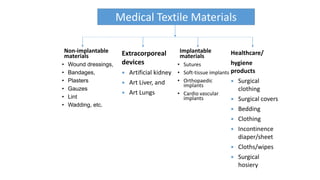
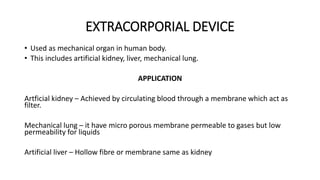
The document discusses medical textiles, which combine textile technology and medical sciences. Medical textiles have a wide range of applications from simple wipes and bandages to complex implants. Materials for medical textiles must be non-toxic, sterile, strong and durable while also being biocompatible. Medical textiles are classified based on usage into healthcare/hygiene products, extracorporeal devices, implantable materials, and non-implantable materials. The future of medical textiles is promising as research and development continues to improve materials and applications.