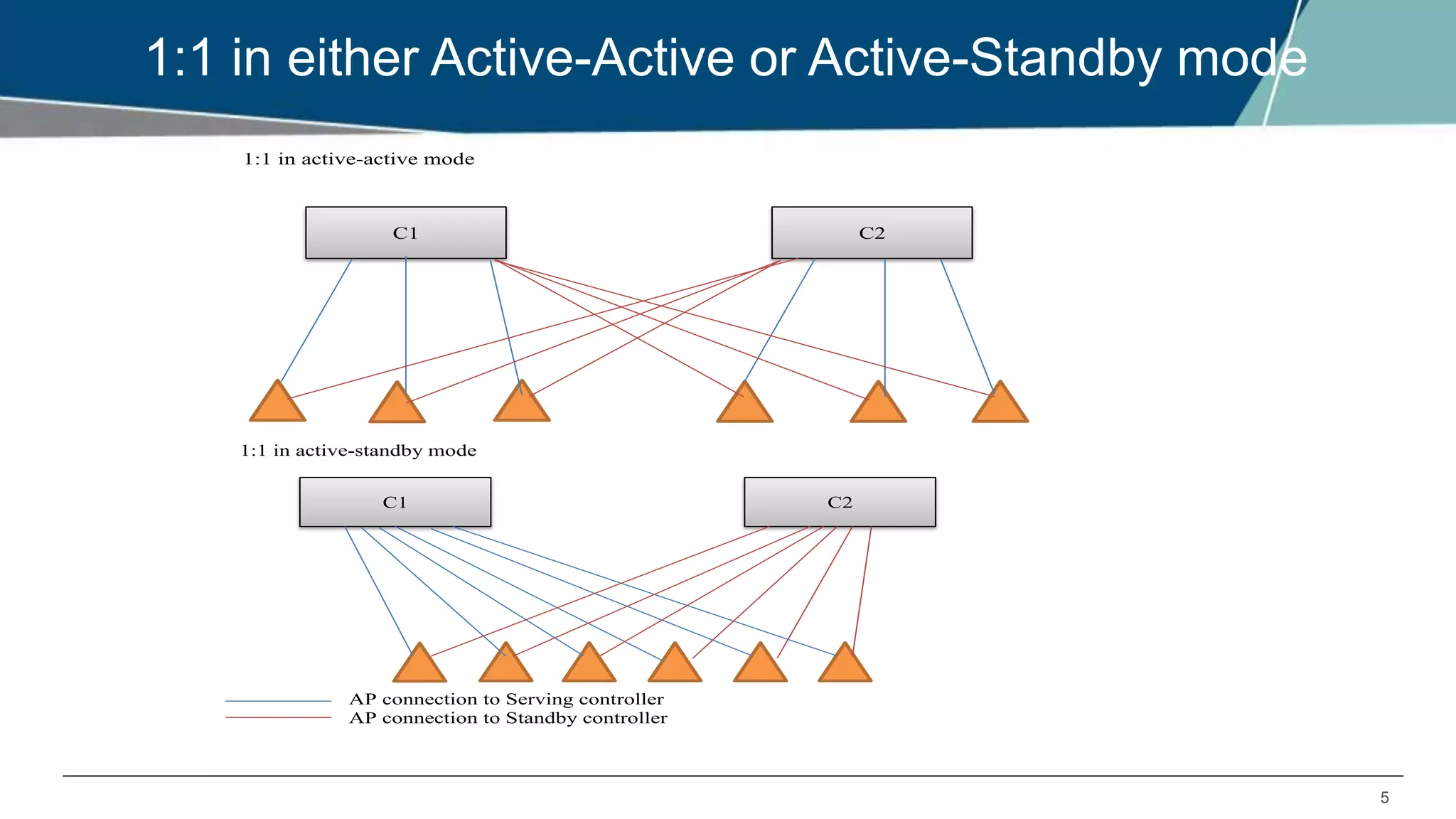
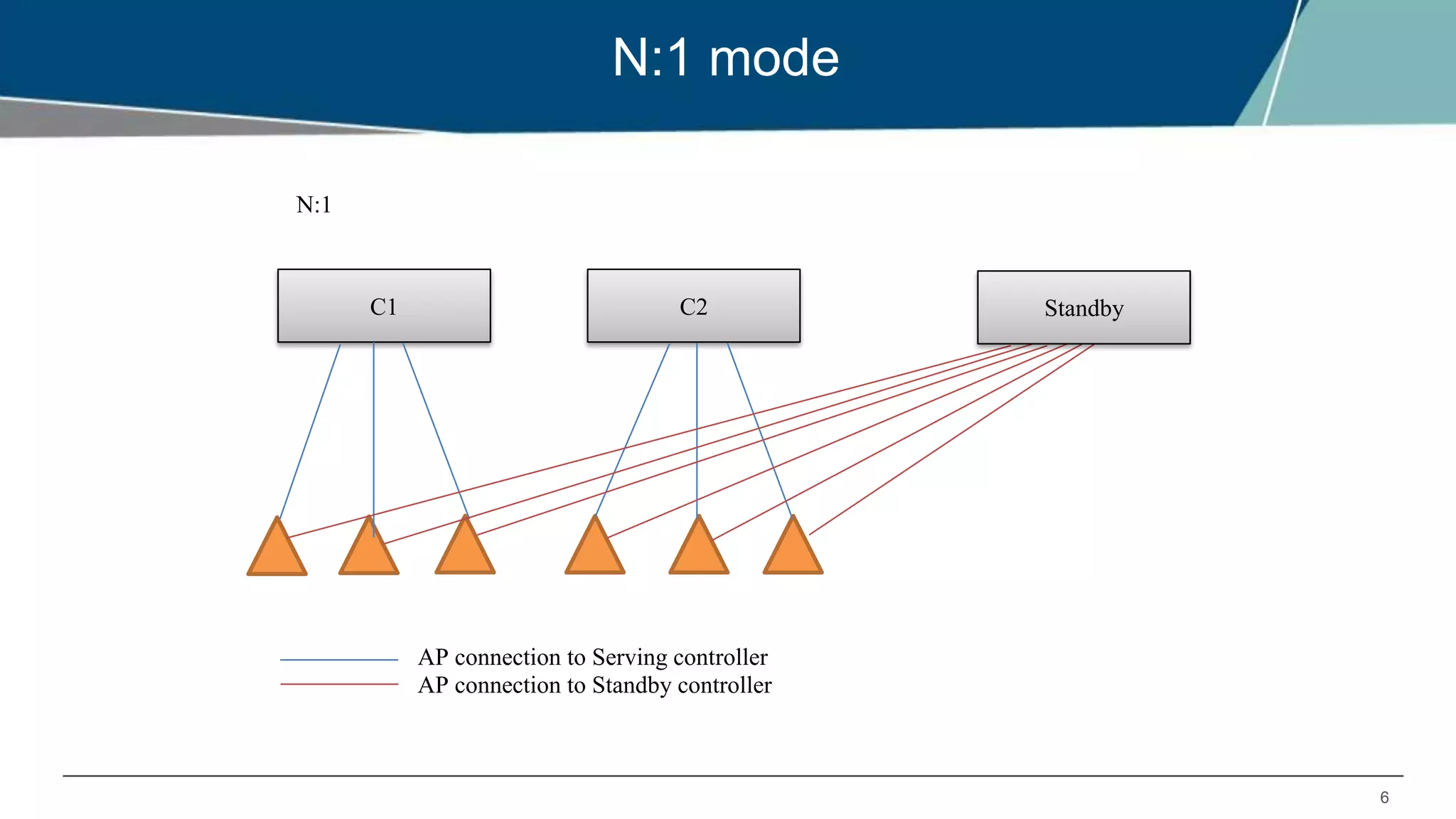
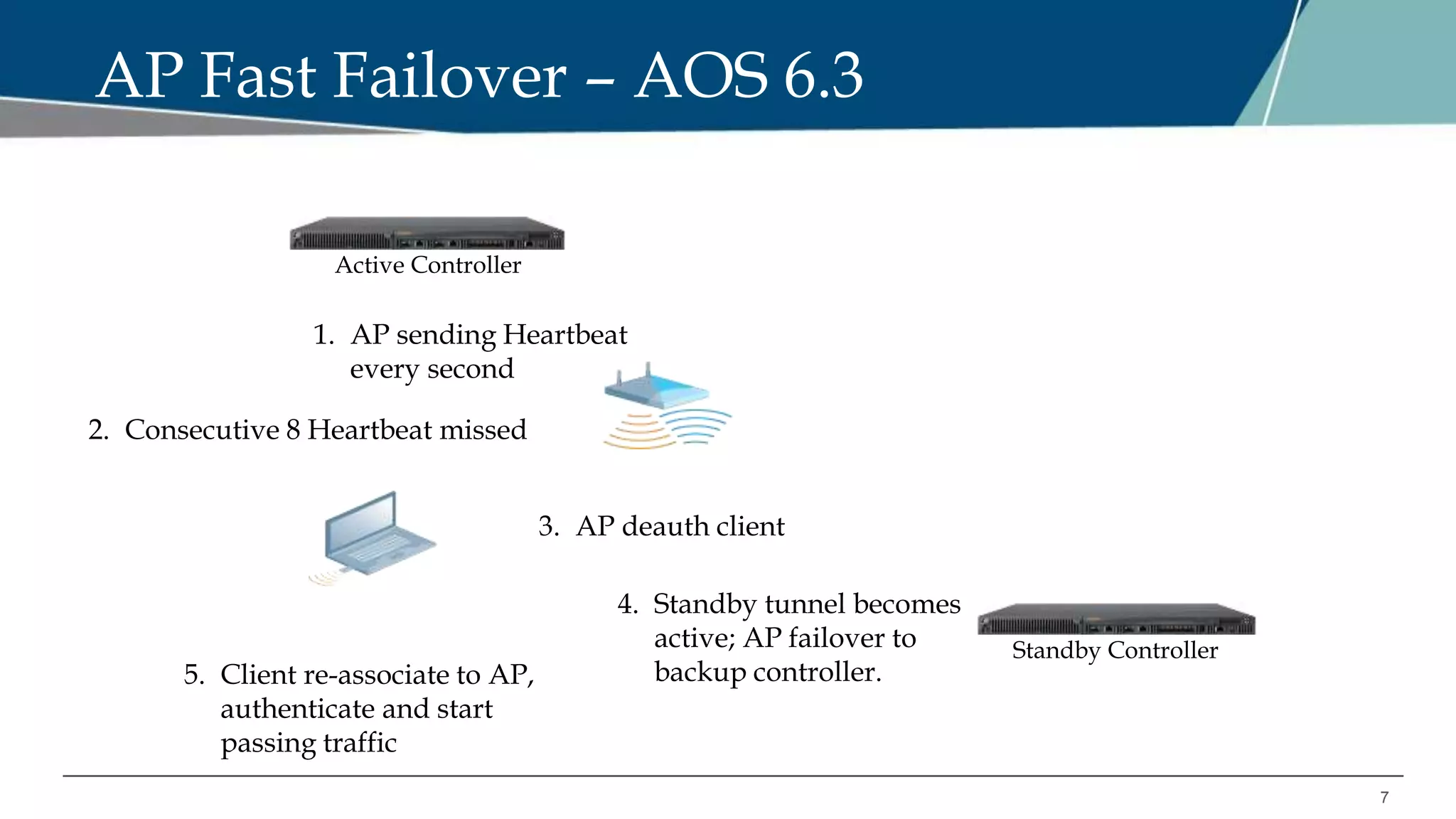
