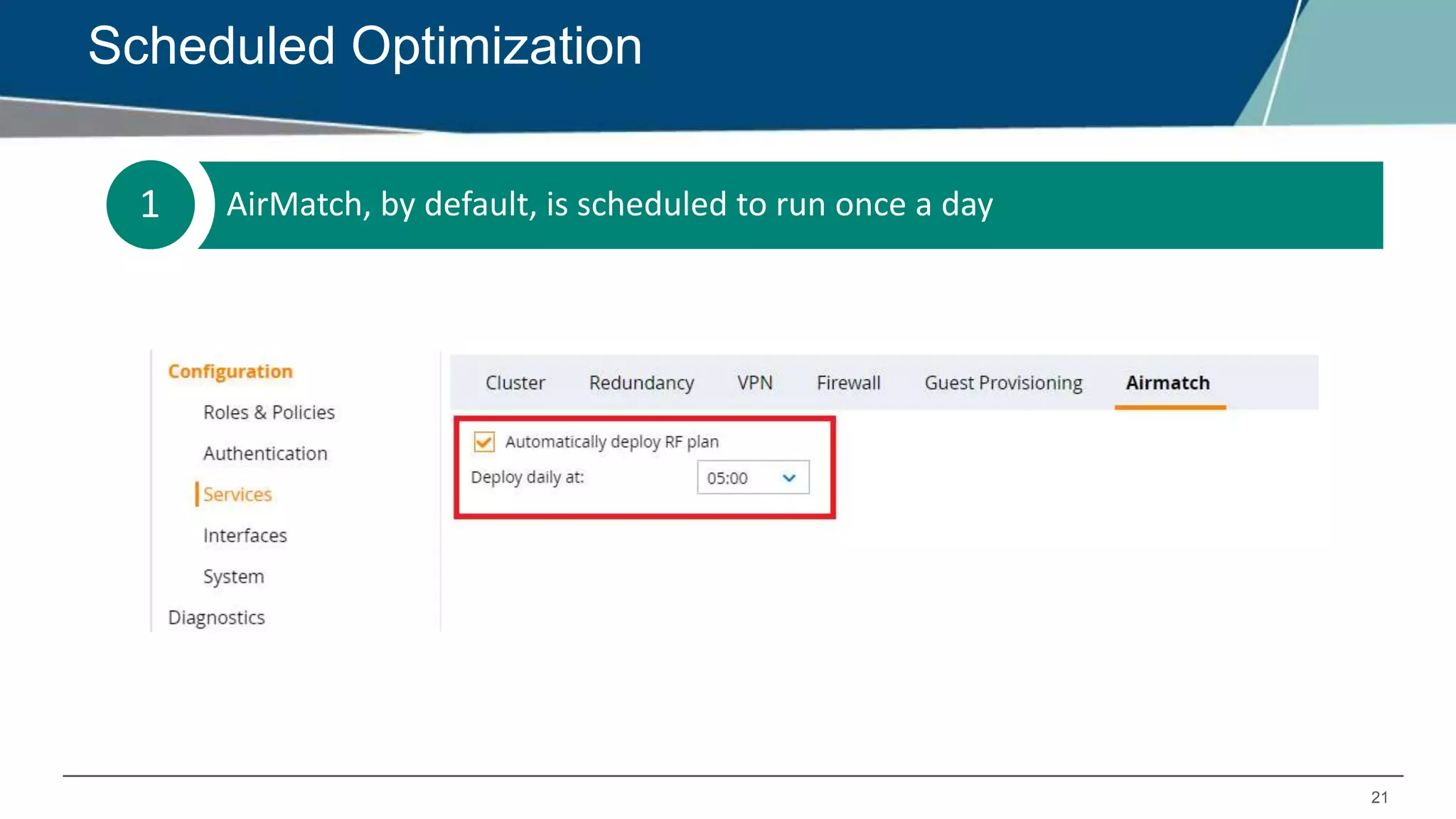
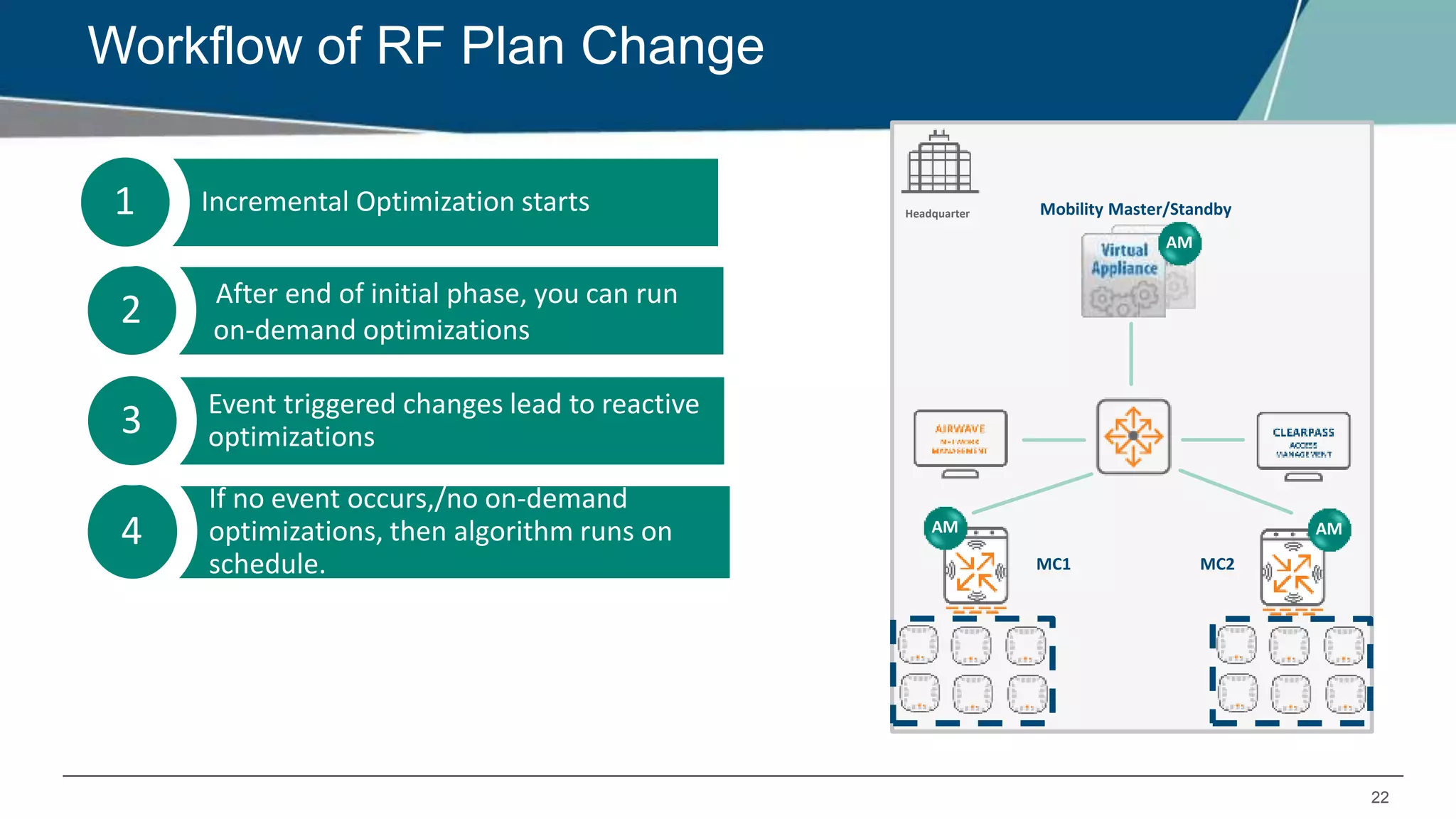
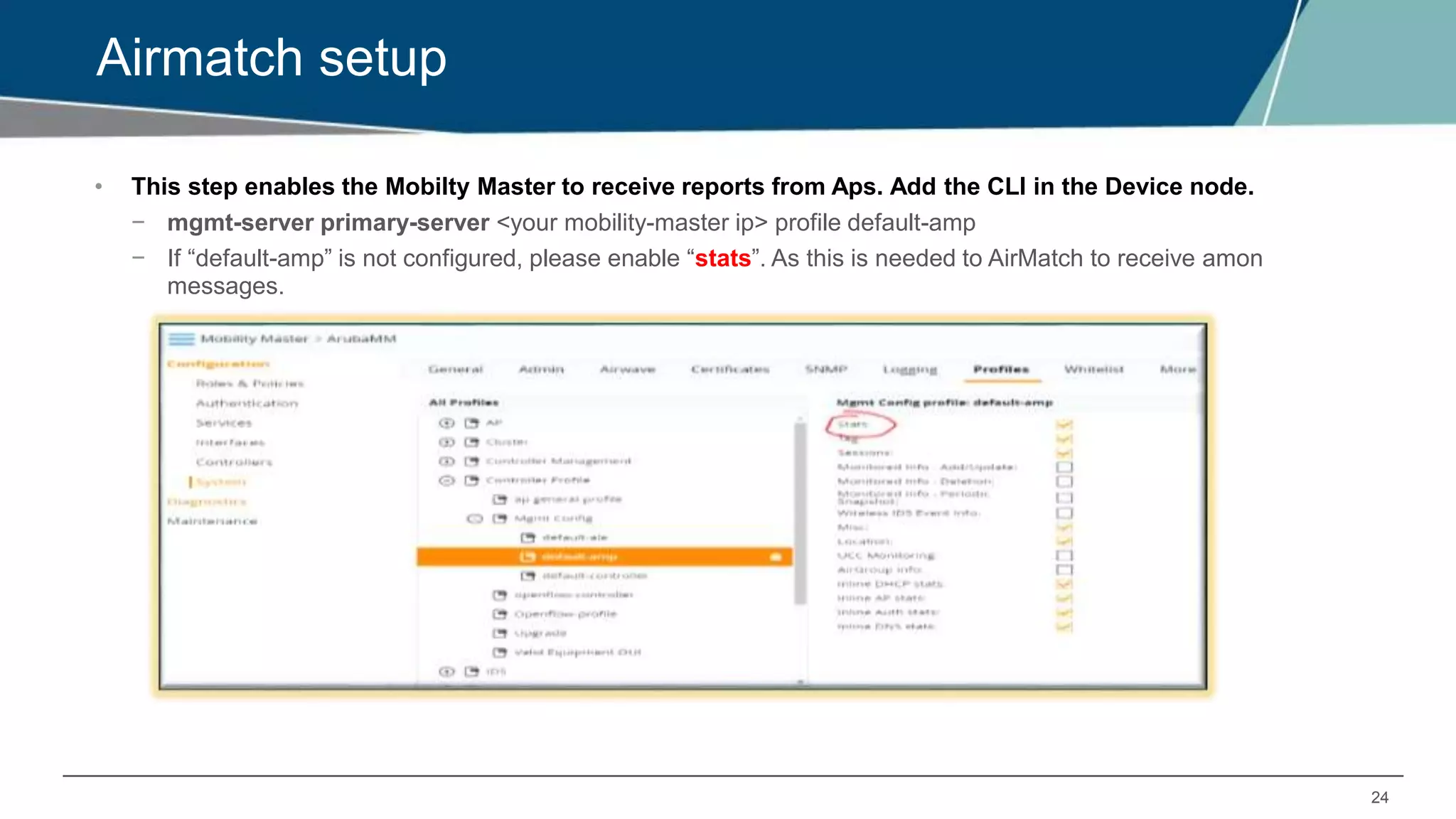
Airmatch is a centralized RF optimization service that enhances network performance by collecting comprehensive data and optimizing channel, bandwidth, and EIRP settings. Unlike the reactive nature of ARM, Airmatch allows for scheduled and event-driven optimizations, ensuring better decision-making for RF management. The document outlines the setup, operations, and advantages of Airmatch, highlighting its capacity for long-term network stability.








