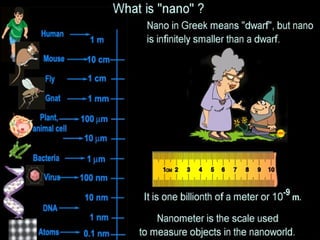
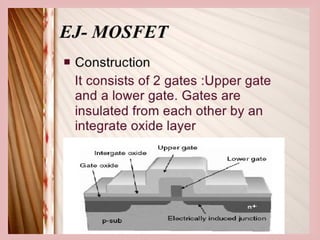
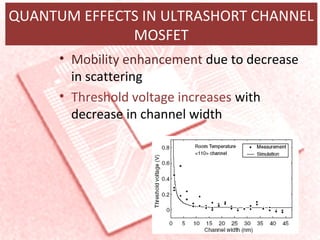
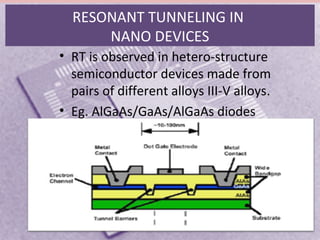
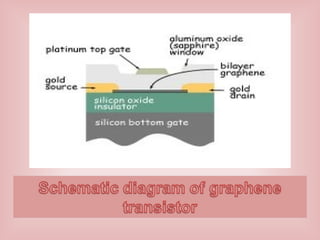
This document provides an overview of nanoelectronics. It defines nanoelectronics as a branch of engineering that uses electronic components with dimensions measured in nanometers. The document discusses how nanoelectronics can be used to reduce the size of electronic devices. It also outlines several applications of nanoelectronics in electronics, energy, and displays. Finally, it discusses future opportunities for nanoelectronics in areas like flexible electronics, wireless devices, and molecular devices.