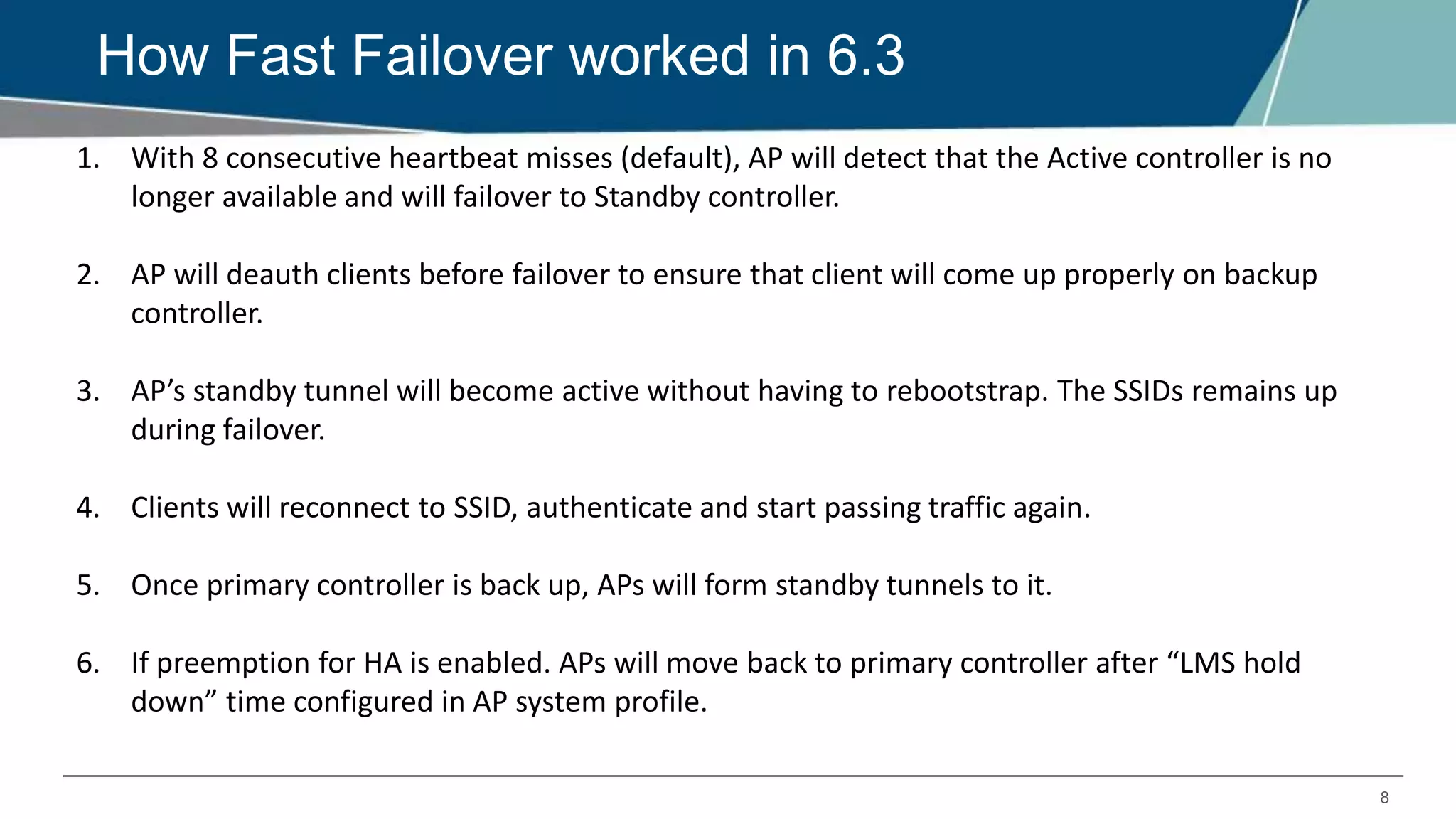
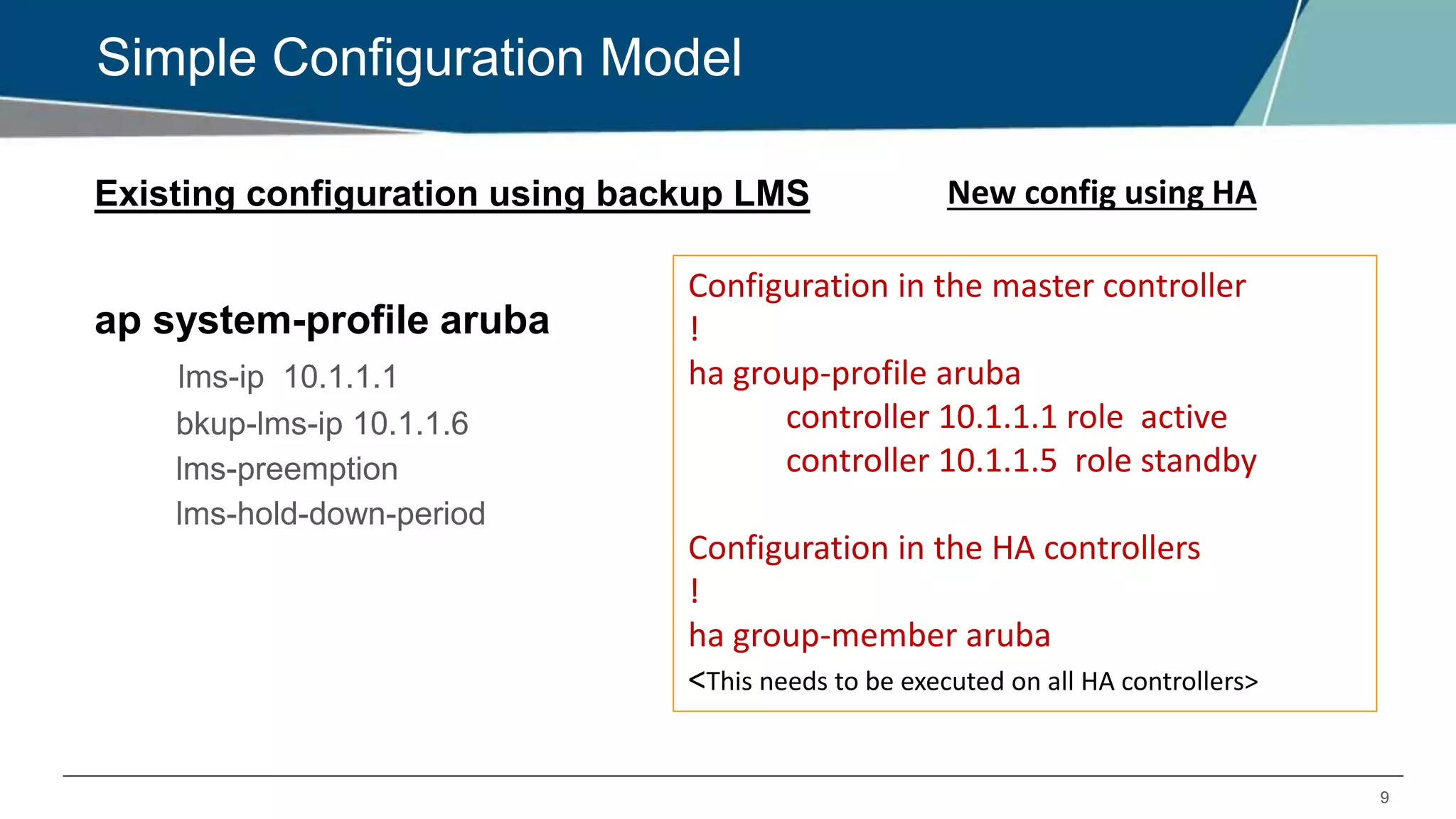
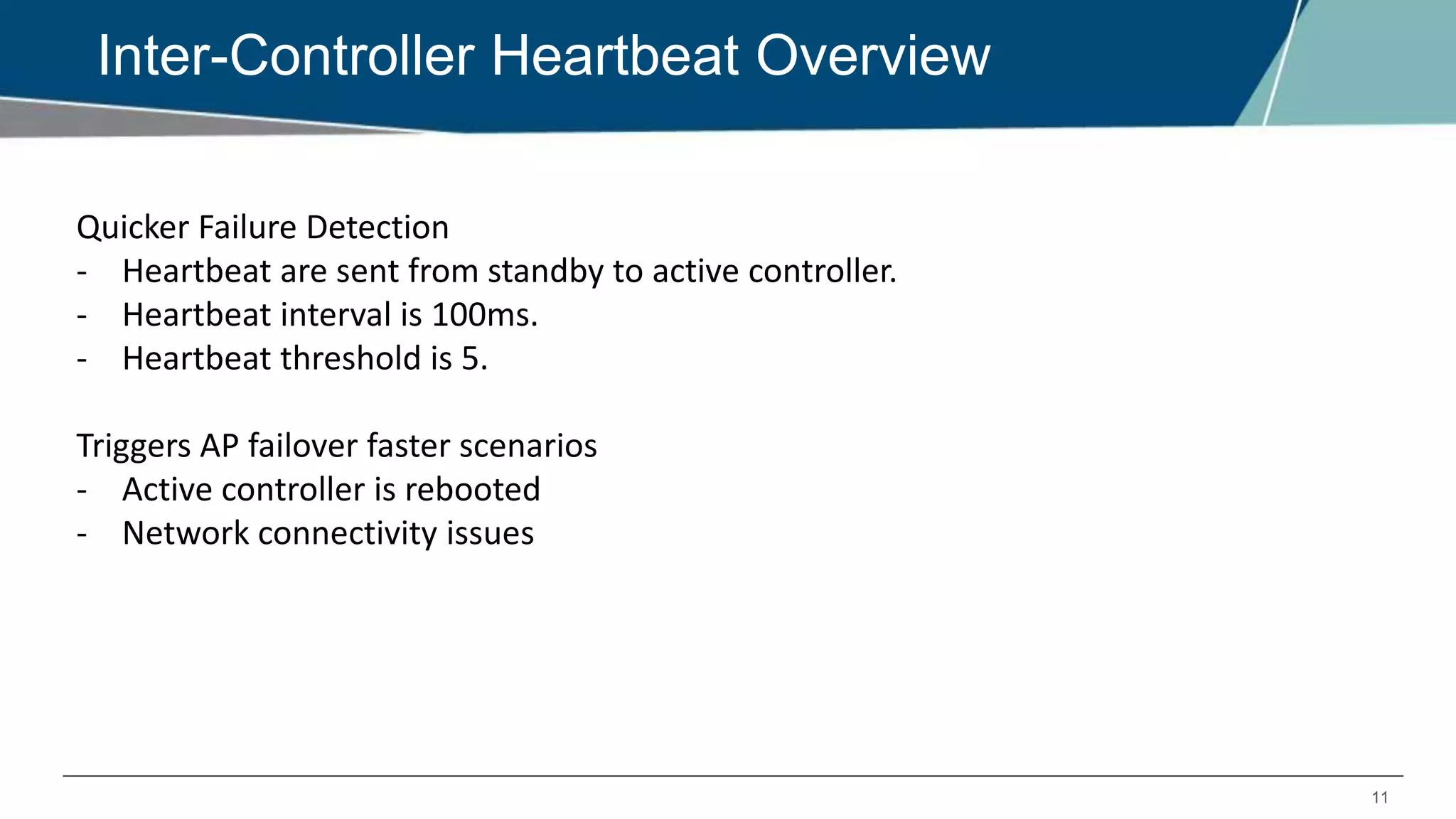
