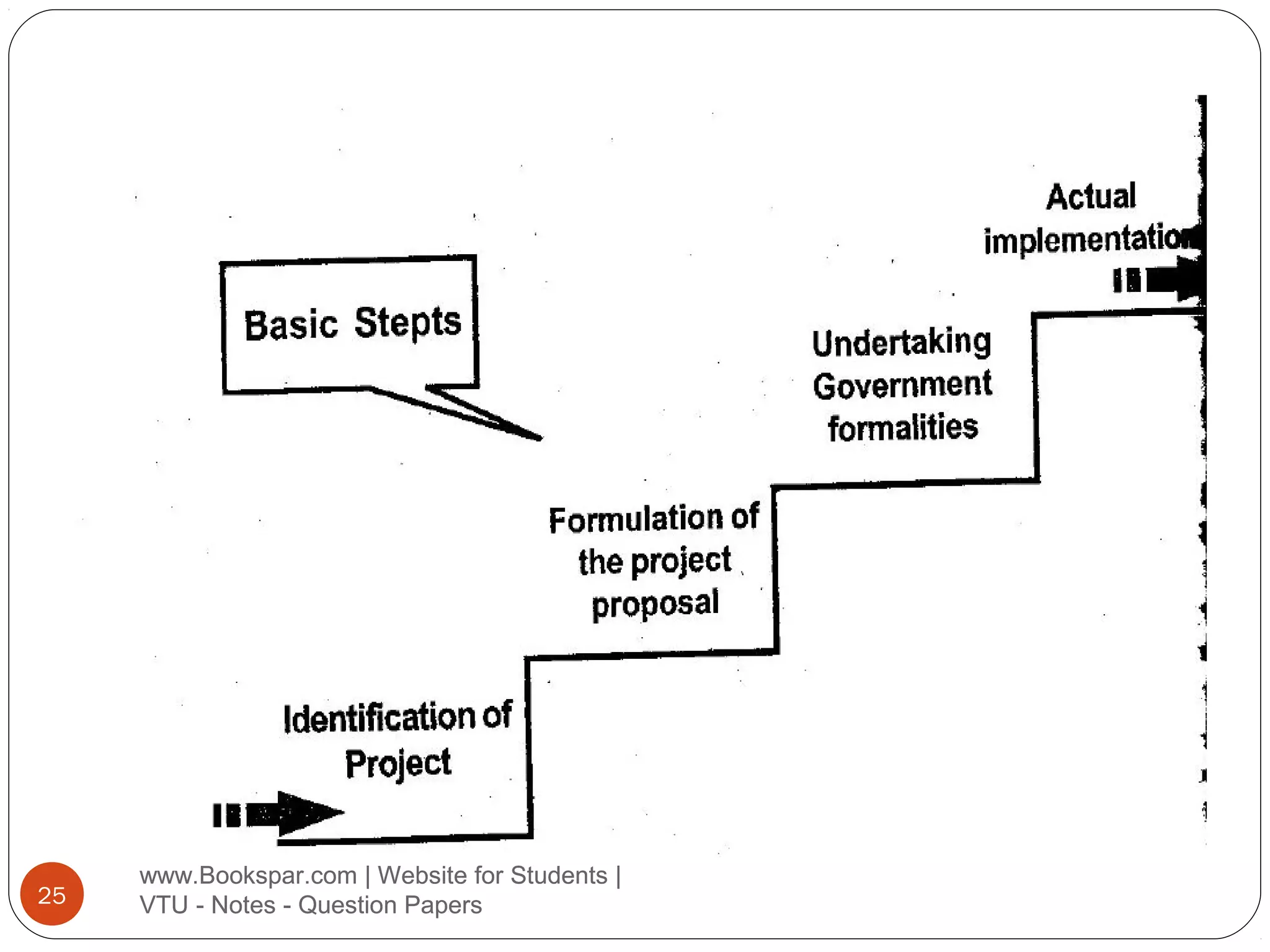
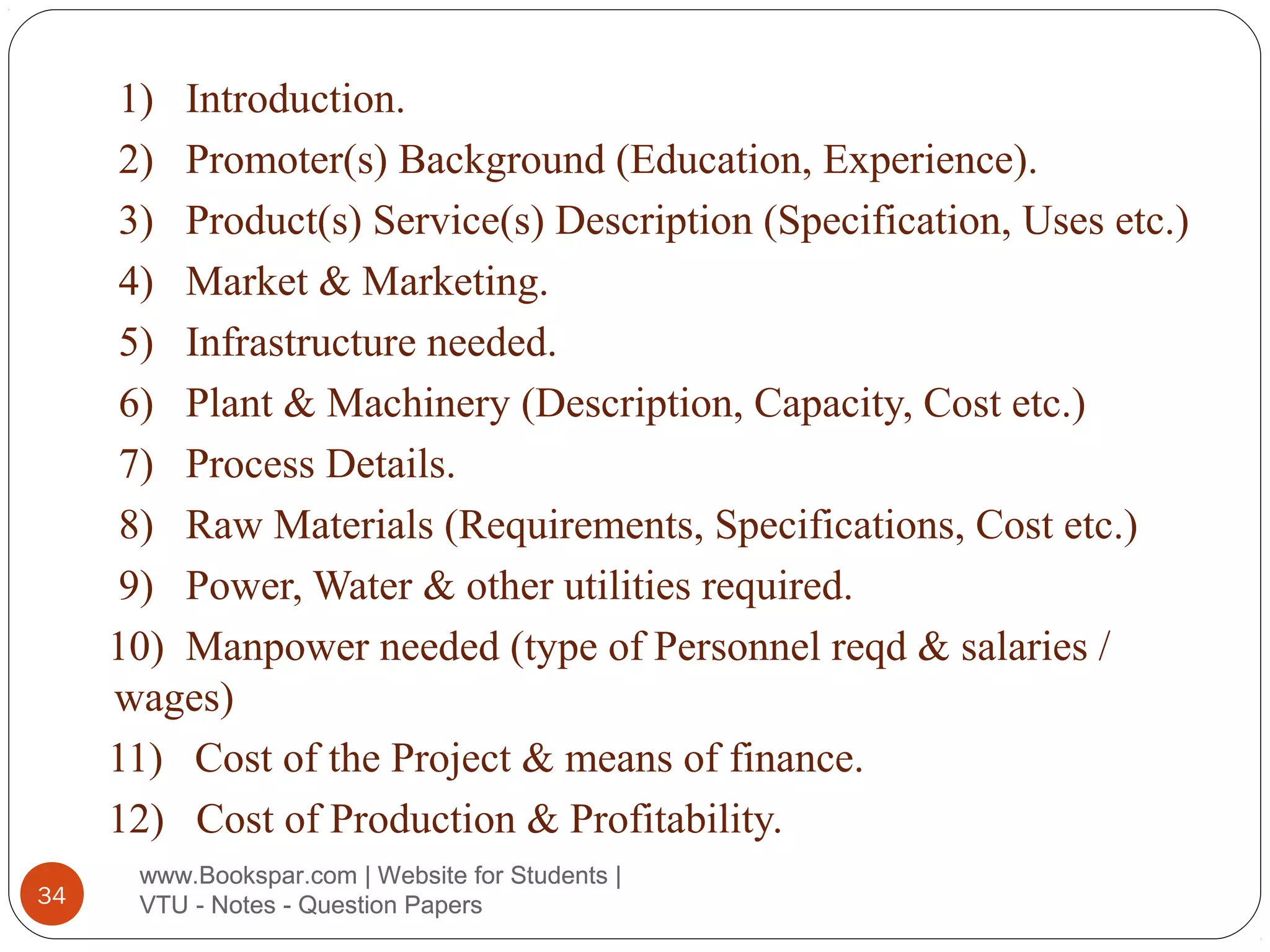
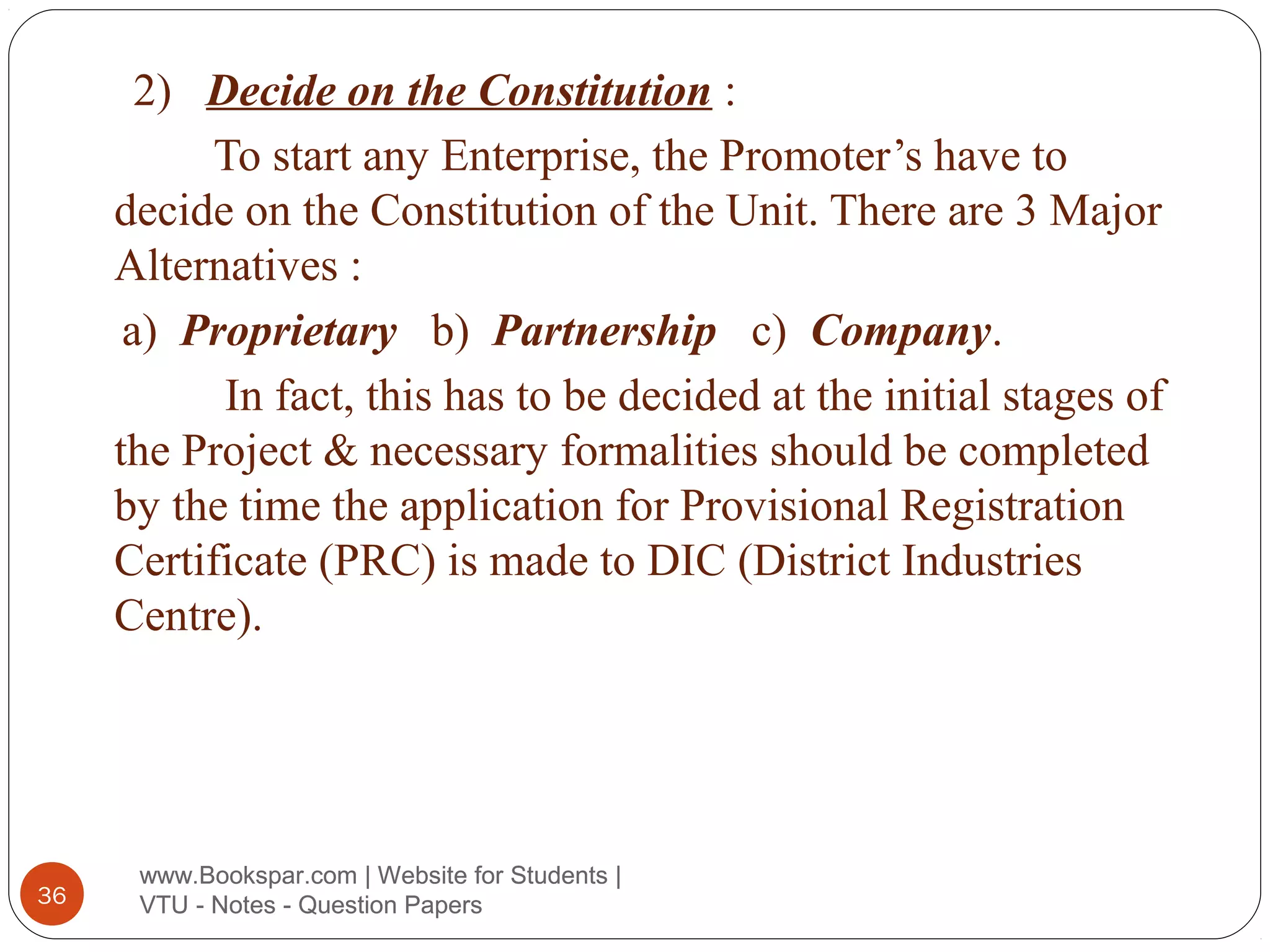
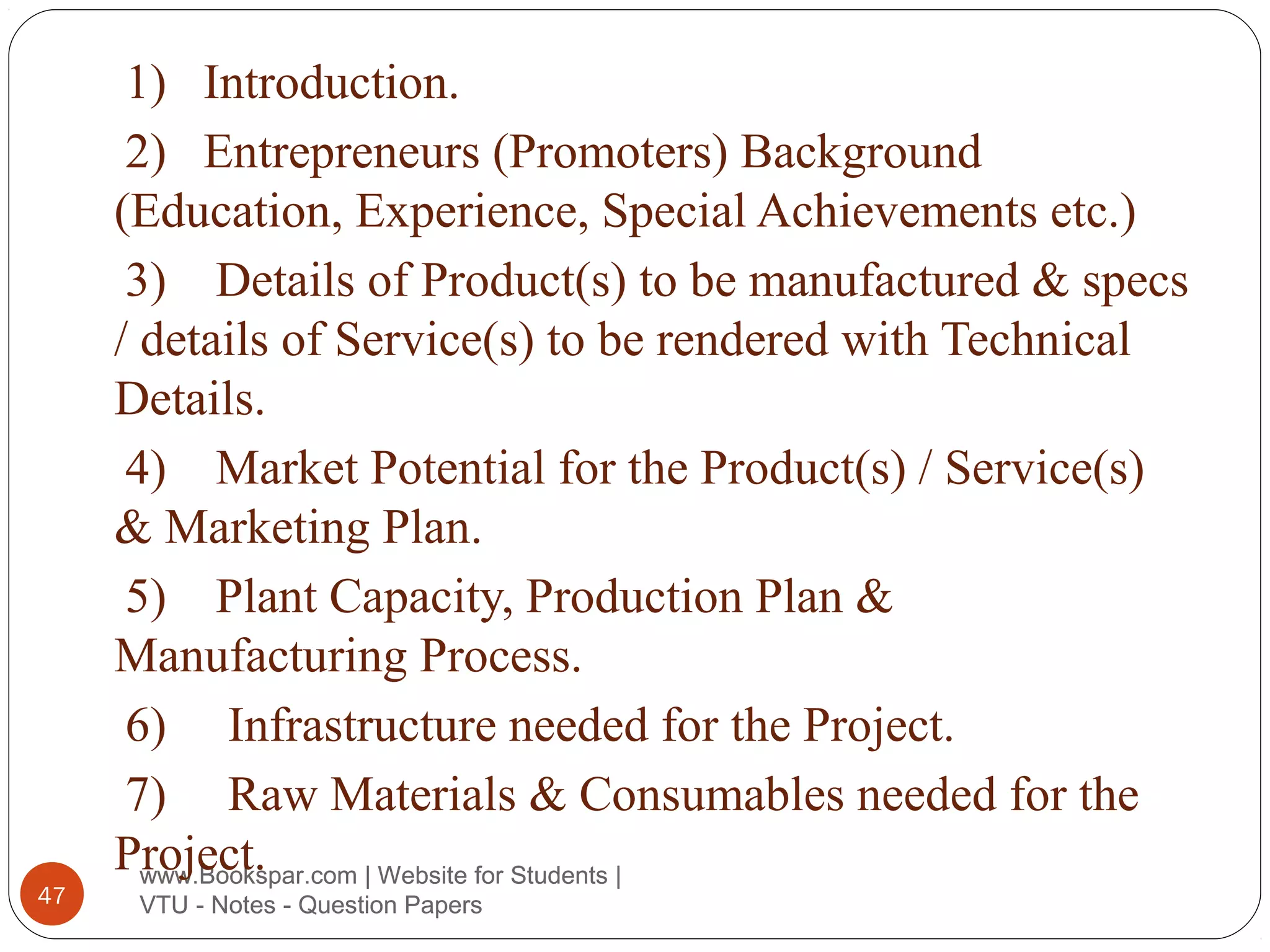
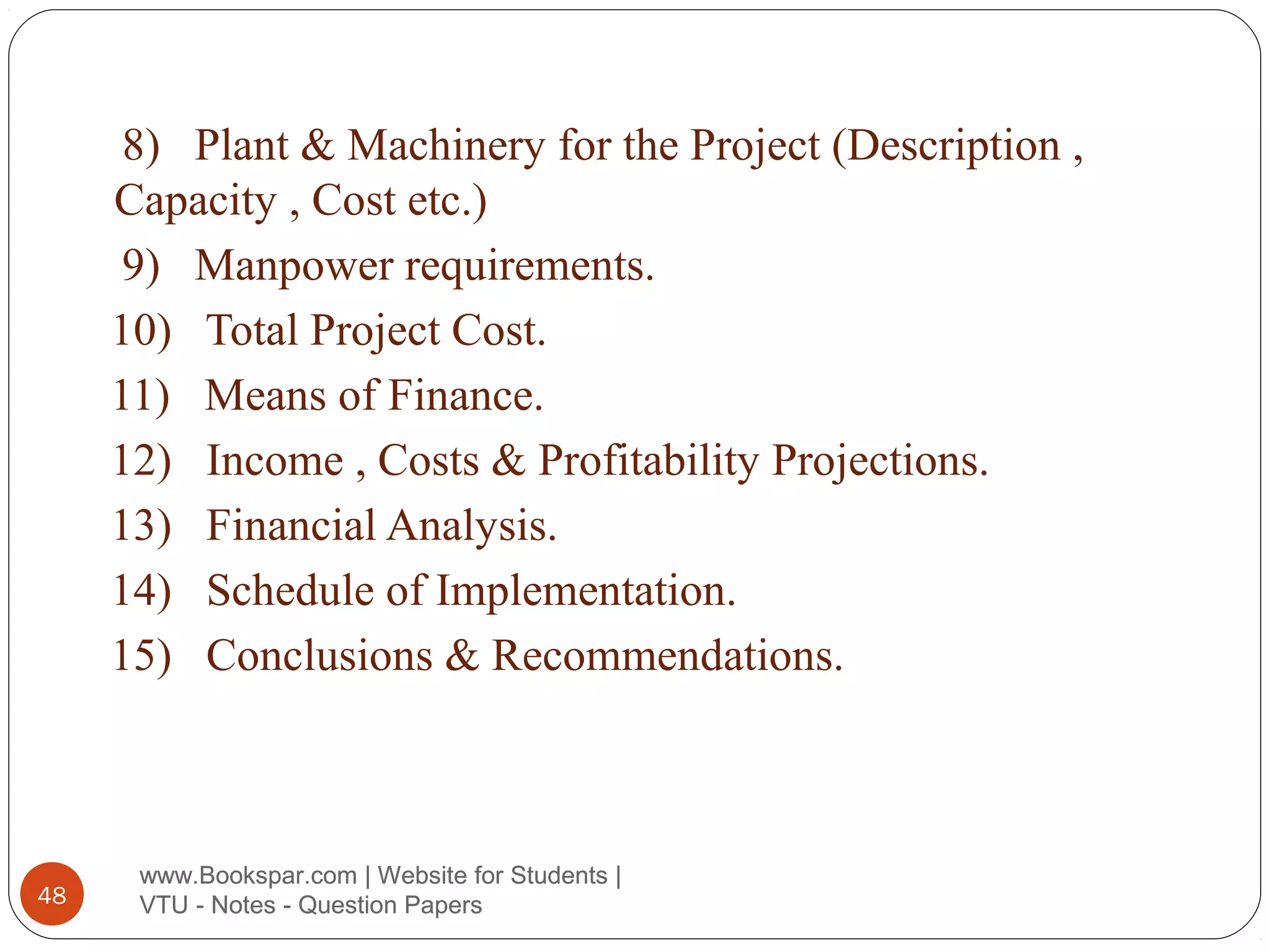
The document provides information on starting small scale enterprises in India. It discusses rules and regulations small enterprises must follow, including not polluting the environment, exploiting labor, or cheating customers. It also lists important acts related to small enterprises, such as those governing factories, labor disputes, contracts, wages, and more. The document defines small enterprises and categories within small enterprises, such as tiny industries, export-oriented units, and service businesses. It discusses characteristics, advantages, and the role of small enterprises in economic development, including increasing employment, production, and exports over decades. Finally, it outlines the steps to start a small enterprise, including selecting a project and location, feasibility studies, deciding the business structure, and obtaining necessary approvals