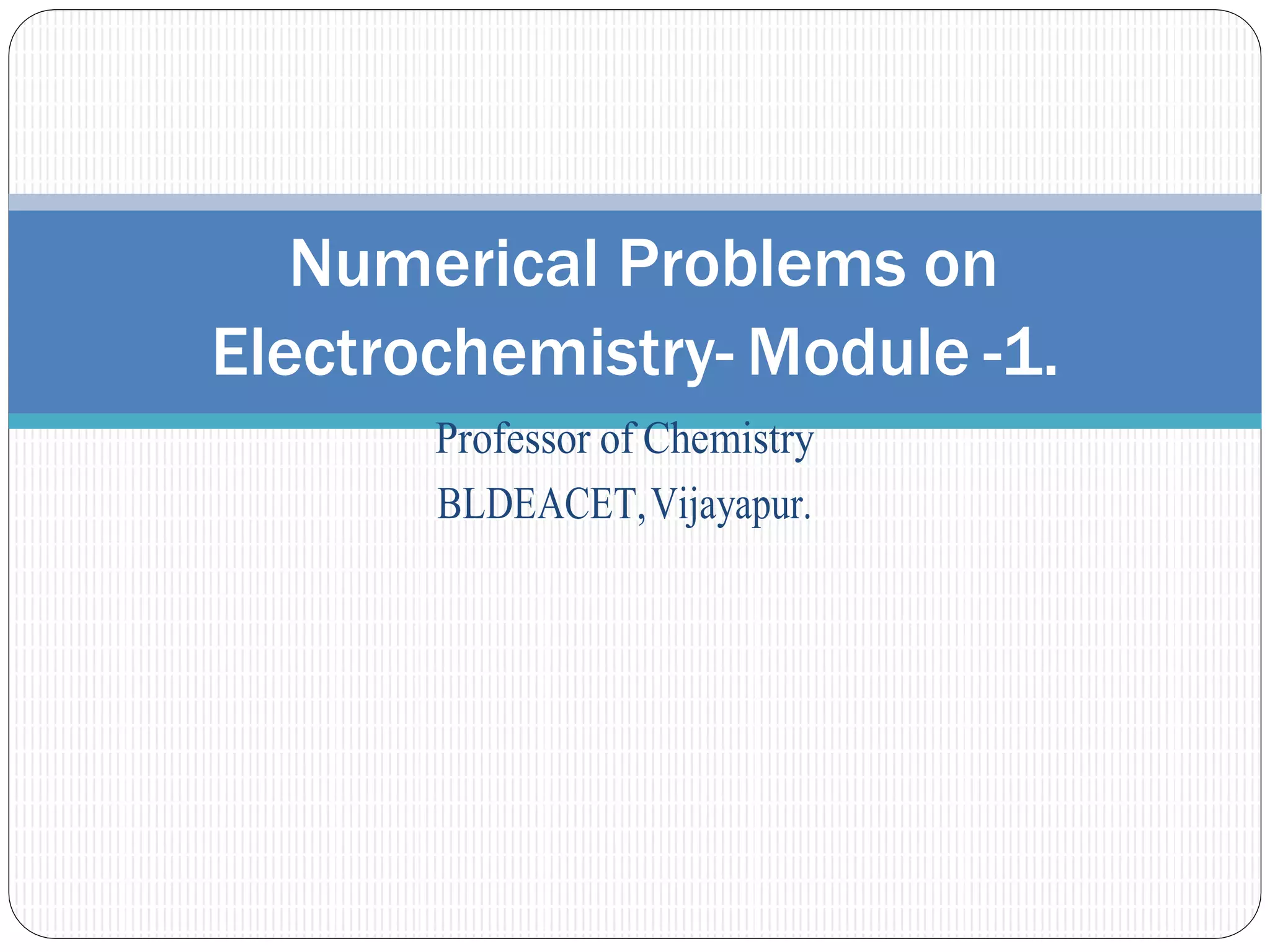
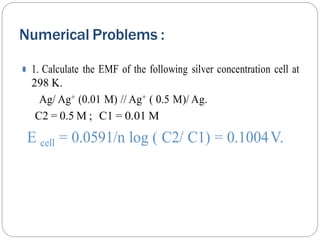
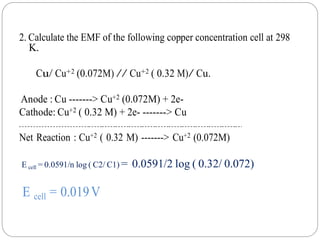
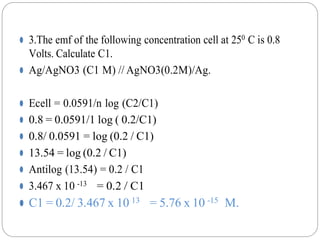
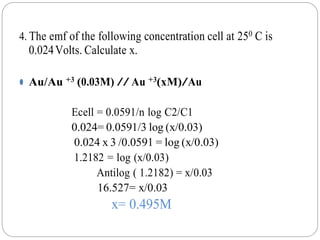
1. The document provides numerical problems and explanations related to electrochemistry concepts like concentration cells, Nernst equation, standard reduction potentials, and calculating cell potentials.