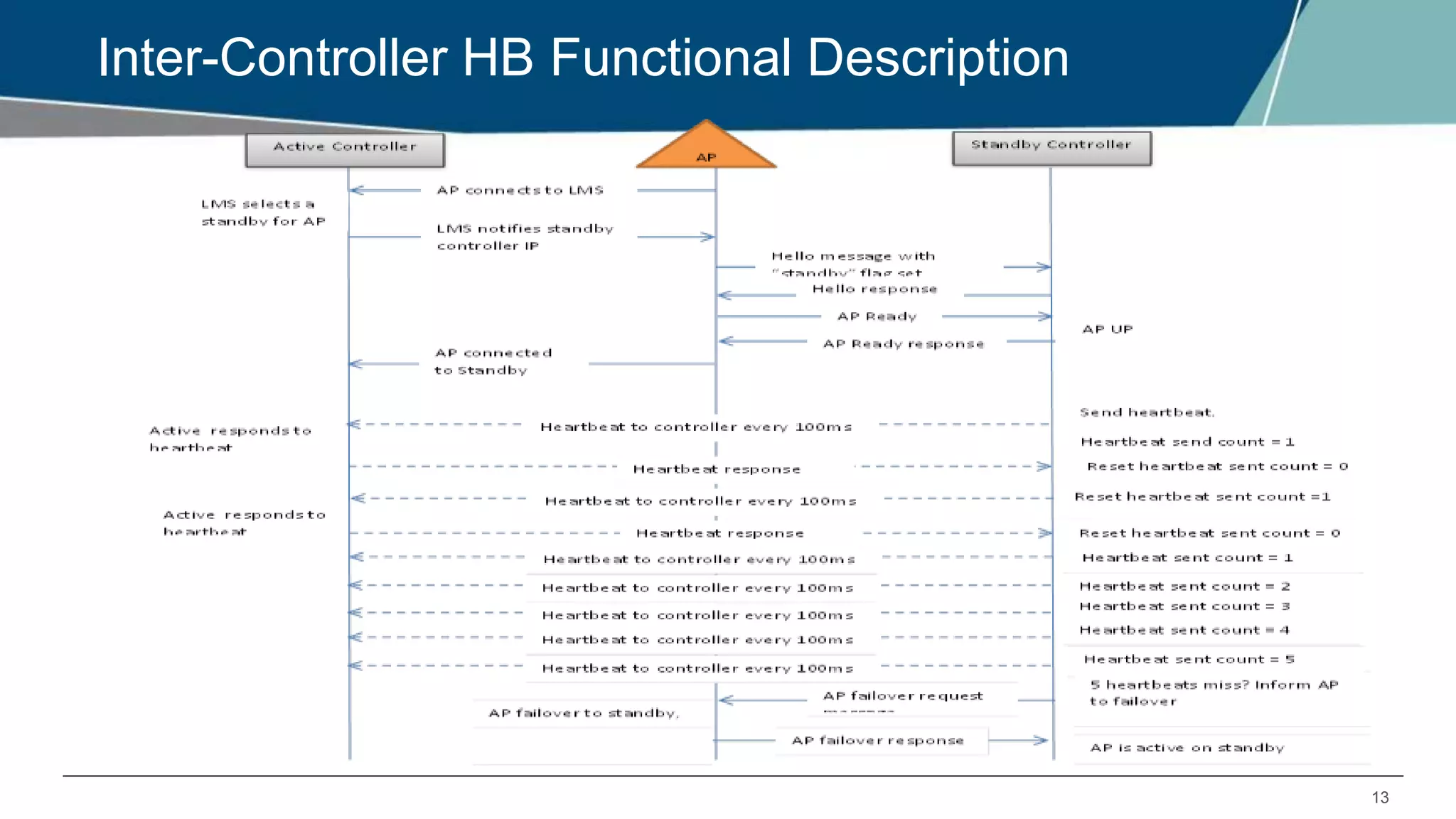
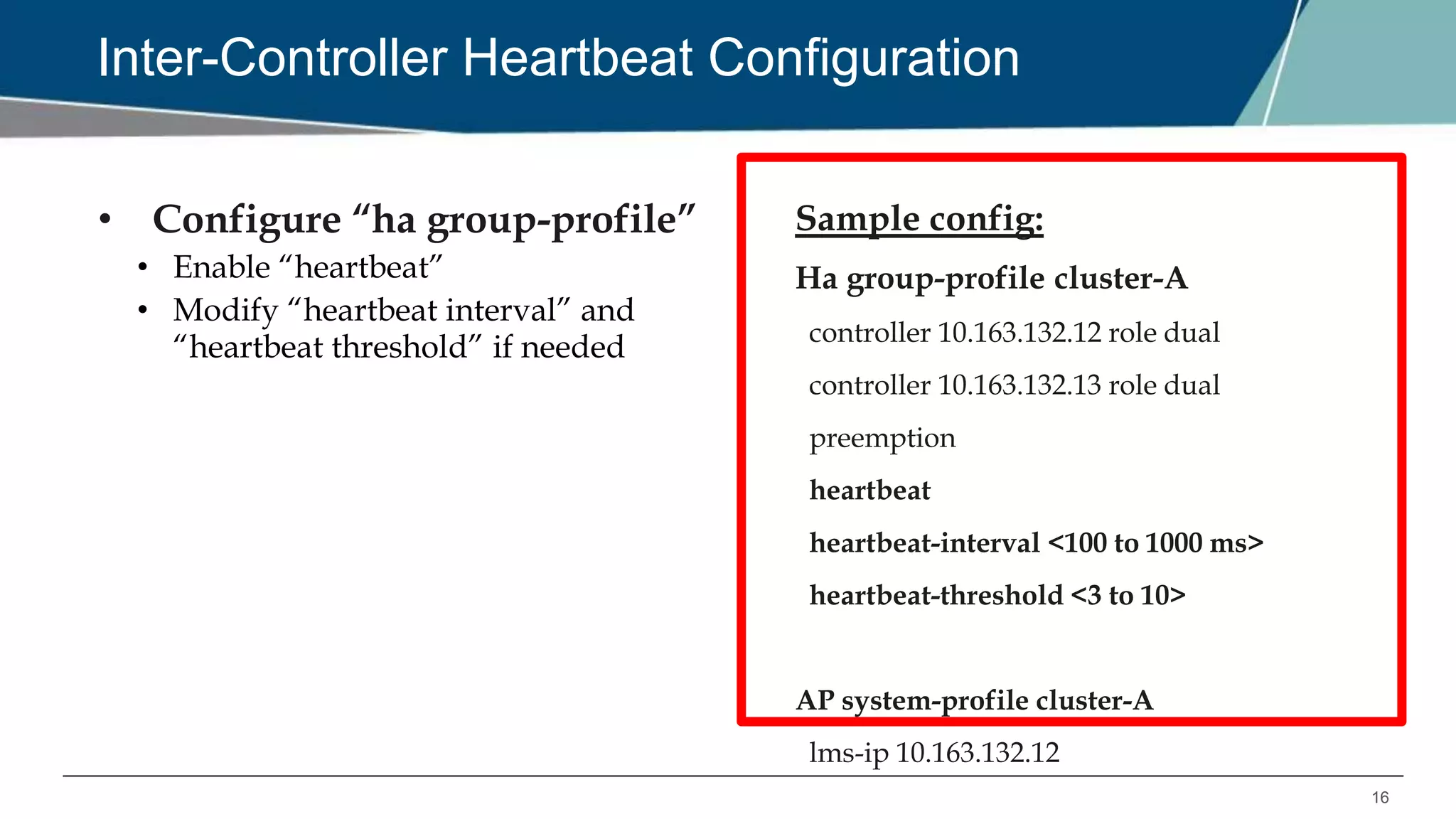
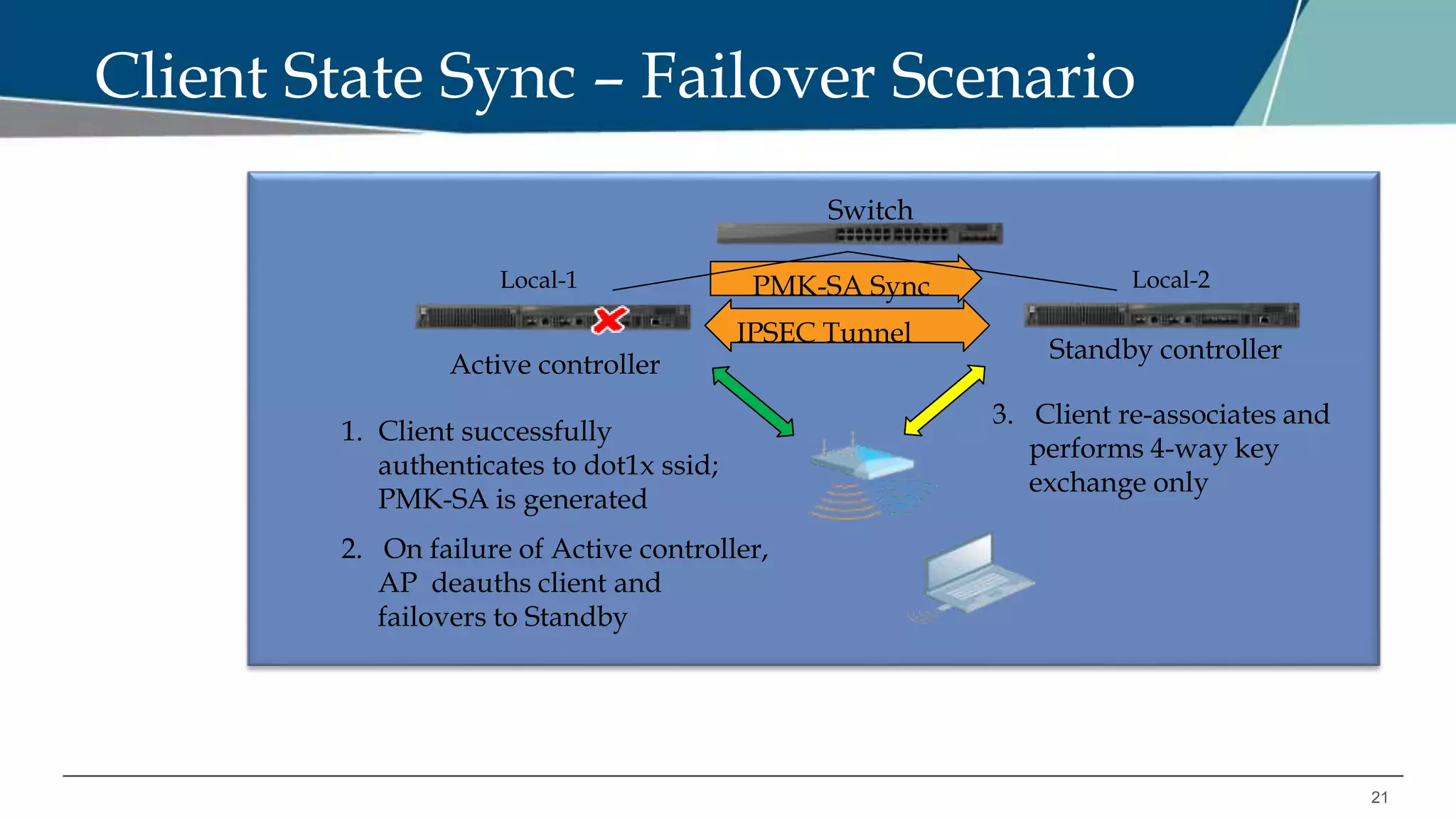
