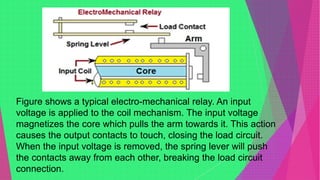
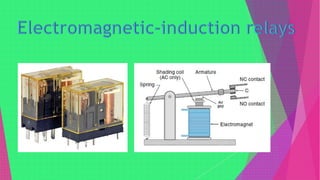
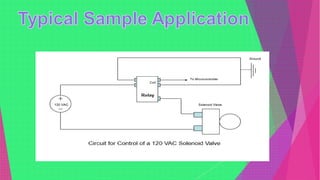
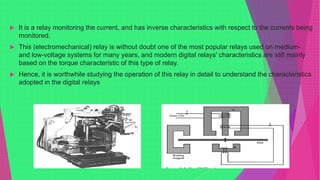
An electromagnetic relay uses electromagnetic induction to control the opening and closing of contacts to control electric circuits or devices. It contains an electromagnet that activates a set of contacts. When voltage is applied to the electromagnet coil, the contacts close to allow current to flow. When voltage is removed, a spring returns the contacts to the open position. Electromagnetic relays allow low-power control circuits to switch higher-power devices and are widely used, though solid-state relays are increasingly replacing them.