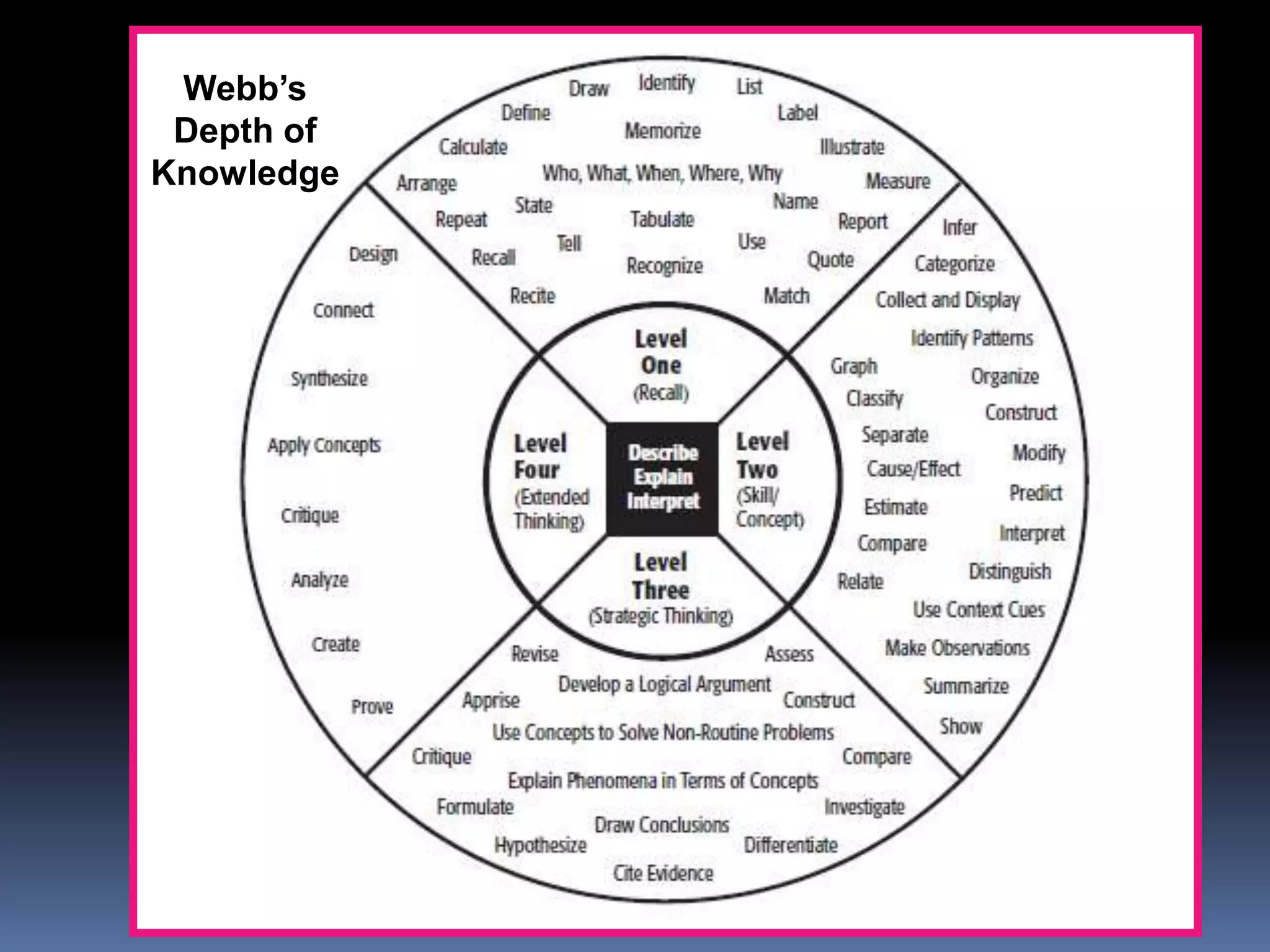
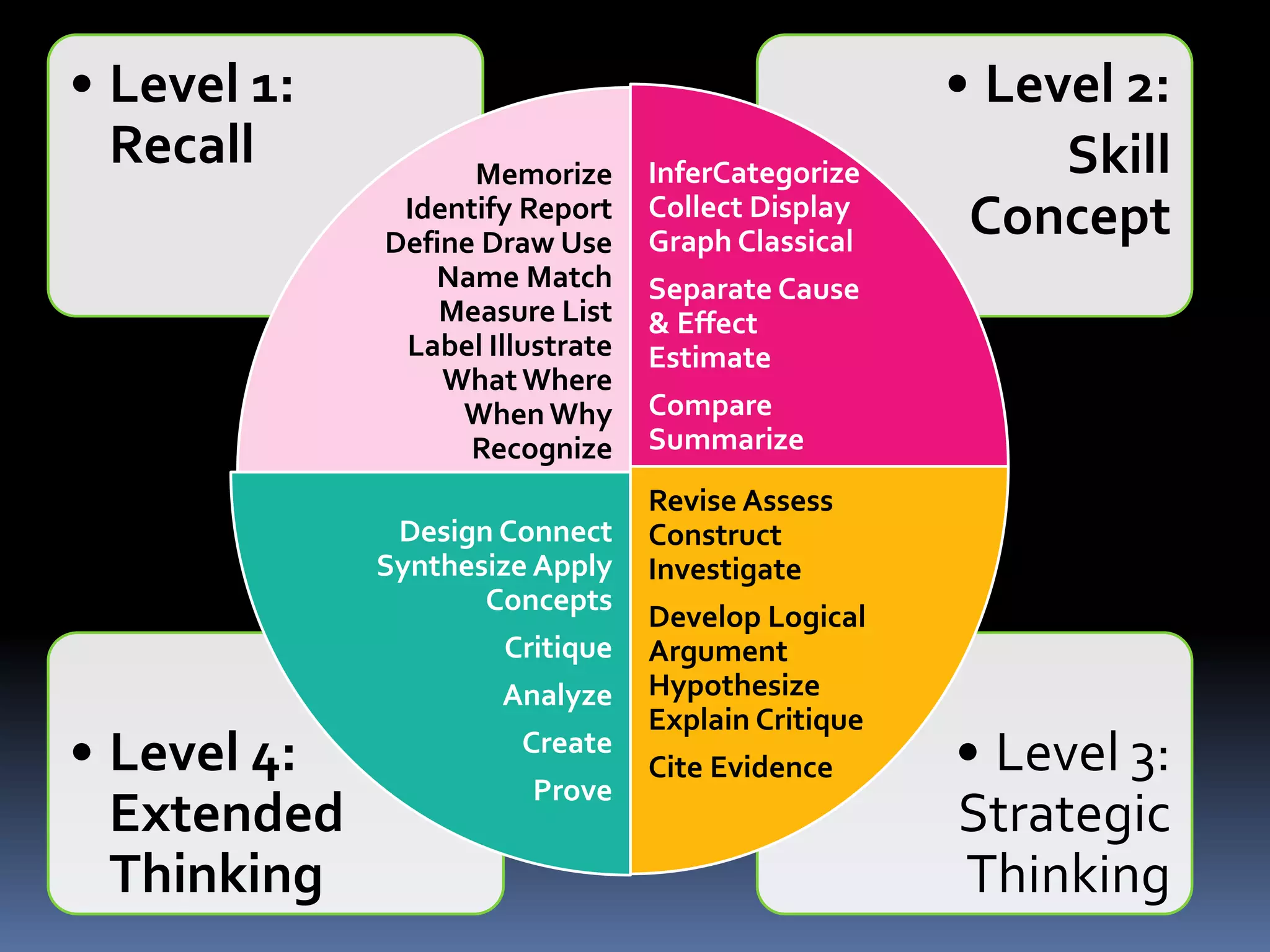
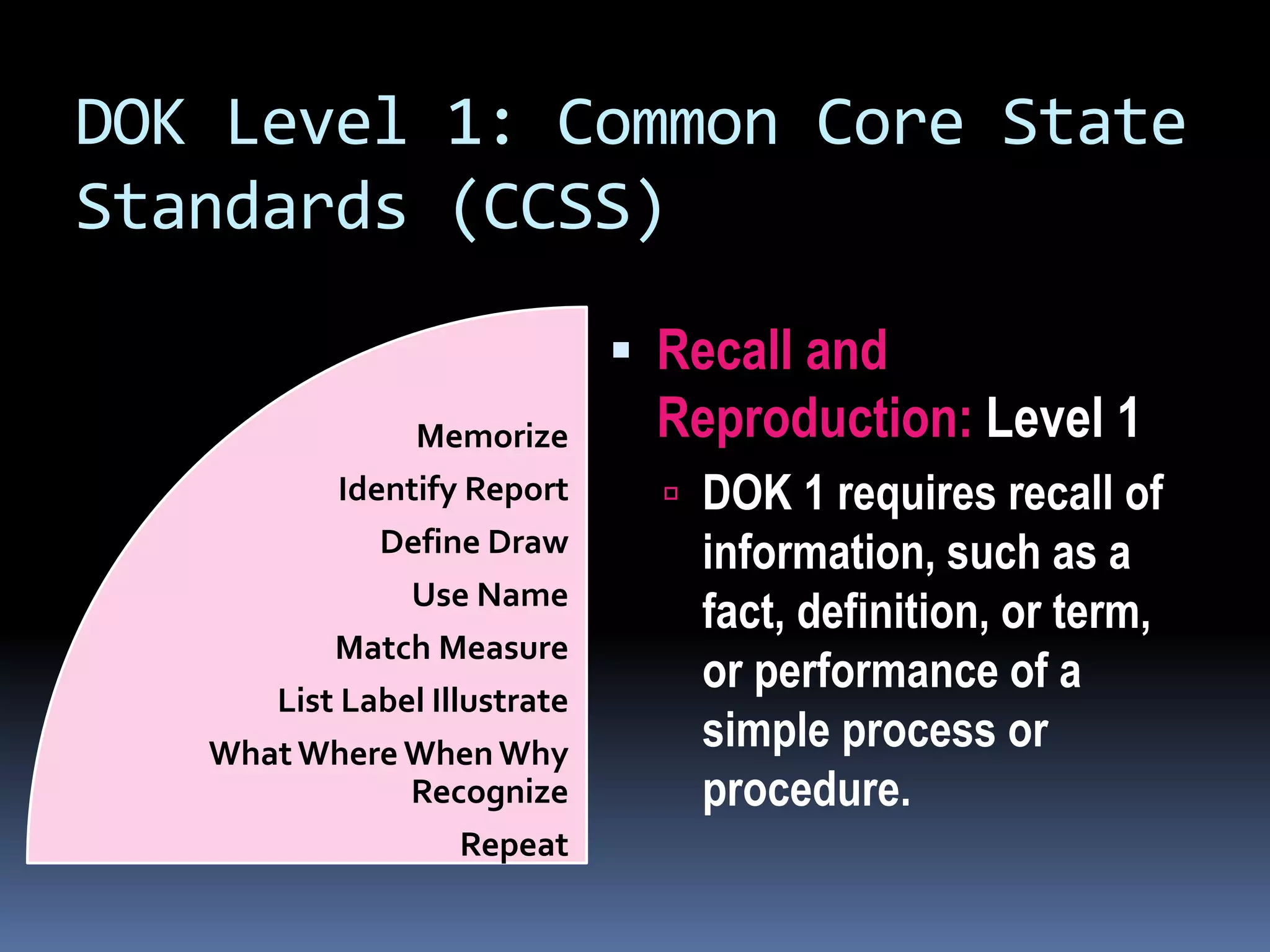
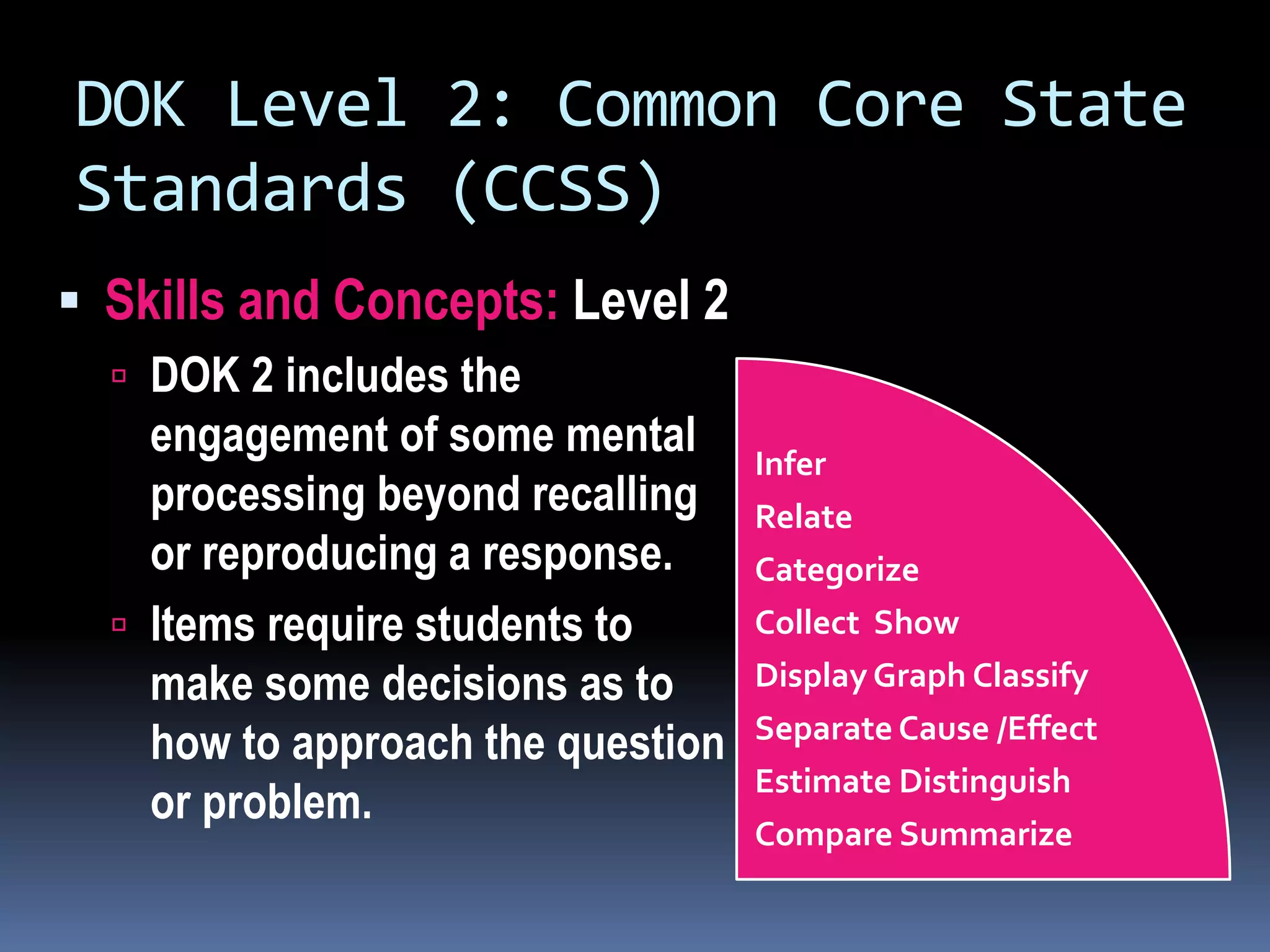