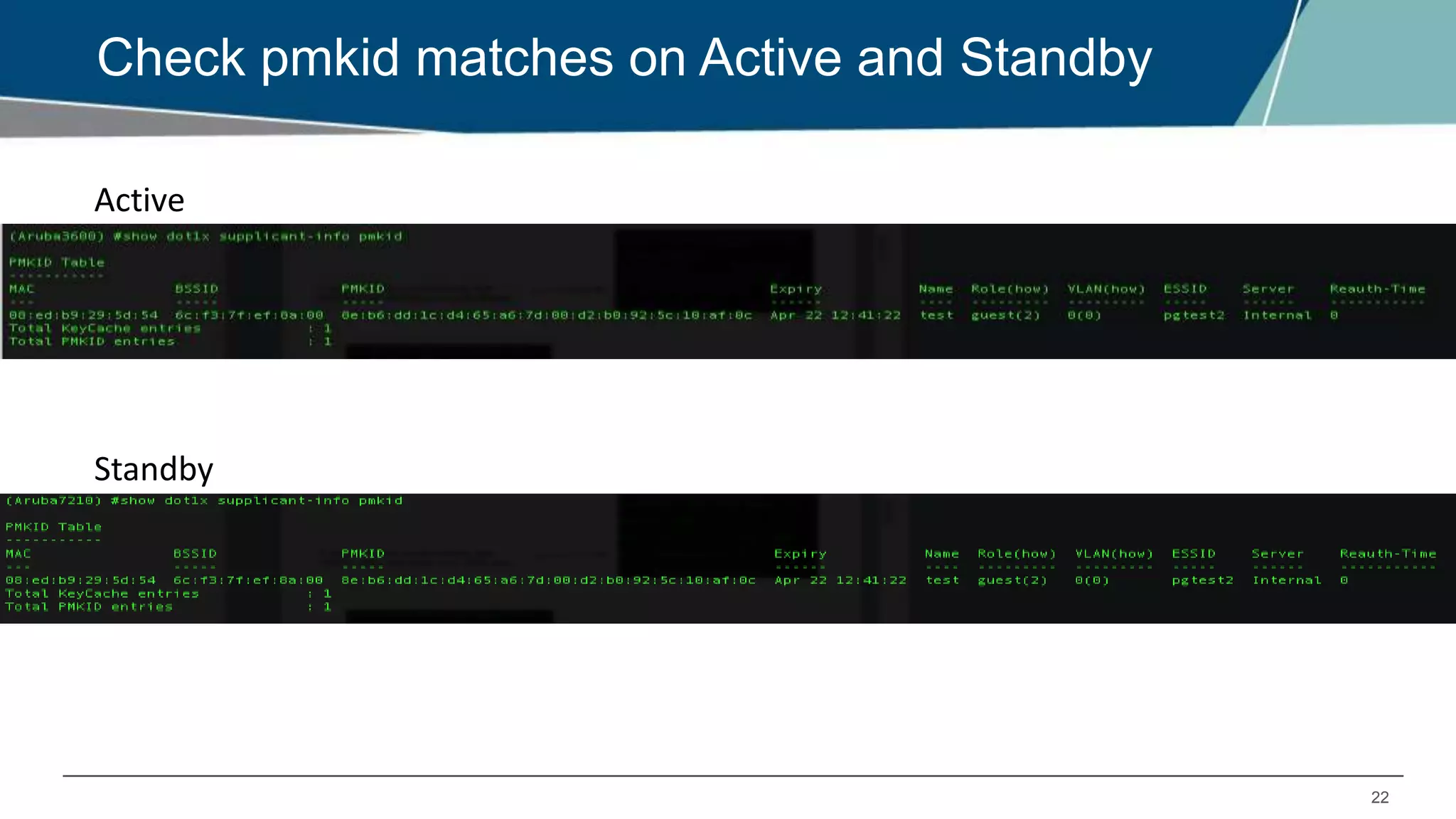
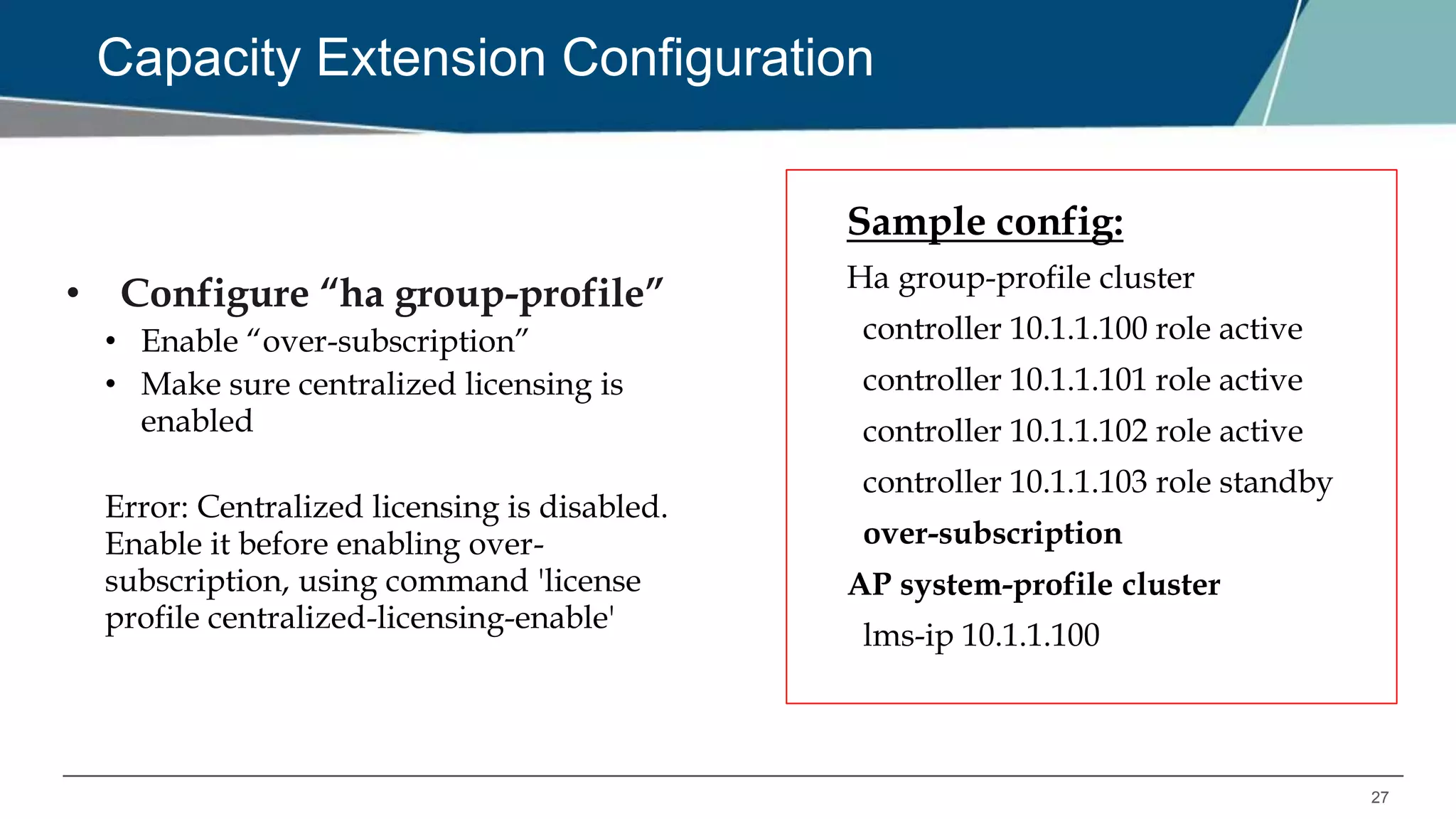
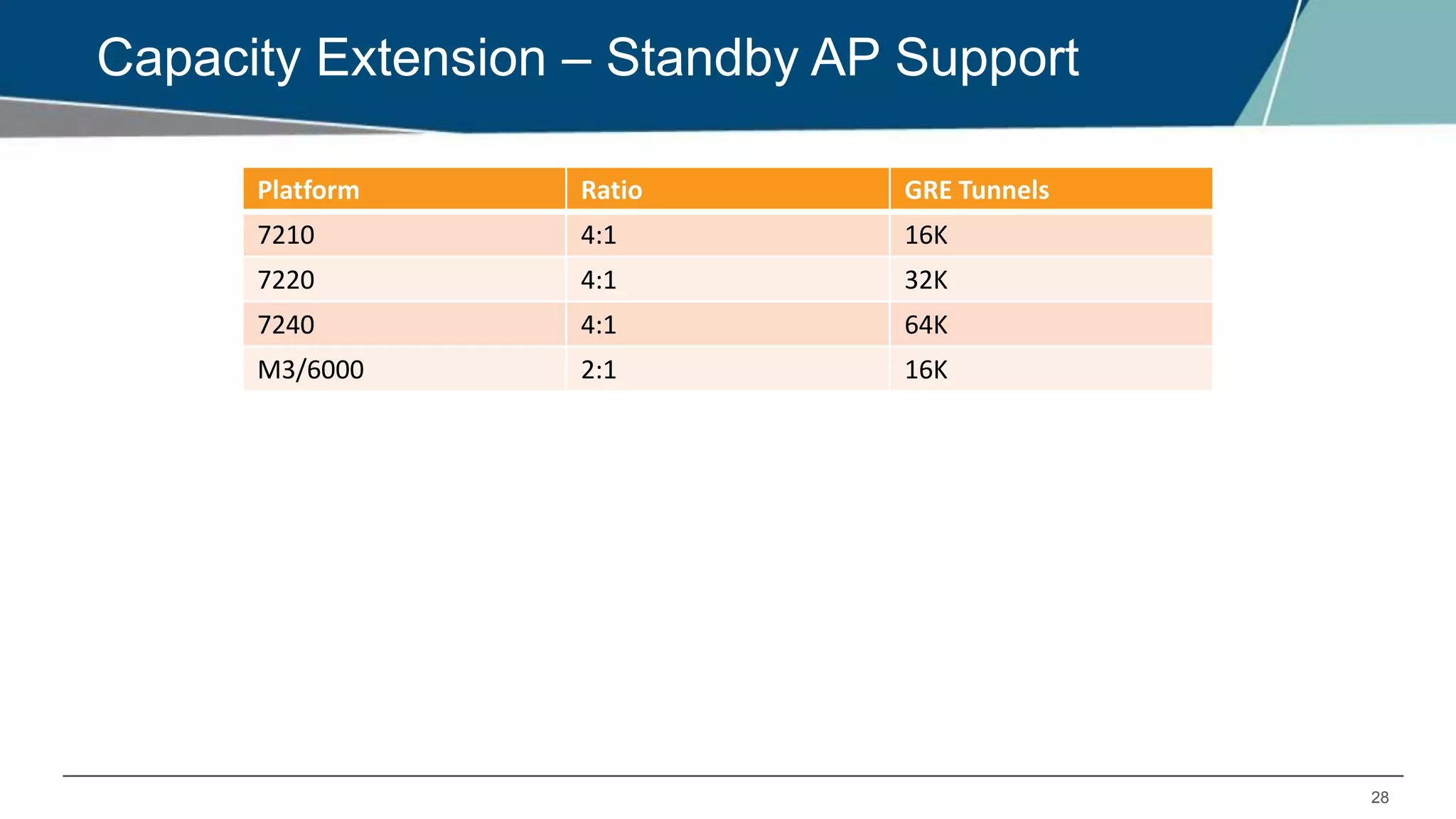