![33
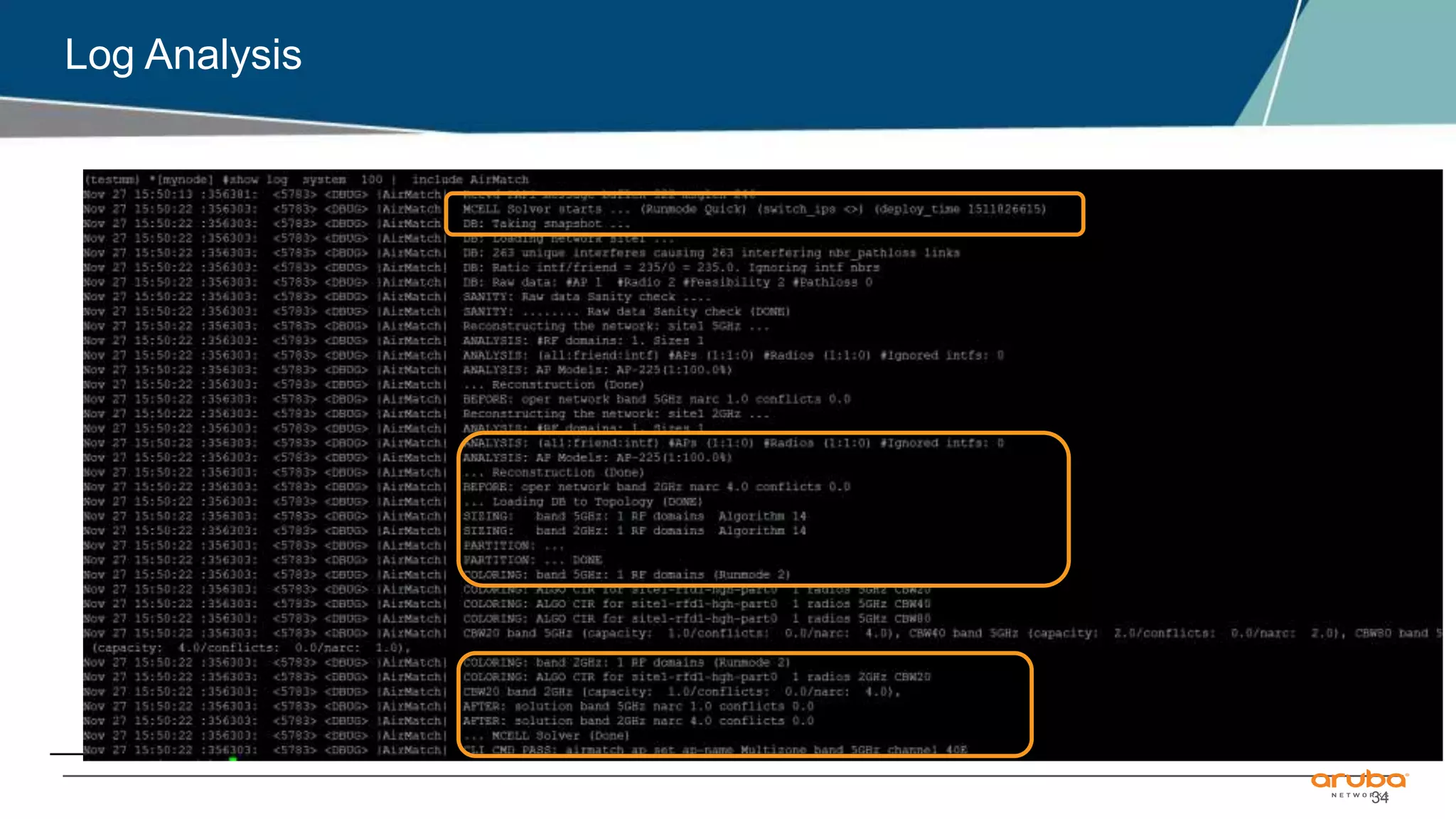
Enabling logging & running AirMatch
(testmm) *[mynode] (config) #logging system level debugging
(testmm) *[mynode] (config) #exit
(testmm) *[mynode] #airmatch runnow quick](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatdoesairmatchdodifferentlyv2-171204094140/75/EMEA-Airheads-What-does-AirMatch-do-differently-v2-32-2048.jpg)