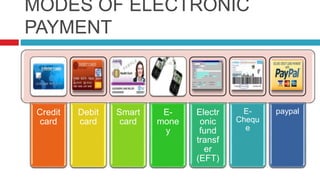
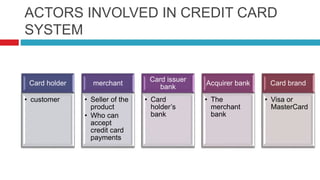
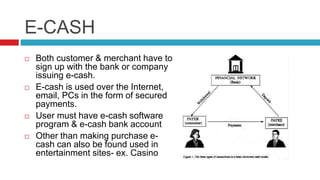
This document discusses various electronic payment systems including credit cards, debit cards, smart cards, e-money, electronic fund transfers, e-checks, PayPal, digital cash, and smart cards. It provides details on each payment method such as how they work, the parties involved in transactions, and examples of use. The key advantages of electronic payments are described as being paperless, user friendly, and reducing costs of transactions and labor.