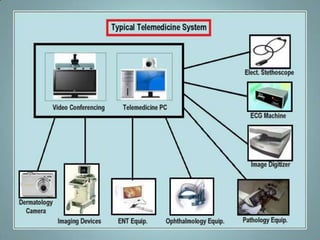
This document provides an overview of e-health applications and services. It discusses how next generation networks and quality of service can help enable tele-consultation services, mobile health, and disease management. The benefits of e-health include improved communication, decision support, and reporting. However, challenges remain regarding information quality, infrastructure, and legal/financial issues. Future work includes advancing technologies and prioritizing information flow to help people lead healthier lives.