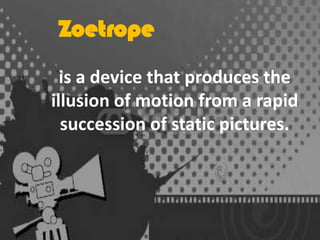
Motion Media is defined as graphics that use video and/or animation to create the illusion of motion or a transforming appearance. Early motion media devices included the thaumatrope, phenakistoscope, stroboscope, zoetrope, and praxinoscope - toys from the 19th century that used persistence of vision to create the illusion of movement. Modern motion media includes video, animation, and combinations of the two. Video uses recorded moving images while animation creates motion through rapid display of sequentially different static images. Motion media has various applications in education by making lessons more engaging and accessible through video-based materials, interactive videos, and video conferences.