2. Ten sample problems are worked through step-by-step to demonstrate how to calculate cell potentials using concentration, temperature, and standard reduction potential values.
3. The document concludes by providing two sample homework problems for students to practice calculating cell potentials based on given standard electrode potentials and ion concentrations.
![Nernst equation for a cell:
At 298 K / 250 C ,
Ecell = E0
cell - 0.0591/n{log [species oxidised ]/[species reduced ]}
⚫ E0
cell = E0
cathode - E0
anode
⚫ n= number of electrons transferred](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalproblemspdf-210603053308/85/Numerical-problems-on-Electrochemistry-6-320.jpg)
![Nernst equation: Numerical Problems:
1. An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe electrode dipped in
0.1M FeSO4 and Ag electrode dipped in 0.05M AgNO3
solution.Write cell representation, cell reaction and calculate
EMF of the cell at 298 K given that the standard reduction
potentials of Fe and Ag electrodes are -0.44 V and +0.80 V
respectively.
Representation : Fe/ (0.1M) FeSO4 // (0.05M) AgNO3/ Ag
Cell Reaction : Fe + 2Ag+ ------ Fe 2+ + 2Ag
⚫ Ecell = E0
cell - 0.0591/ n {log [Fe2+ ]/ [Ag+] 2}
⚫ = 1.24 – (0.0295) {log [0.1]/ [0.05] 2}
⚫ = 1.24 - (0.0295) {log 40} = 1.24-0.047 = 1.193Volts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalproblemspdf-210603053308/85/Numerical-problems-on-Electrochemistry-7-320.jpg)
![2.Calculate emf of following cell at 298 K.
Ni(s)/ Ni2+ (0.01 M) // Cu2+ (0.5M)/Cu (s)
Given: Std EP of Ni= -0.25V and Std EP of Cu= 0.34V.
Ni + Cu 2+ ------ Ni2+ + Cu
reduced oxidized
Ecell = E0
cell - 0.0591/ n {log [Ni2+ ]/ [Cu 2+ ]}
E0
cell = 0.34 – (- 0.25) = ).34+ 0.25 = 0.59V
Ecell = 0.59 - 0.0591/ 2 {log [0.01 ]/ [0.5] }
=0.59- (0.0295) log (0.02) = 0.59- (0.0295)x (-1.698)
= 0.59 +0.05 = 0.64V.
Ecell = 0.64V](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalproblemspdf-210603053308/85/Numerical-problems-on-Electrochemistry-8-320.jpg)
![⚫ 3. Calculate emf of following cell at 298 K.
⚫ Fe(s)/ Fe2+ (0.02 M) // Cd2+ (1.0M)/Cd (s)
⚫ Given: Std EP of Fe= -0.44V and Std EP of Cd= -0.40V.
⚫ Ecell = E0
cell - 0.0591/ n {log [Fe2+ ]/ [Cd 2+ ]}
⚫ = (-0.40 + 0.44) - 0.0591/2{log [0.02 ]/ [1.0]}
⚫ = 0.04 – (0.0295) log (0.02)
⚫ Ecell = 0.04+ 0.050 = 0.09Volts.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalproblemspdf-210603053308/85/Numerical-problems-on-Electrochemistry-9-320.jpg)
![cell
4. Calculate emf of following cell at 298 K.
Cd(s)/ Cd2+ (0.25M) // Ag+ (0.5M)/Ag (s)
Given: Std EP of Cd= -0.40V and Std EP of Ag= 0.80V.