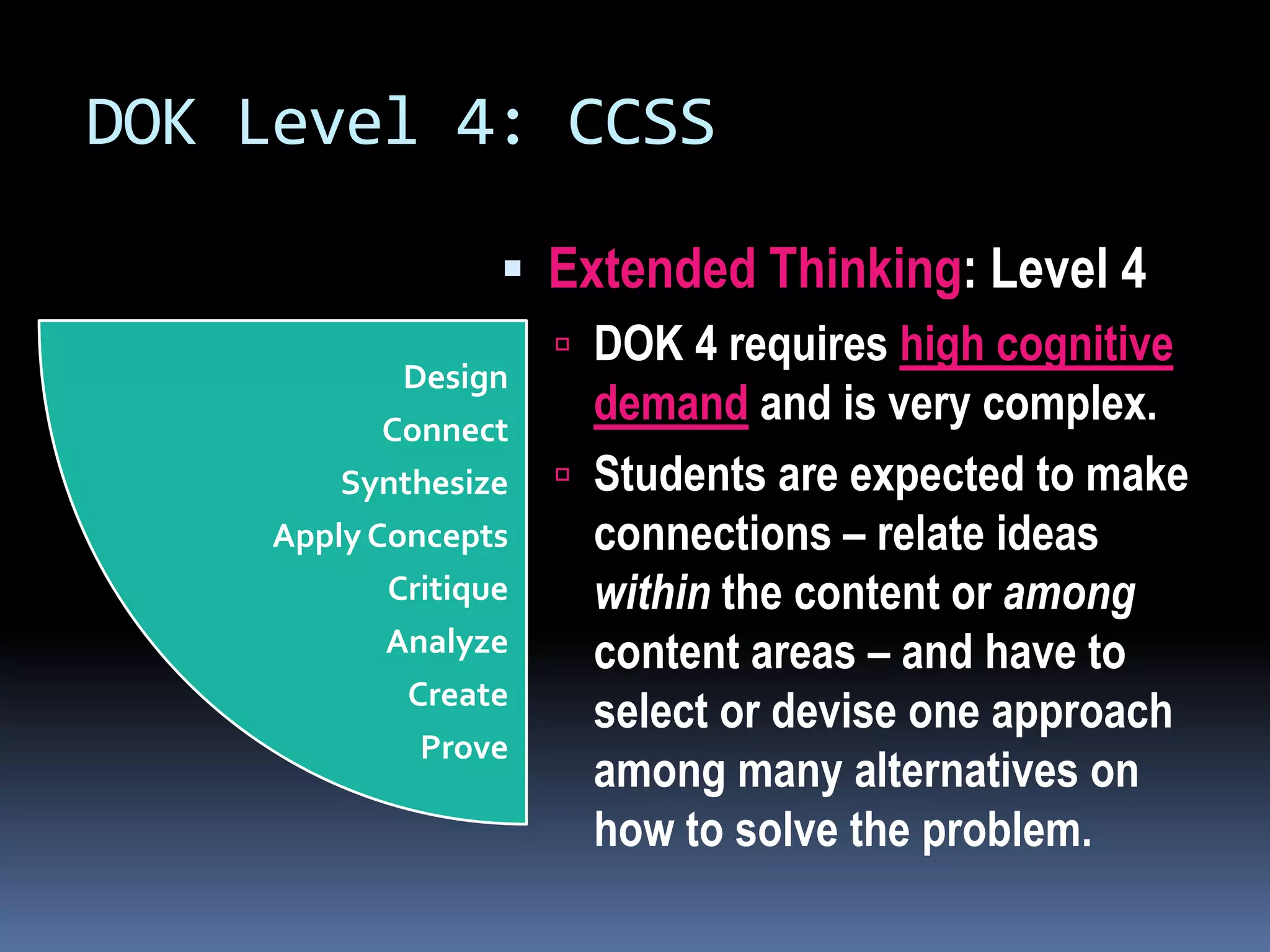
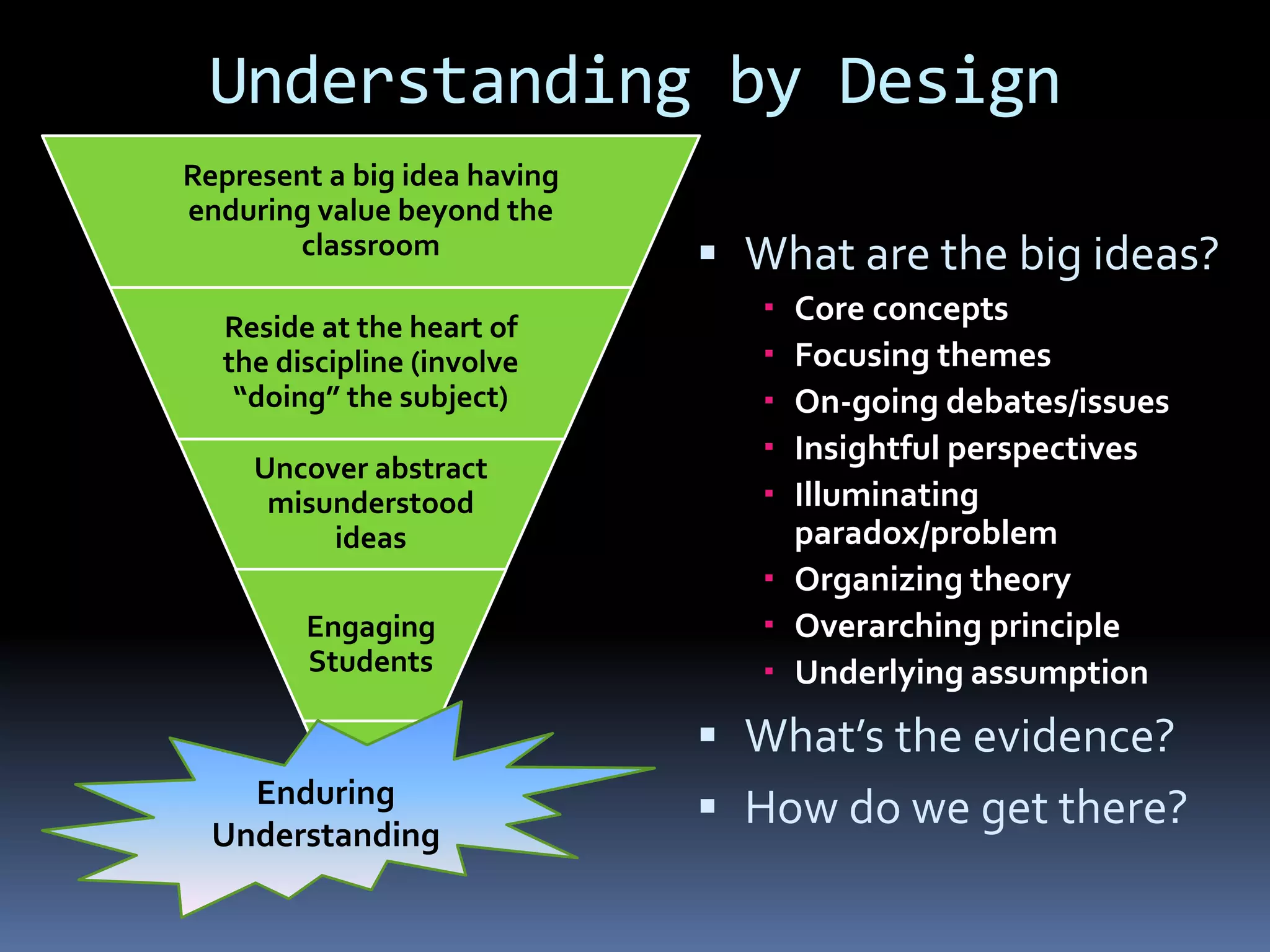
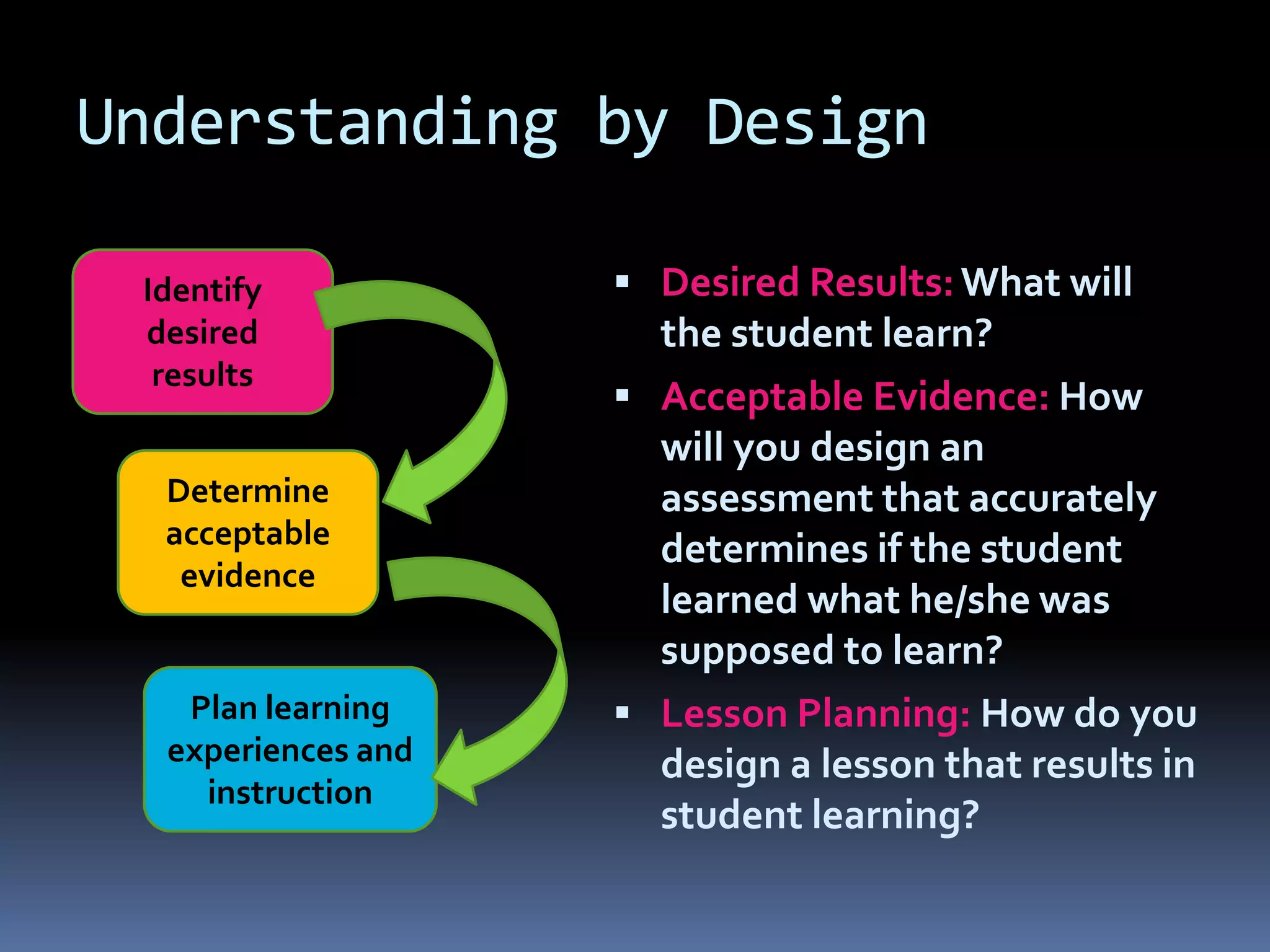
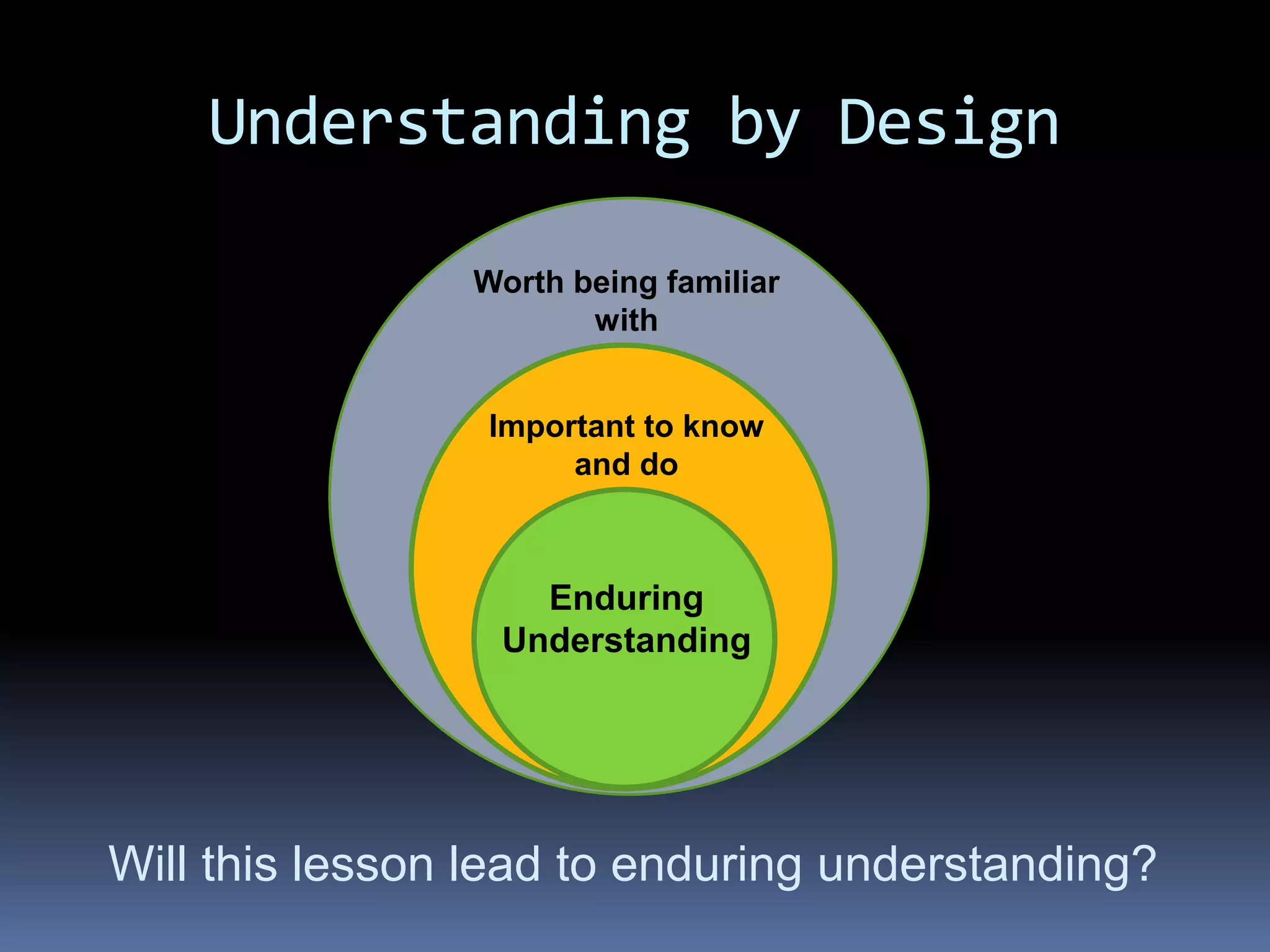
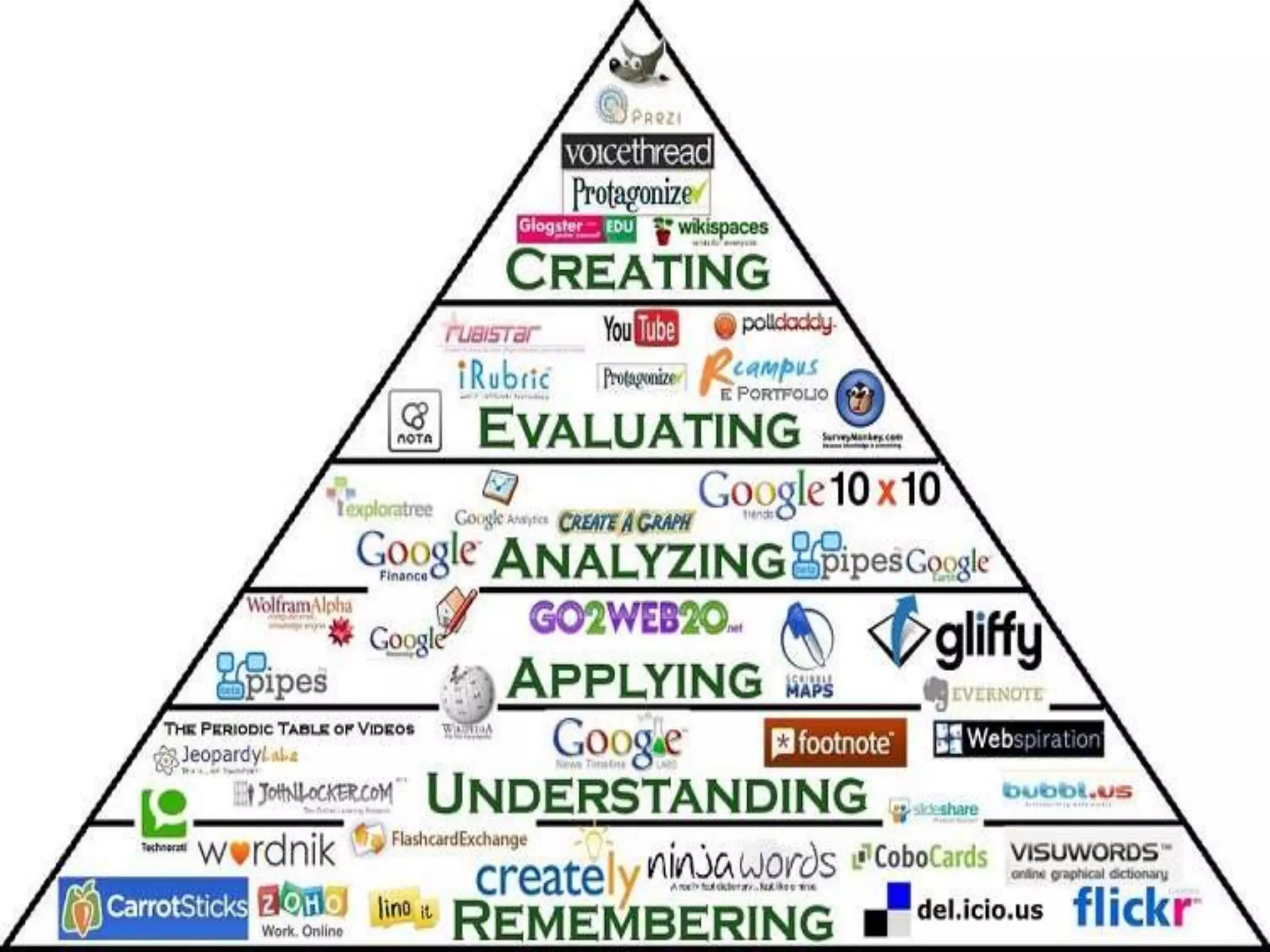
