1. The document discusses electrode potential and how it is measured. Electrode potential is the tendency of an electrode to gain or lose electrons when in contact with its own ions in solution.
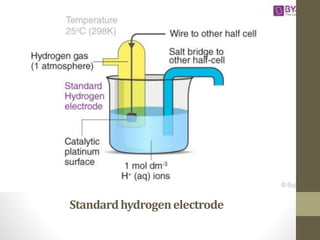
2. Oxidation occurs at the anode where electrons are lost, and reduction occurs at the cathode where electrons are gained. The standard hydrogen electrode is used as a reference to measure other electrode potentials.
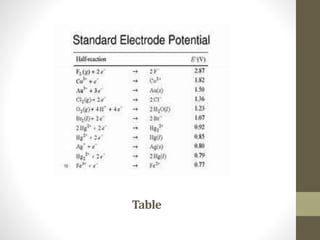
3. Electrode potentials can be oxidation potentials if the electrode loses electrons or reduction potentials if it gains electrons. Nernst theory explains how solution pressure and osmotic pressure determine electrode behavior.