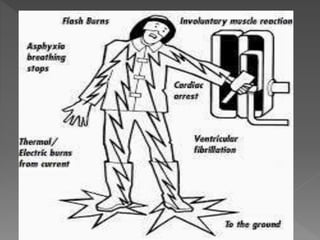
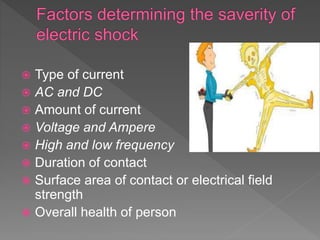
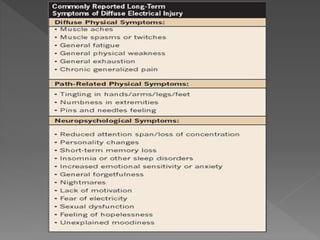
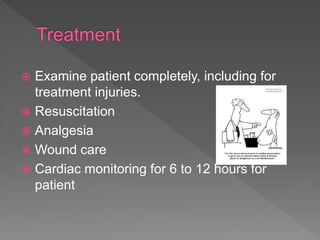
This document discusses electric shocks and injuries from electrical current. It notes that electric shocks can occur through poorly insulated wires, ungrounded equipment, or using devices while in contact with water. Injuries from electric shocks range from no harm to death, and depend on factors like current type/amount, contact duration and area. Common injuries include burns, cardiac arrest, and muscle/nerve damage. It provides guidance on first aid for electric shock victims, including turning off the power source without touching the person, calling for emergency help, performing CPR if needed, and treating for burns or other injuries.