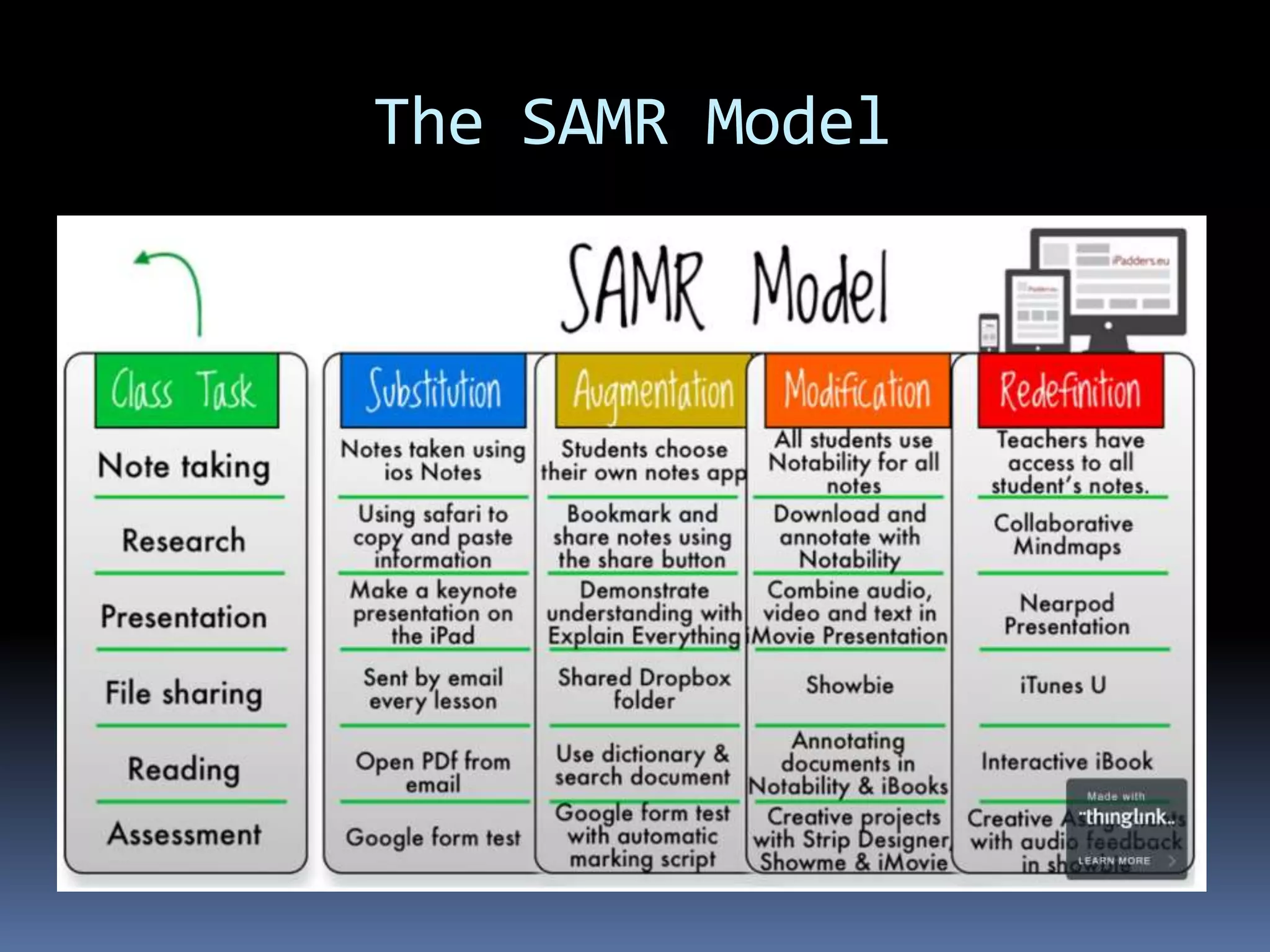
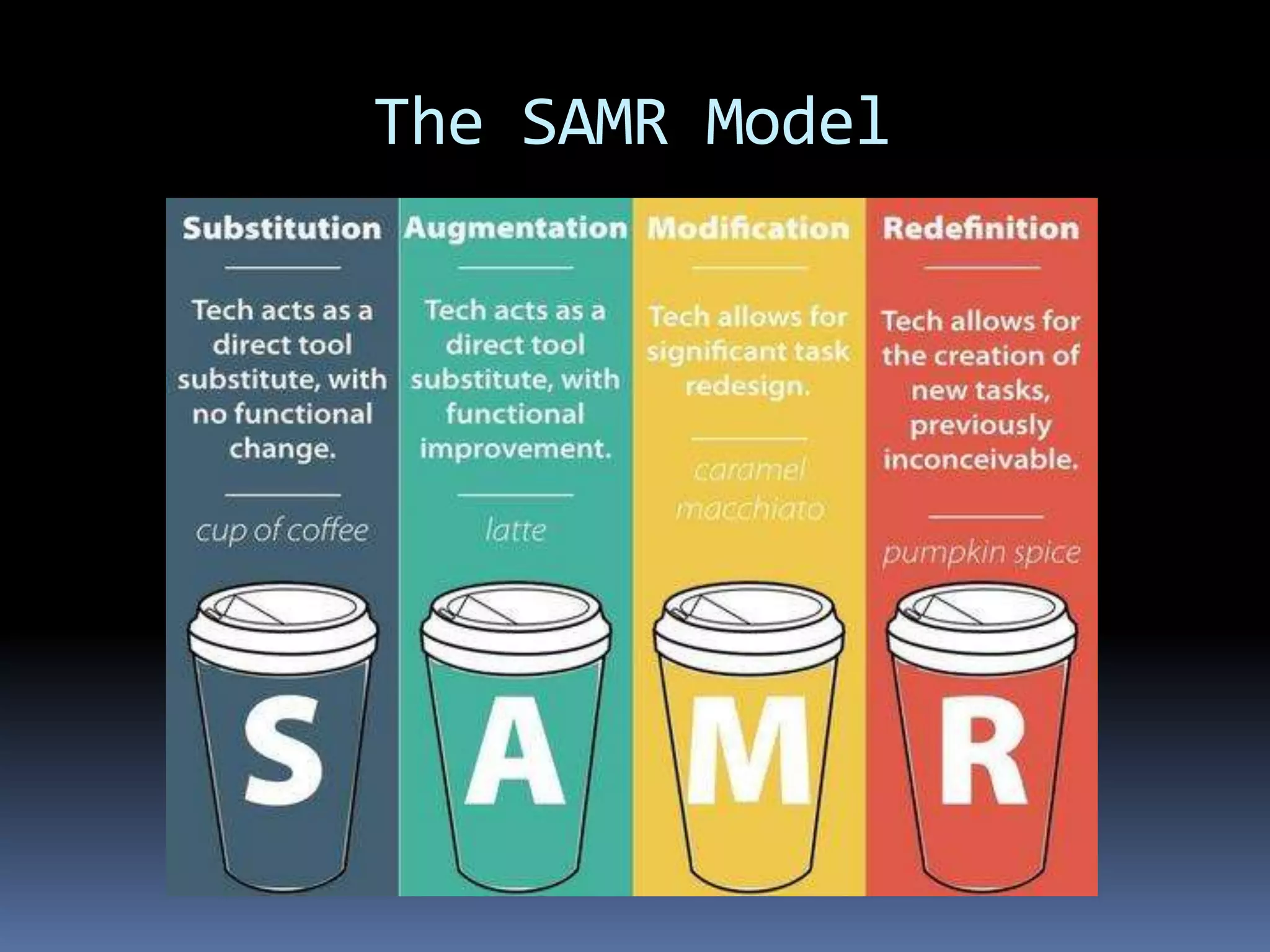
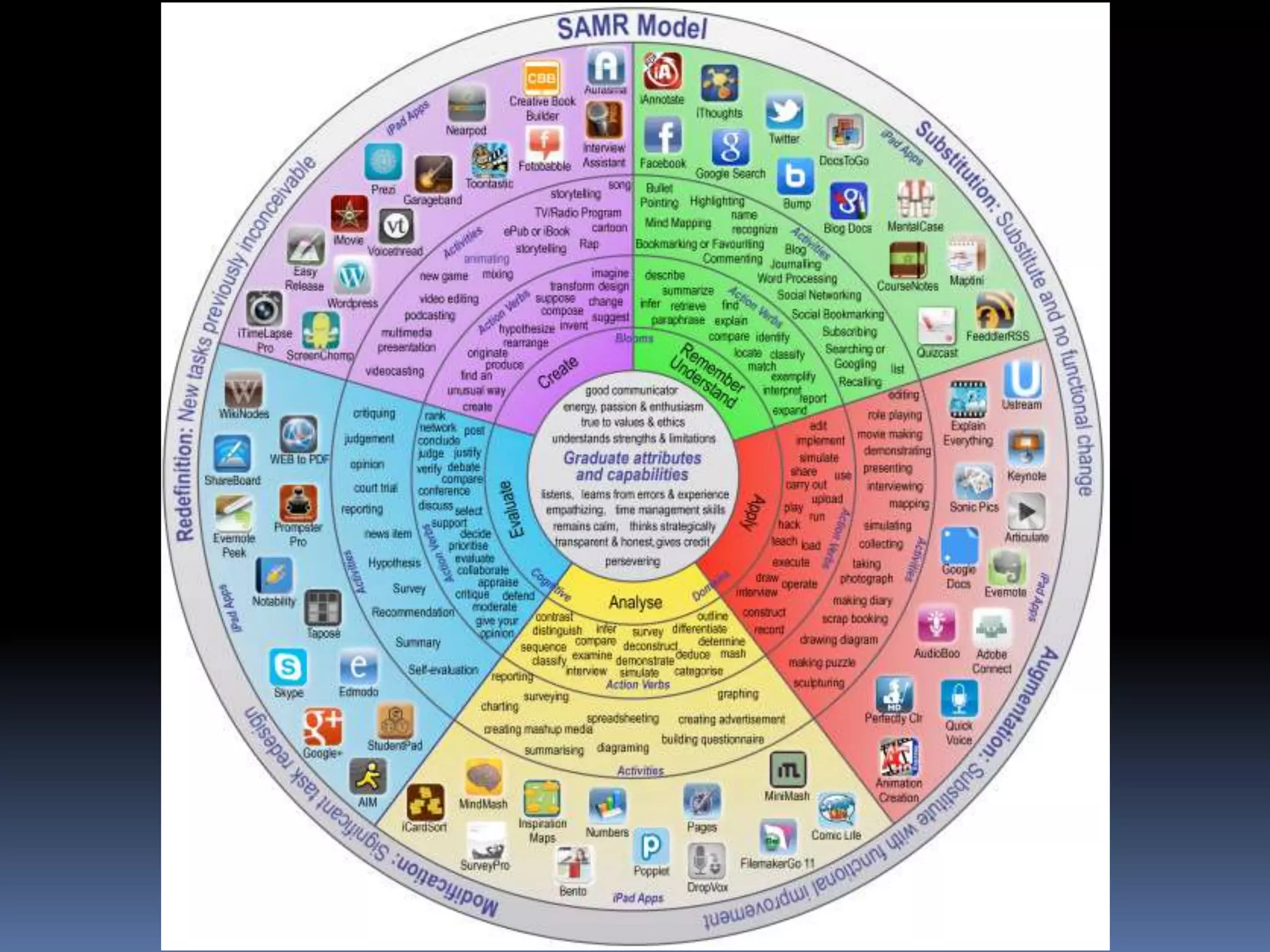
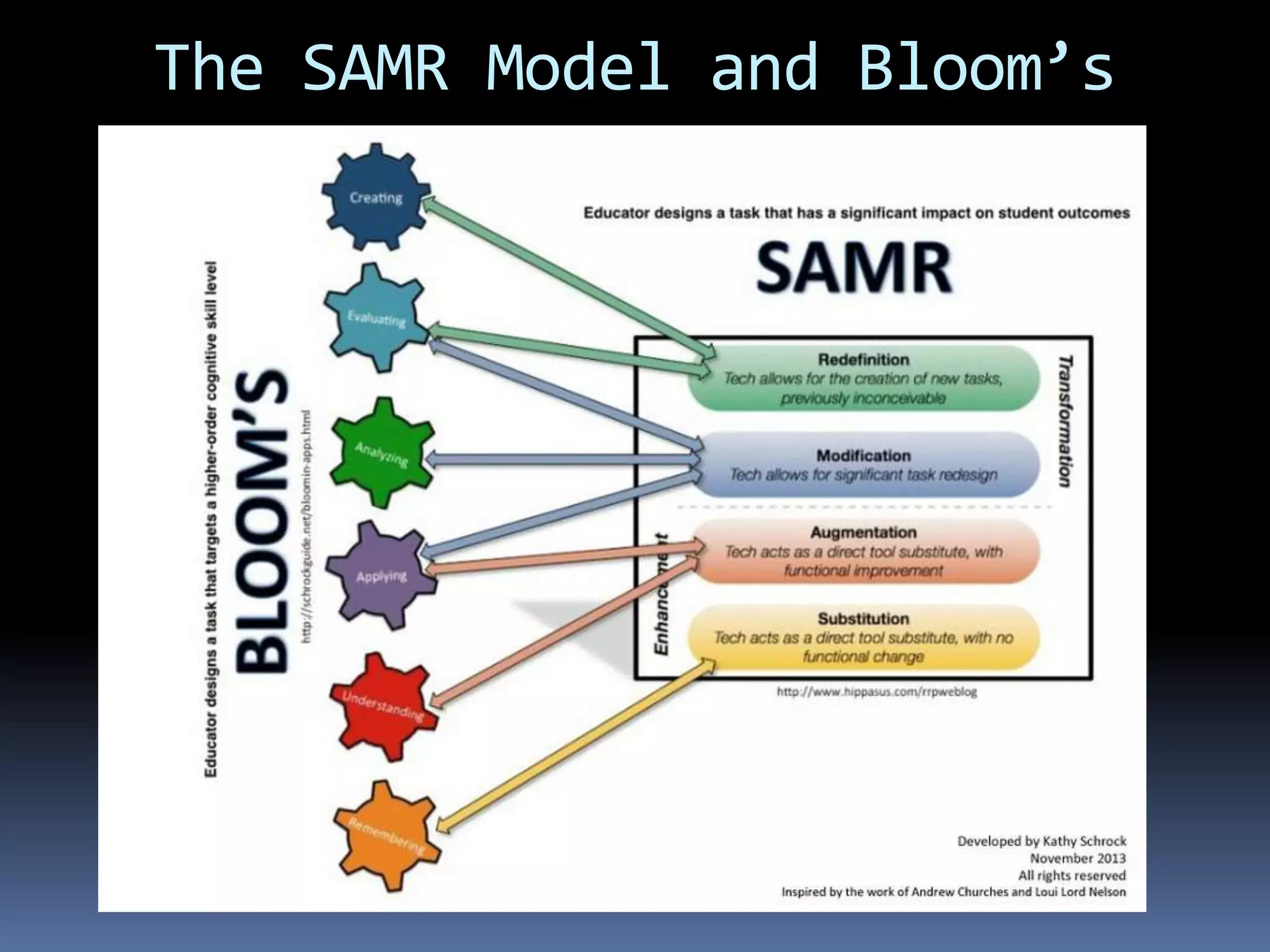
