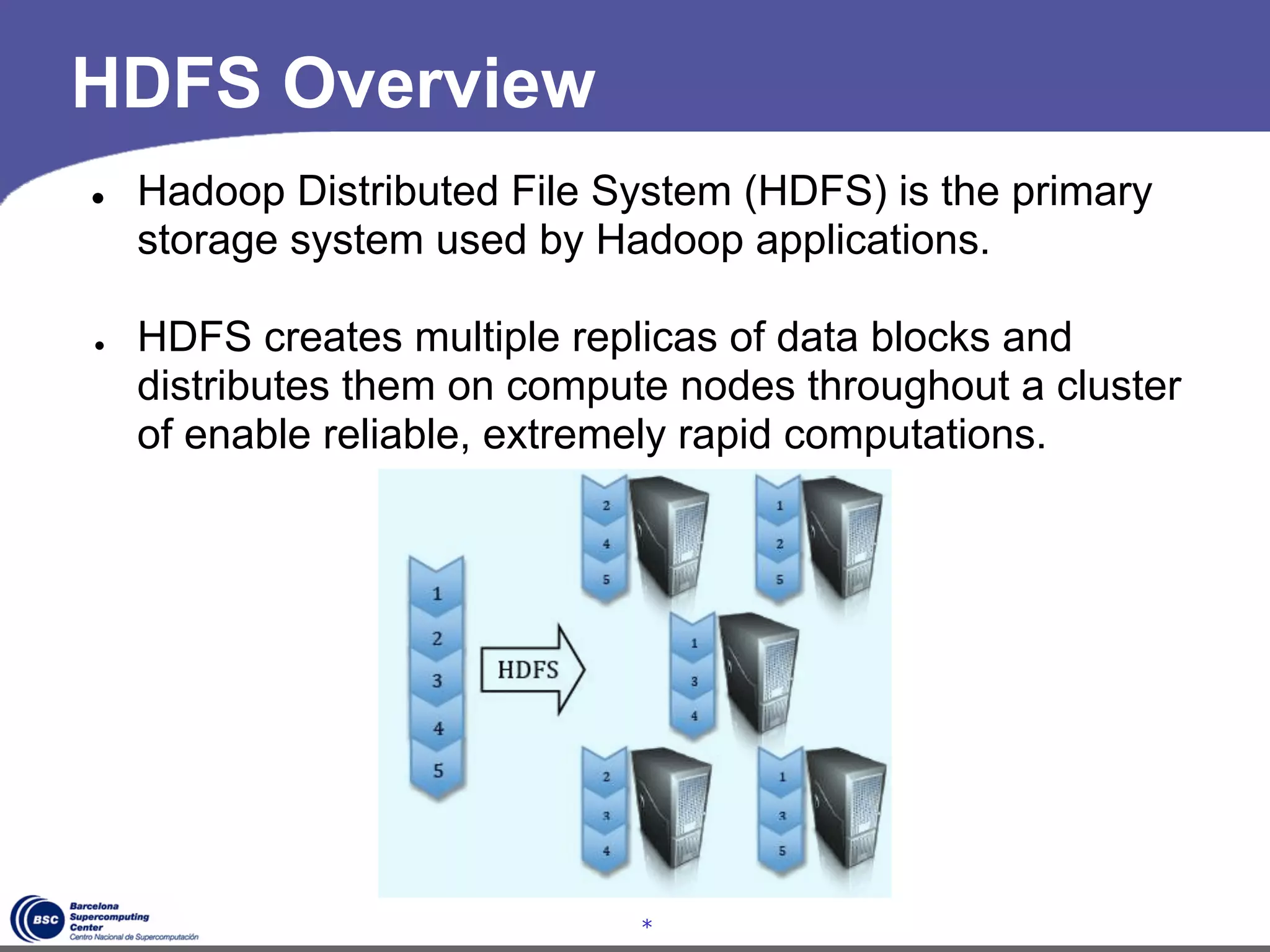
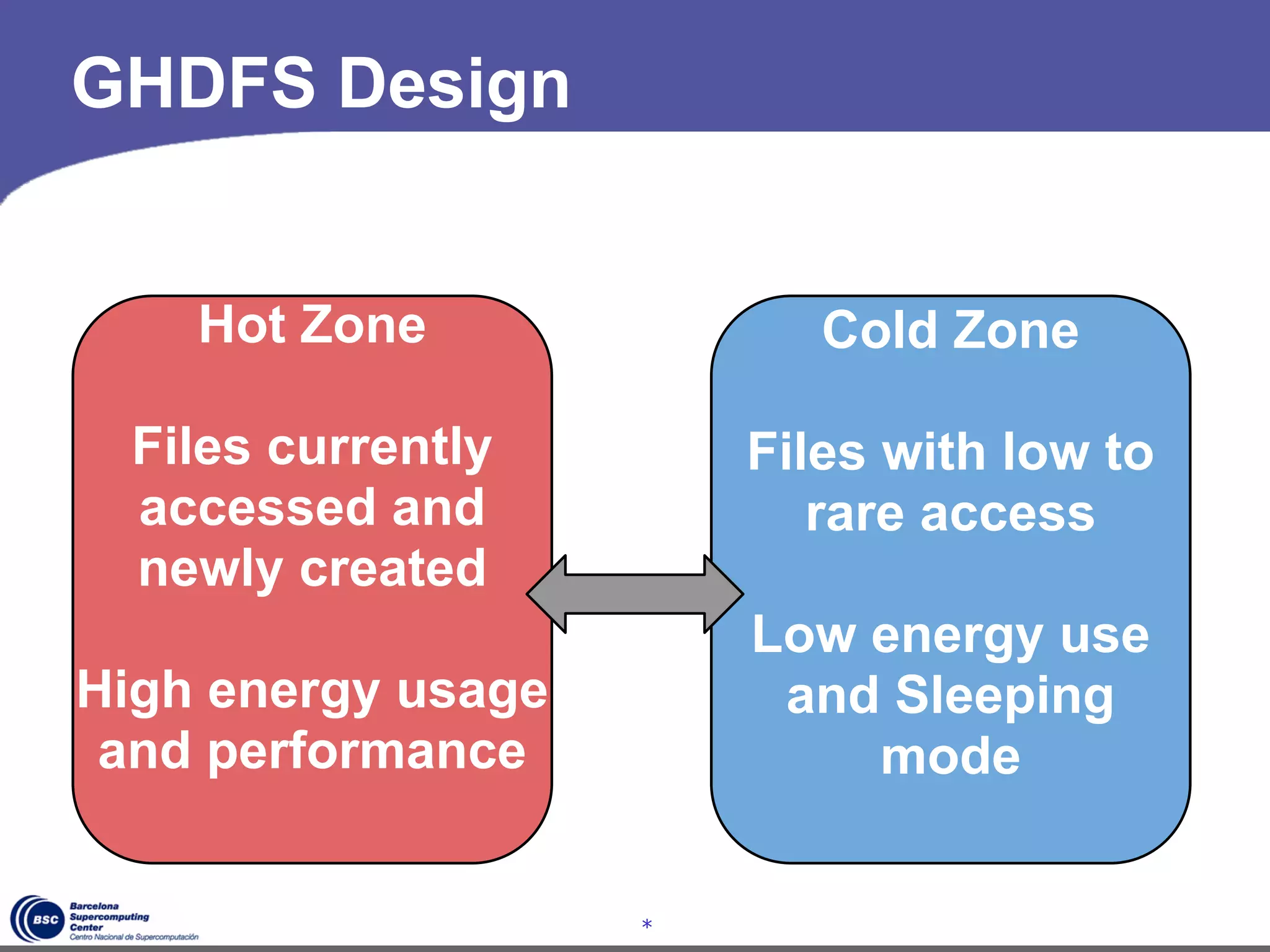
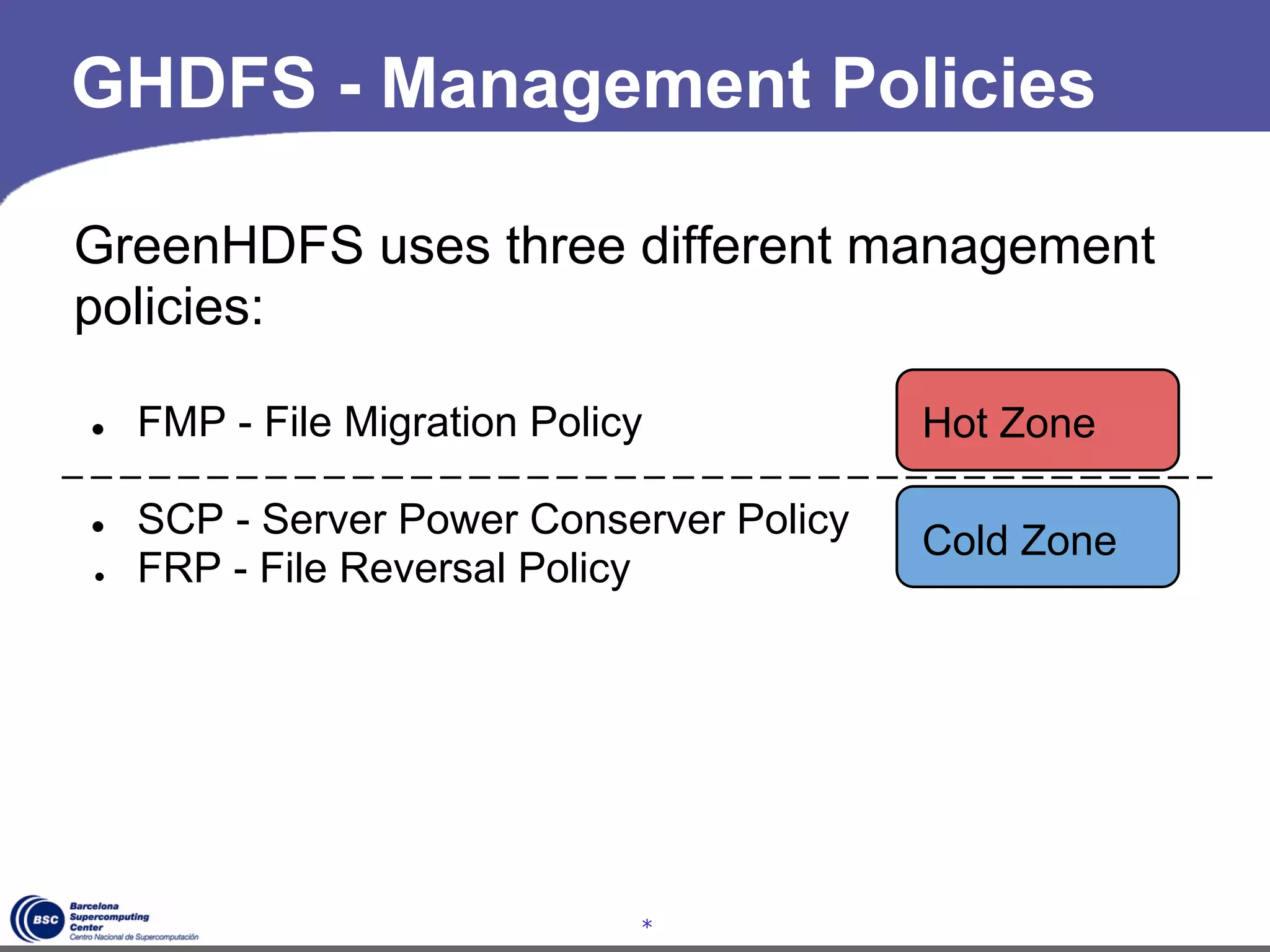
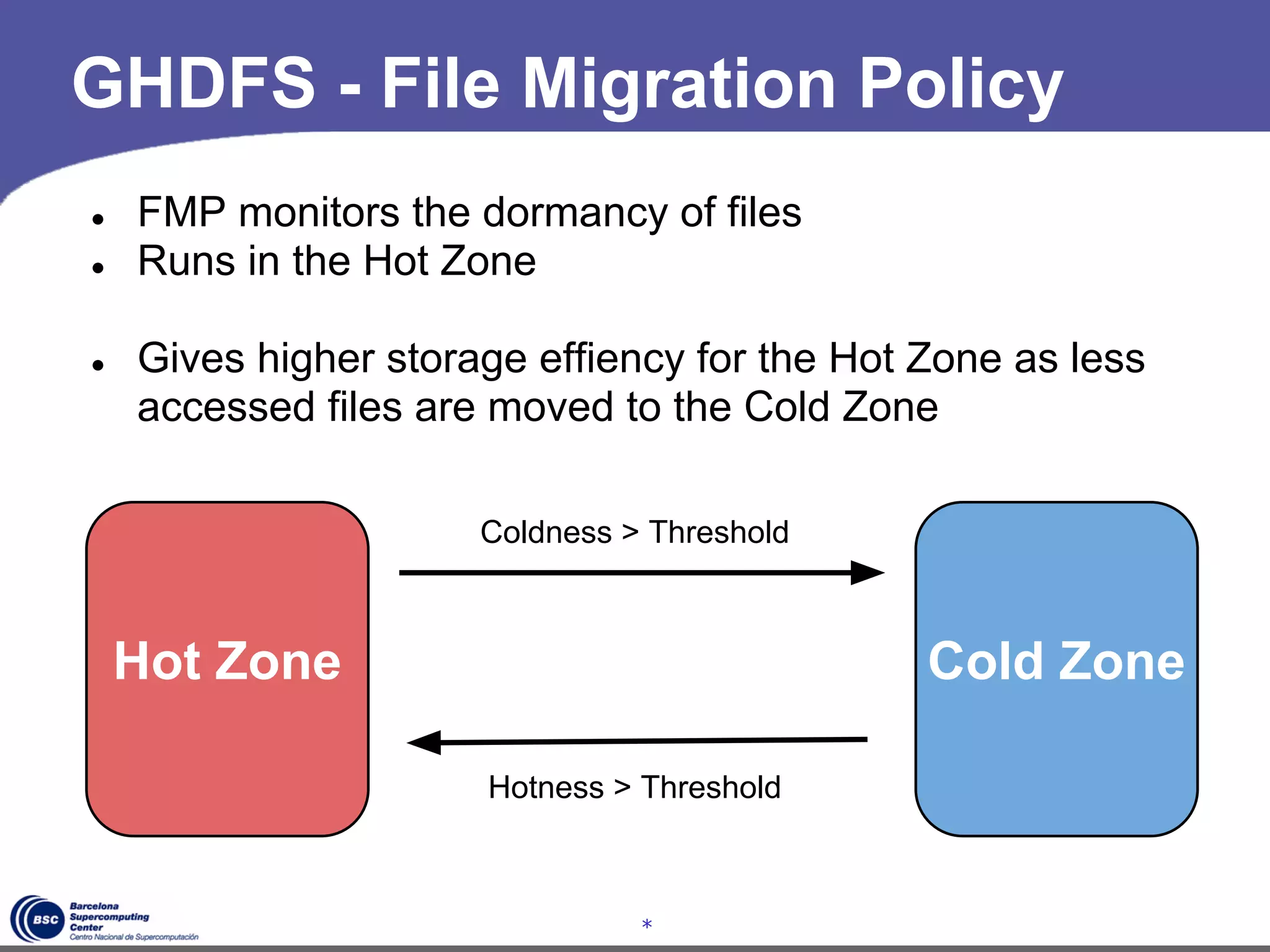
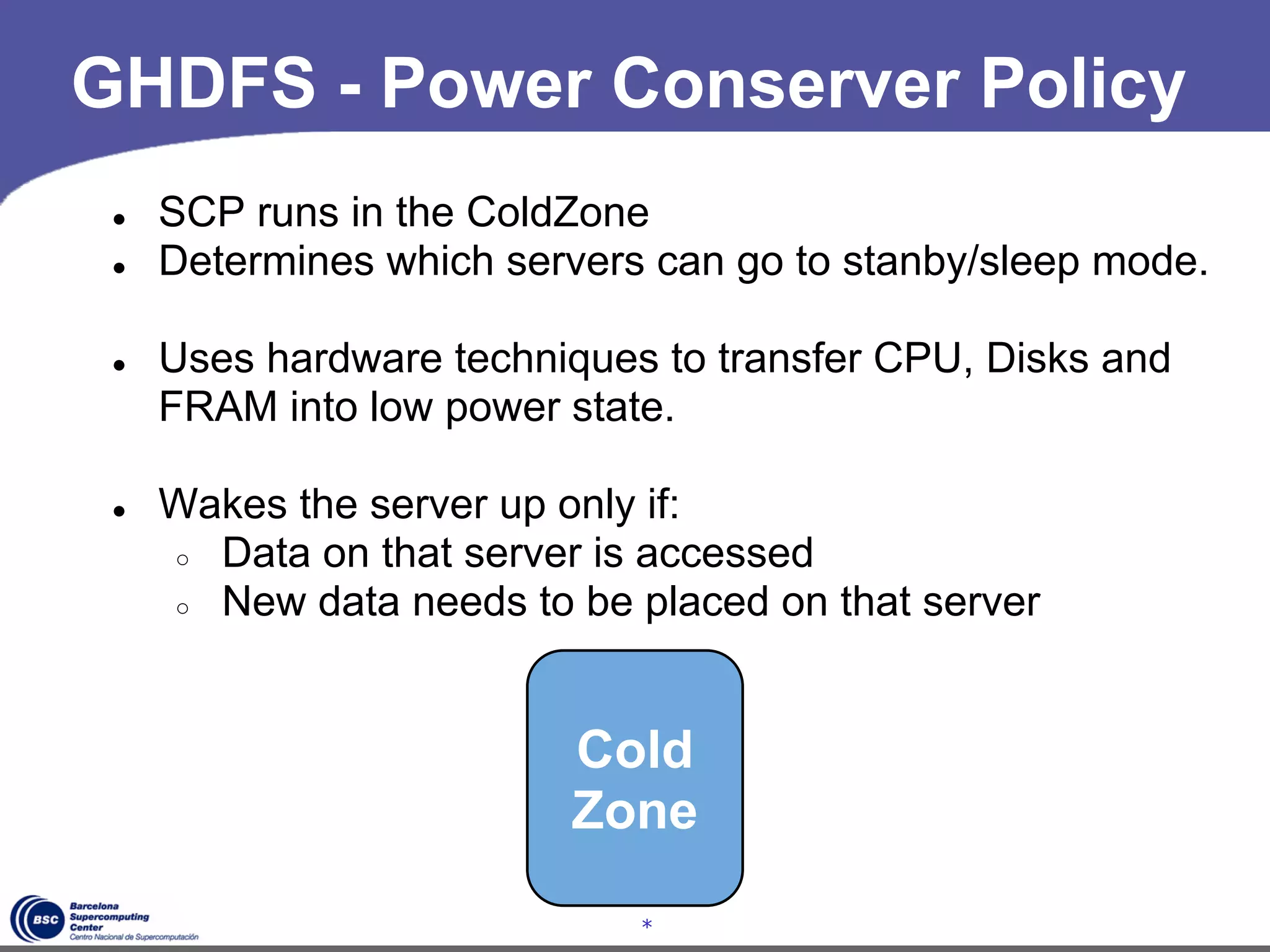