Cd + 2Ag+ ---- Cd2+ + 2Ag
2 moles of Ag+ and 1 mole of Cd involved in reaction.
Ecell = E0 - 0.0591/ n {log [Cd2+ ]/ [Ag+] 2}
E0
cell = 0.80 + 0.40 = 1.2V
Ecell = 1.2 - 0.0591/ 2 {log [0.25]/ [0.5] 2}
Ecell = 1.2 - 0.0591/ 2 {log [0.25 ]/ [0.25]}
Ecell = 1.2V](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalproblemspdf-210603053308/85/Numerical-problems-on-Electrochemistry-10-320.jpg)

![⚫ Ecell = E0
cell - 2.303 RT / nF{log [Zn2+ ]/ [Ag+] 2}
= (0.80+0.76) - 2.303 x8.314x297/2x96500{log [0.005 ]/ [0.1] 2}
= 1.56 – {5686.701/ 193000 [log (0.5)] }
= 1.56 – {0.0294 x (-0.301)}
= 1.56 + 0.008849
Ecell = 1.5688Volts.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalproblemspdf-210603053308/85/Numerical-problems-on-Electrochemistry-12-320.jpg)
![6. Compute the cell potential at 22.30C of the Ag+/ Ag
couple with respect to Cu+2/Cu if the concentration
of the Cu ion and Ag ion are 4.2x10-6 M and 1.3x10-3
M respectively. E0 of Ag and Cu are 0.8V and 0.34V
respectively.
Ecell = E0
cell - 2.303 RT / nF{log [Cu2+ ]/ [Ag+] 2}
= 0.46 - 2.303 x8.314x295.3/2x96500{log [4.2x10-6]/
[1.3x10-3] 2}
= 0.46 – {(5654.151/193000) log (3.23)}
= 0.46 – 0.0149 = 0.4451V.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalproblemspdf-210603053308/85/Numerical-problems-on-Electrochemistry-13-320.jpg)
![Cu /Cu Cu /Cu
Cu /Cu
7. Calculate the standard electrode potential E0
Cu+2/Cu
if its electrode potential E, at 250C is 0.296V when the
concentration of Cu+2 ions is 0.015M.
E +2 = E0 +2 + 0.0591/n log [Cu+2]
0.296 = E0 +2 + 0.0591/2 log [0.015]
E0
Cu
+2
/Cu = 0.296 - 0.0591/2 log [0.015]
= 0.296 + 0.0540
E0
Cu
+2
/Cu =0.35 V.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalproblemspdf-210603053308/85/Numerical-problems-on-Electrochemistry-14-320.jpg)
![9. Calculate the reduction electrode potential of copper when it is in
contact with 0.5 M copper sulphate solution at 298 K. The E0 value of
copper is 0.34V.
E Cu
+2
/Cu = E0
Cu
+2
/Cu + 0.0591/n log [Cu+2]
= 0.34 + 0.0591/2 log [0.5]
=0.34 + (0.0295) ( -0.30)= 0.34 - 0.0088
E Cu
+2
/Cu = 0.3312V.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalproblemspdf-210603053308/85/Numerical-problems-on-Electrochemistry-15-320.jpg)

![Home Tasks:
1. A cell is constructed by coupling a zinc electrode dipped in
0.5 M ZnSO4 and a nickel elecorde dipped in 0.05 M
NiSO4. Write the cell representation and cell reaction.
Calculate the EMF of the cell , given the standard electrode
potential of Zn and Ni are -0.76 V and -0.25 V respectively.
[ Ans: 0.48V]
2. A cell is formed by coupling a Nickel electrode dipped in
0.01 M Ni2+ solution and a lead electorde dipped in 0.5 M
Pb2+ solution. Write the cell representation and cell
reaction. Calculate the EMF of the cell , given the standard
electrode potential of Ni and Pb are -0.25 V and -0.13V
respectively. [ Ans: 0.17V]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalproblemspdf-210603053308/85/Numerical-problems-on-Electrochemistry-17-320.jpg)