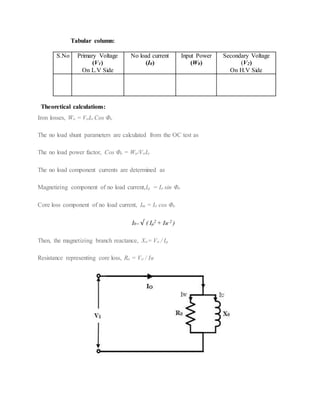
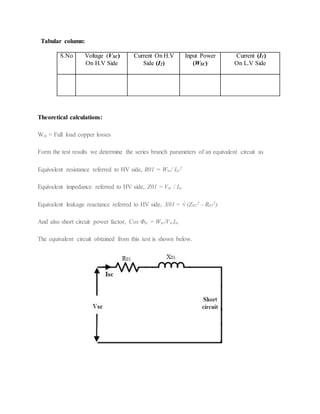
The document describes tests conducted on a single-phase transformer to determine its efficiency and regulation. An open circuit test was conducted to measure no-load losses. A short circuit test was used to determine copper losses and develop an equivalent circuit model. Efficiency was calculated at various load levels and power factors based on losses from the two tests. Regulation was also calculated using the short circuit test results. Plots of efficiency versus load and tables of efficiency and regulation values are presented.