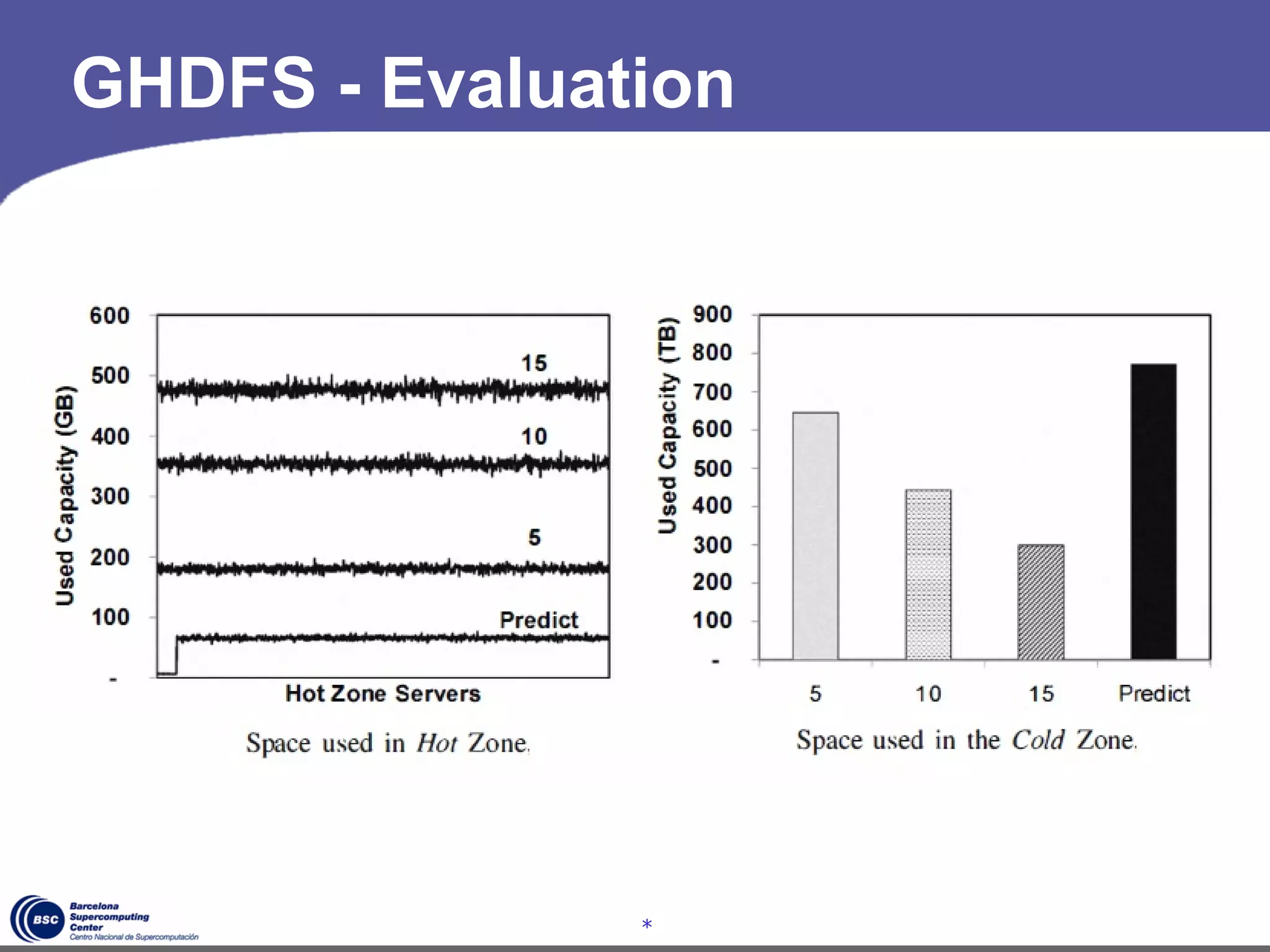
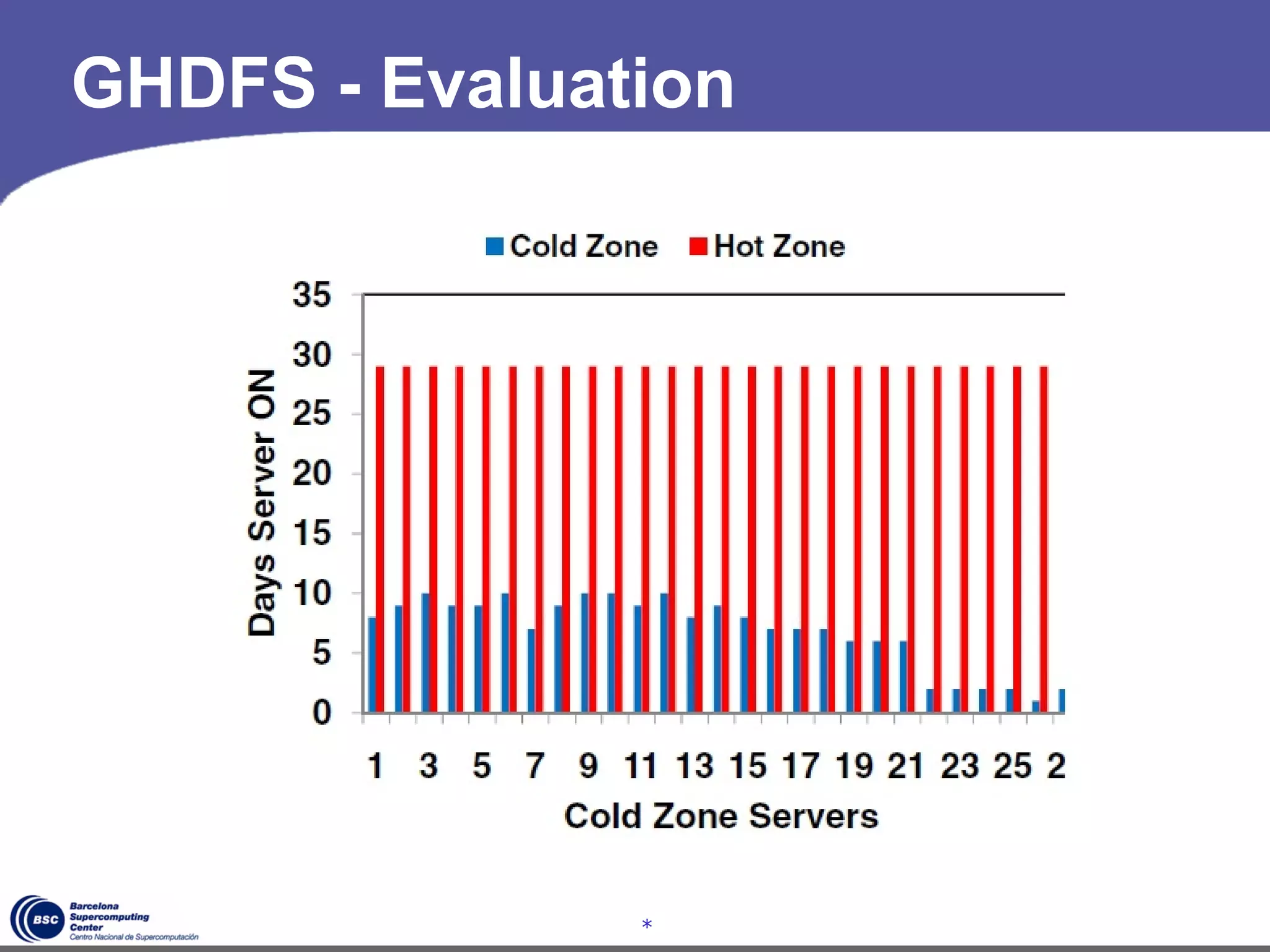
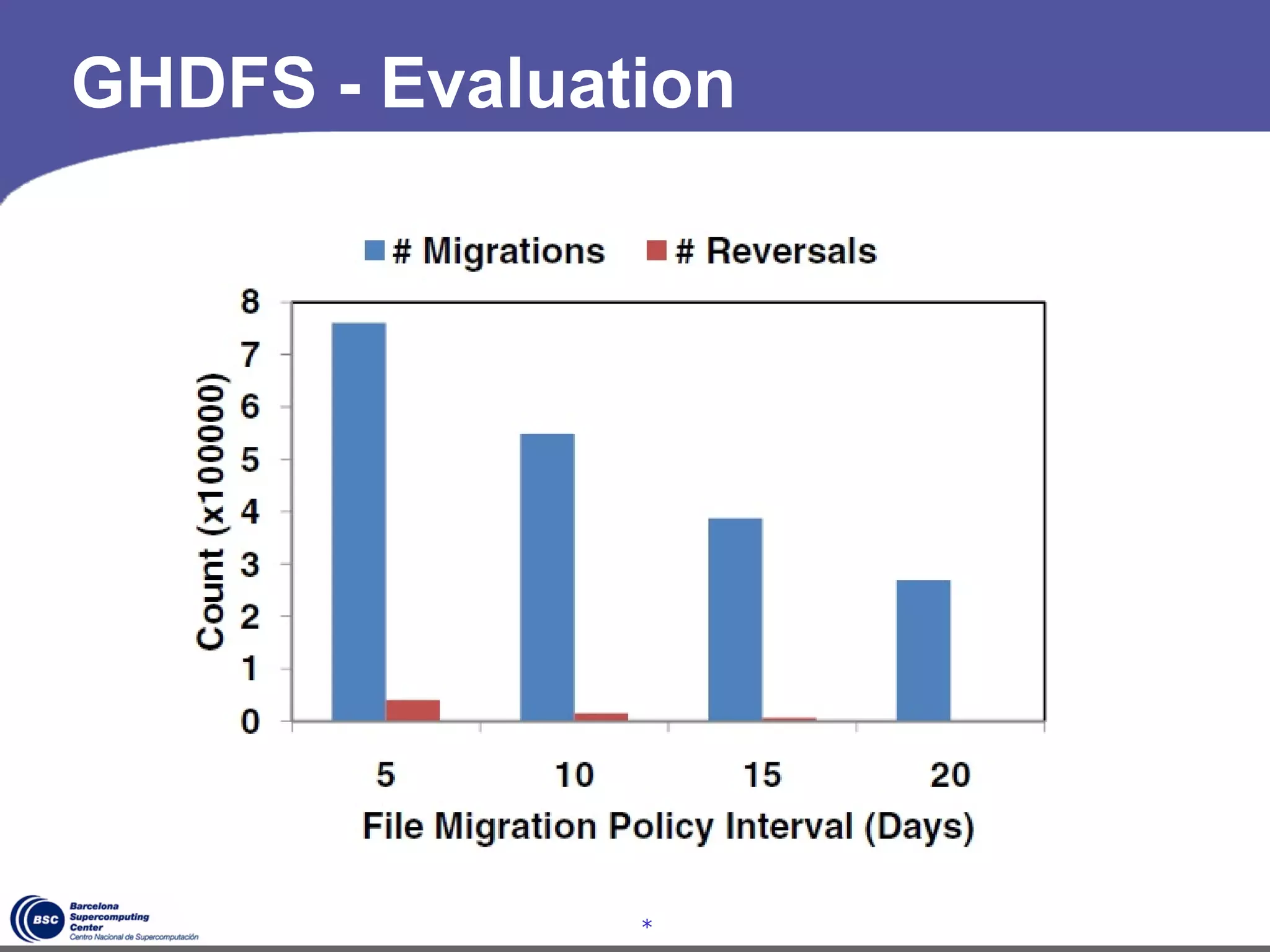
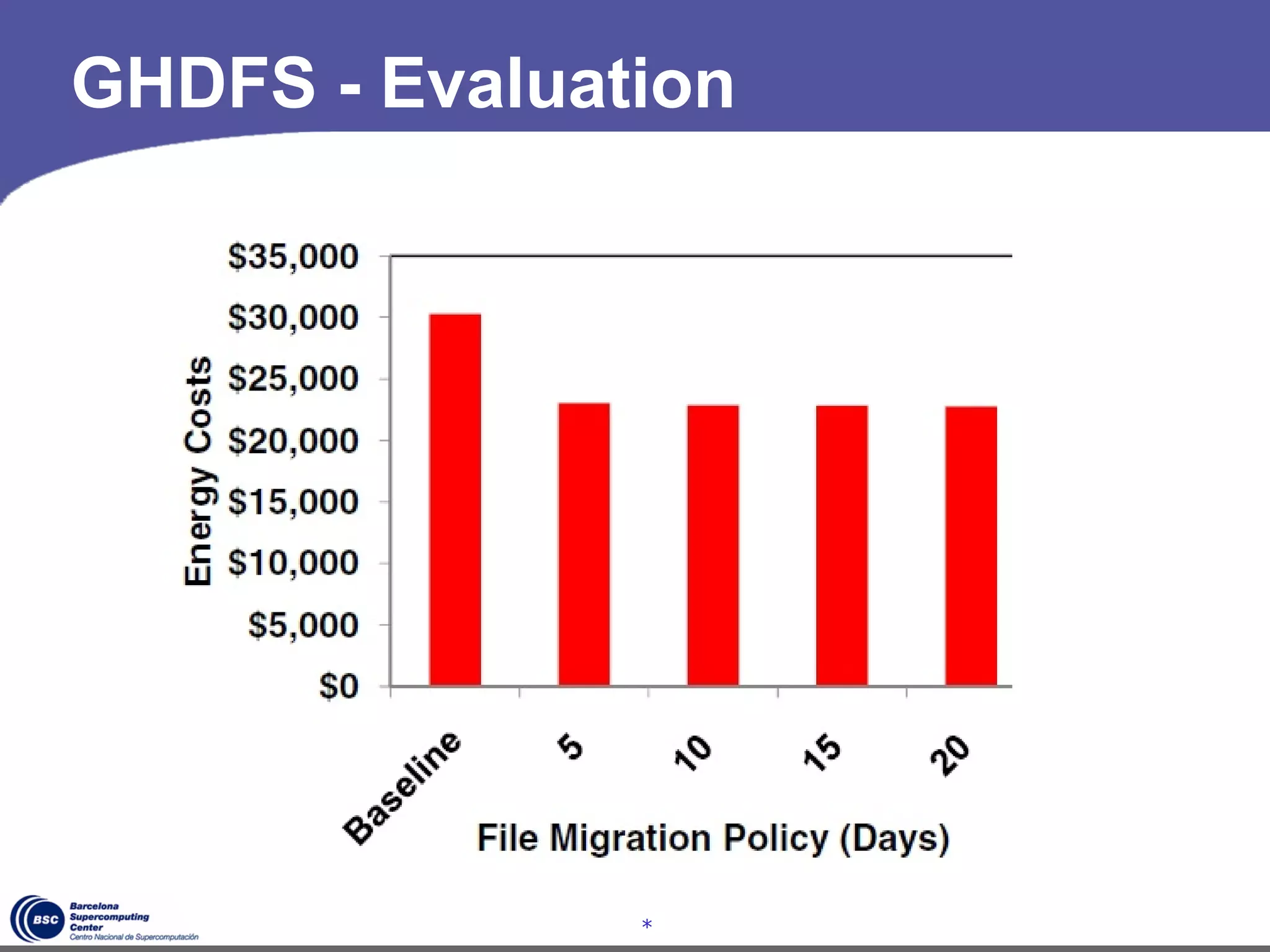
The document discusses GreenHDFS, a self-adaptive variant of HDFS that aims to reduce energy consumption. It does this through techniques like data classification to place "hot" and "cold" data in different zones, power management policies to transition servers to low-power states, and machine learning to predict file access patterns and inform placement. An evaluation of GreenHDFS found it reduced energy consumption by 24% and saved $2.1 million annually in a 38,000 server cluster.
![EEDC
34330
Self-Adapting, Energy-
Execution Conserving Distributed
Environments for File Systems
Distributed
Computing
European Master in Distributed
Computing - EMDC
EEDC Presentation
Mário Almeida– 4knahs[@]gmail.com
www.marioalmeida.eu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eedc-hdfs-marioalmeida-120608070148-phpapp01/75/Self-Adapting-Energy-Conserving-Distributed-File-Systems-1-2048.jpg)






![EEDC
34330
Self-Adapting, Energy-
Execution Conserving Distributed
Environments for File Systems
Distributed
Computing
European Master in Distributed
Computing - EMDC
EEDC Presentation
Mário Almeida– 4knahs[@]gmail.com
www.marioalmeida.eu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eedc-hdfs-marioalmeida-120608070148-phpapp01/75/Self-Adapting-Energy-Conserving-Distributed-File-Systems-26-2048.jpg)