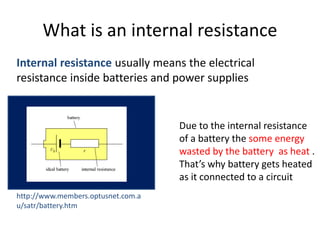
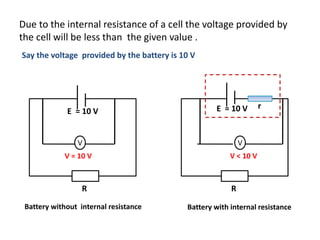
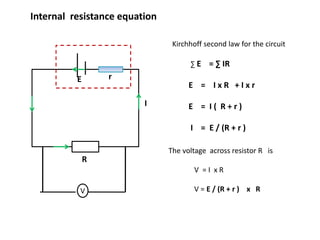
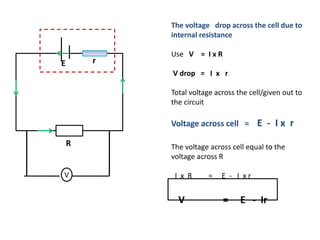
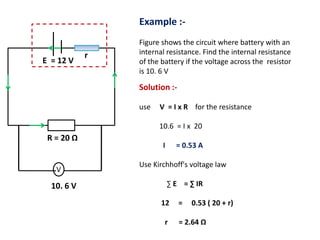
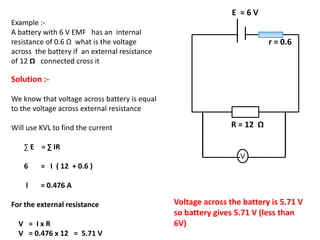
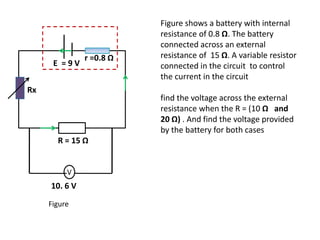
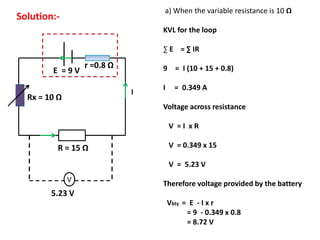
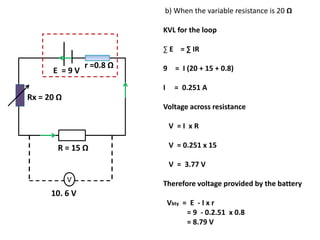
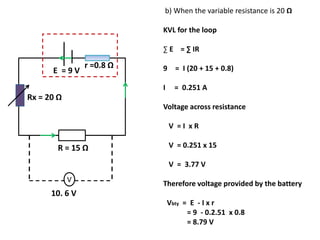
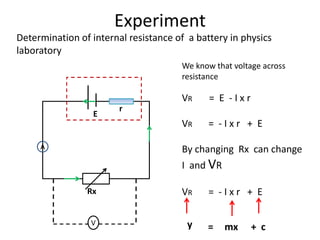
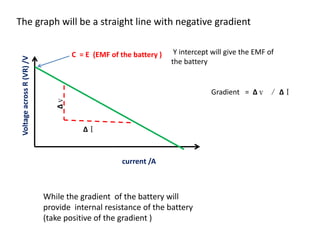
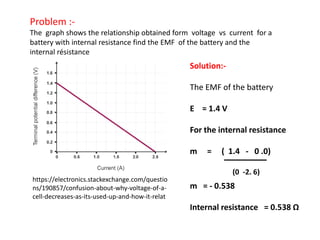
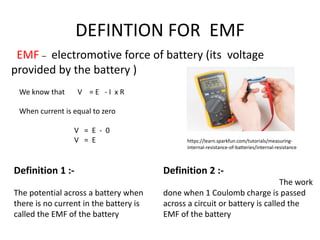
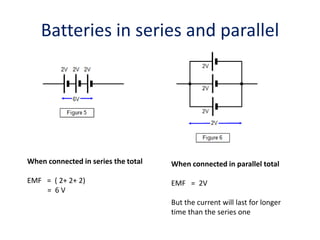
The document defines internal resistance as the electrical resistance inside batteries and power supplies that causes some energy to be wasted as heat. It provides equations relating internal resistance (r), electromotive force (EMF, E), current (I), and terminal voltage (V). Examples are given of using Kirchhoff's laws and these equations to calculate internal resistance, EMF and voltages for circuits with batteries and resistors. An experiment for determining internal resistance by varying resistance and measuring voltage and current is described.