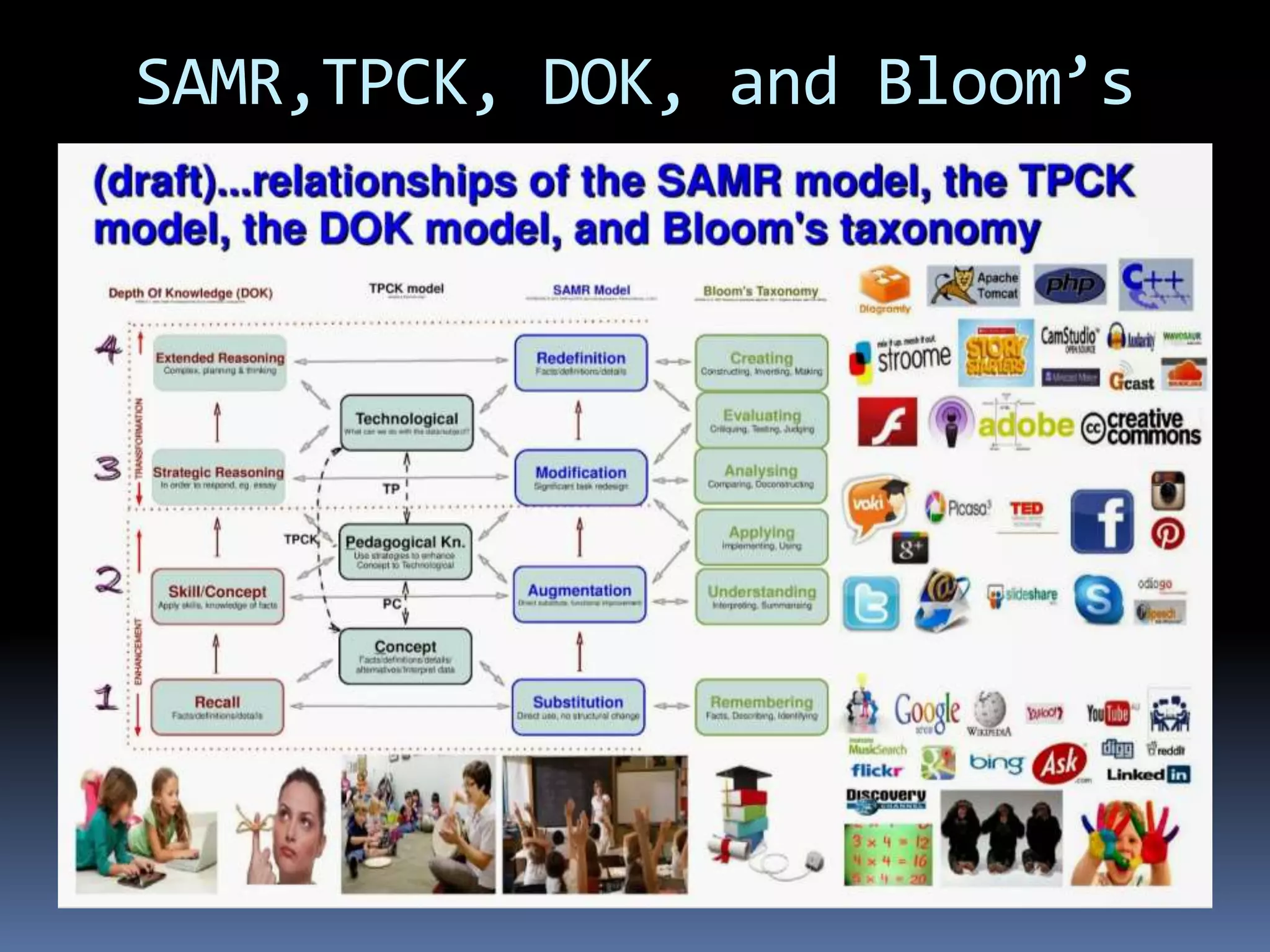
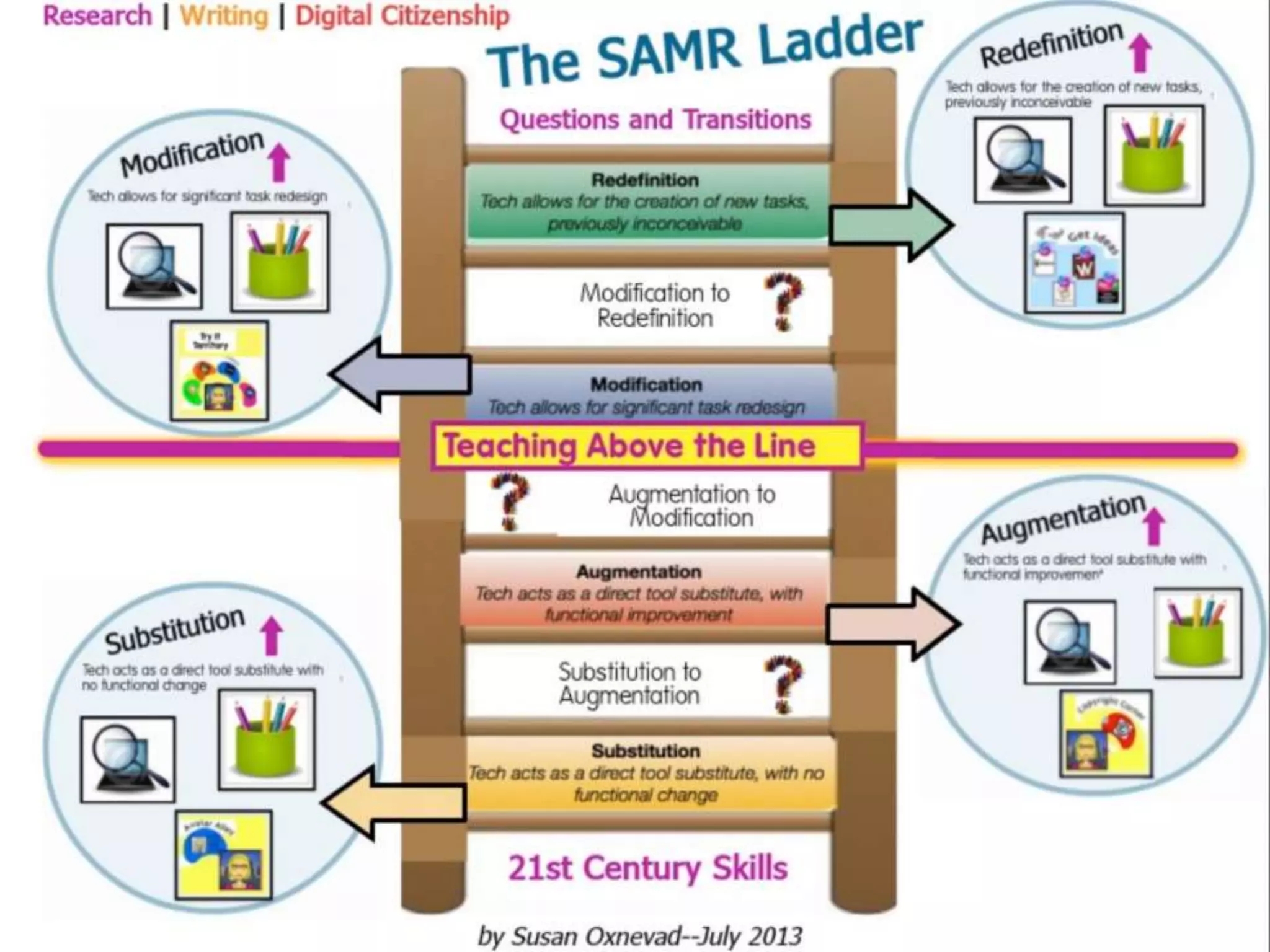
This document discusses different frameworks for designing effective instruction including essential questions, Bloom's taxonomy, depth of knowledge (DOK), understanding by design, and the SAMR model. It explains that essential questions spark curiosity, have no definite answers, and require students to construct their own understandings. Bloom's taxonomy and its revision classify learning objectives from lower to higher order thinking. DOK levels range from recall to extended thinking. Understanding by design focuses lessons around big ideas, enduring understandings, and authentic assessments. The SAMR model evaluates technology integration from substitution to redefinition. These frameworks aim to engage students in strategic, creative, real-world problem solving and thinking.