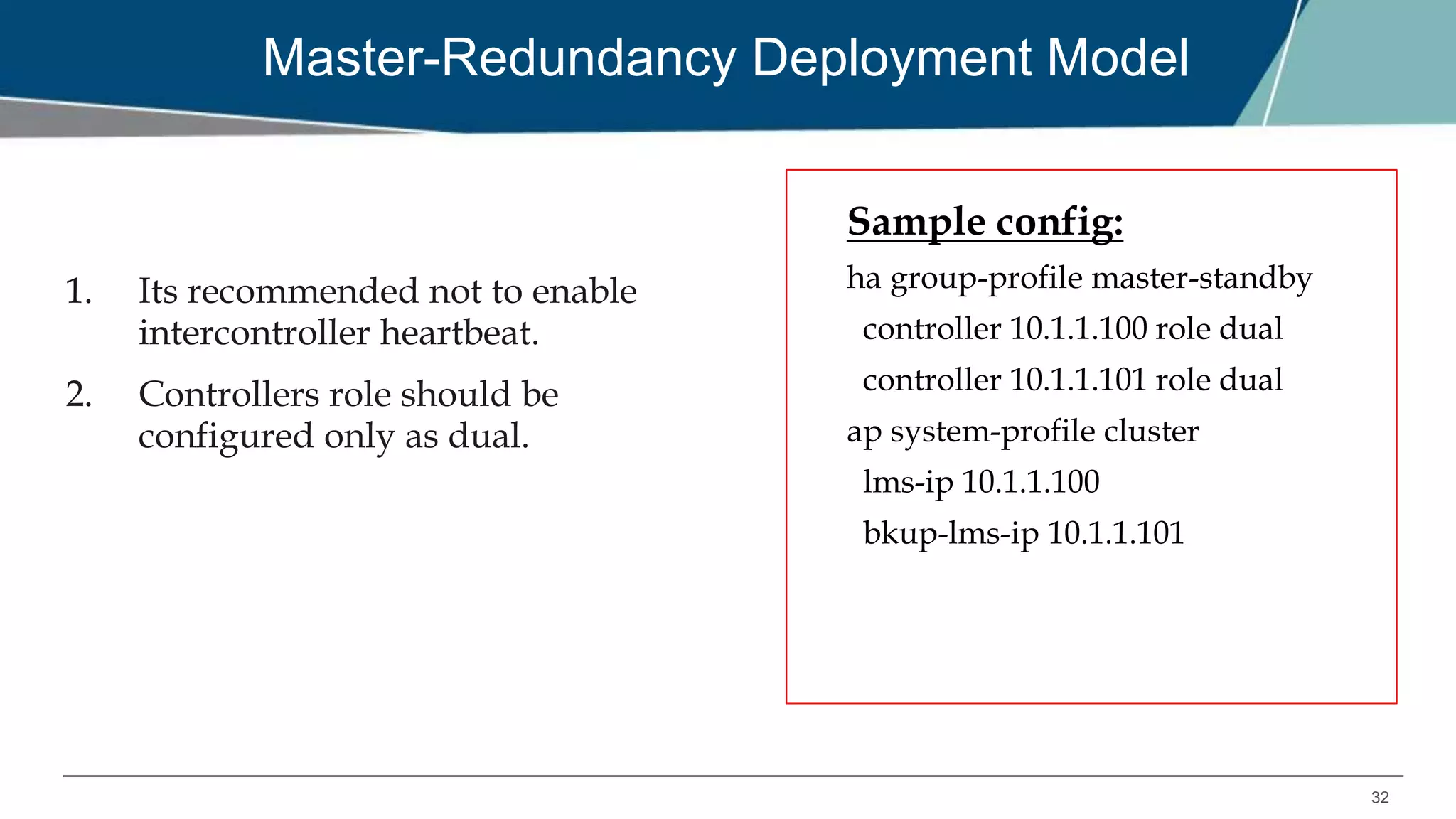
The document details Aruba OS high availability (HA) features, focusing on versions 6.3 and 6.4. Key functionalities include inter-controller heartbeat for faster failure detection, client state synchronization to reduce reconnection times, and capacity extension allowing standby controllers to exceed platform limits. Configuration examples and operational scenarios illustrate how these features enhance system reliability and efficiency during failover situations.