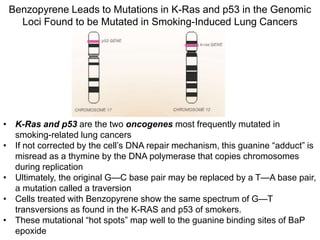
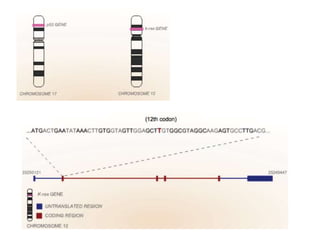
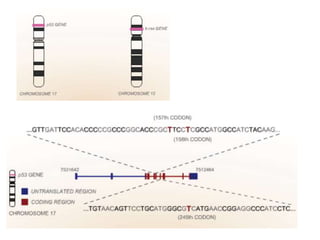
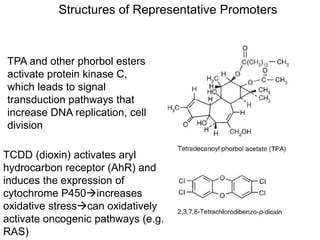
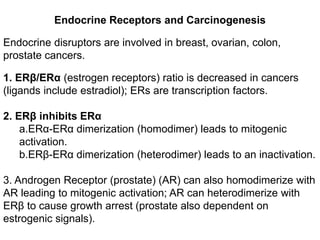
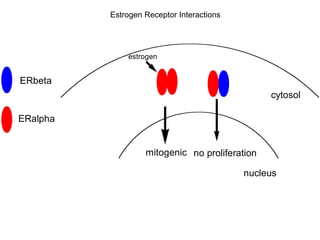
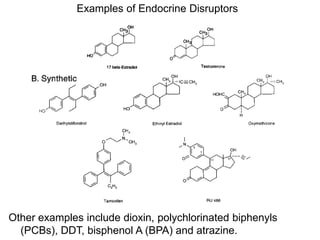
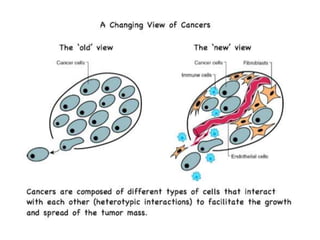
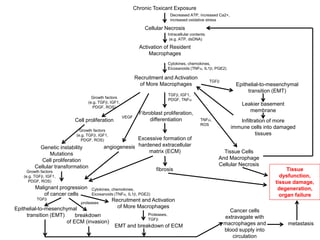
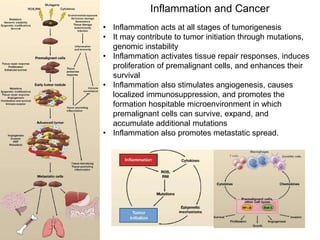
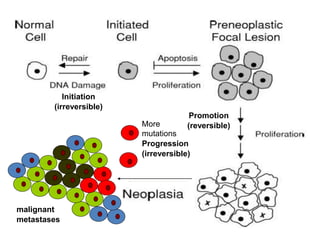
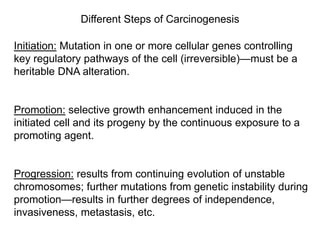
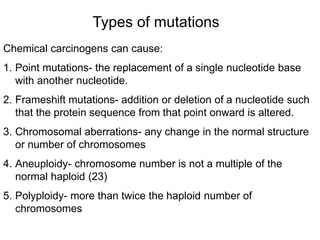
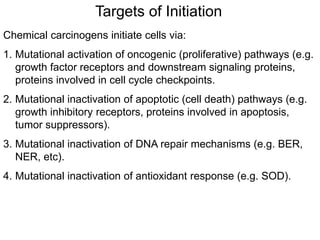
Chemical carcinogenesis involves three main steps: initiation, promotion, and progression. Initiation involves DNA damage from chemical mutagens and fixes mutations irreversibly. Promotion involves selective growth of initiated cells through continuous exposure to tumor promoters. This stage is reversible. Progression results from accumulating mutations during promotion and leads to increased malignancy, invasiveness and metastasis. Inflammation can act at all stages by inducing mutations, stimulating cell growth, and creating an environment conducive to tumor development and spread.




![CYP/PHS
O
EH
HO
OH
CYP/PHS
HO
OH
O
benzo[a]pyrene (+) benzo[a]pyrene
7,8-oxide (-) benzo[a]pyrene
7,8-dihydrodiol
(+) benzo[a]pyrene
7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide
ULTIMATE CARCINOGEN
HN
N
N
N
O
HN
DNA
HO
OH
HO
BaP-N2
-dG DNA adduct
DNA
GST/GSH
OH
GS
inactive (excreted)
O
CYP/PHS
OH
OH
inactive
Phase II
Phase II and
excretion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carcinogenesis-240214055848-fa88a900/85/Carcinogenesis-pptx-14-320.jpg)