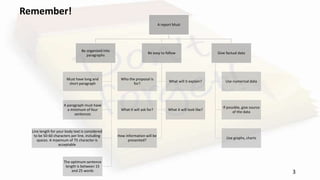
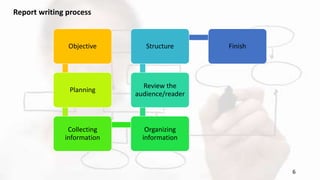
The document outlines the key aspects of effective report writing, including its purpose, structure, and types of reports. It emphasizes the importance of clear organization, factual content, and attention to detail in language and format. Additionally, it provides guidelines on planning, preparing, and reviewing reports to ensure they effectively convey information to a specific audience.