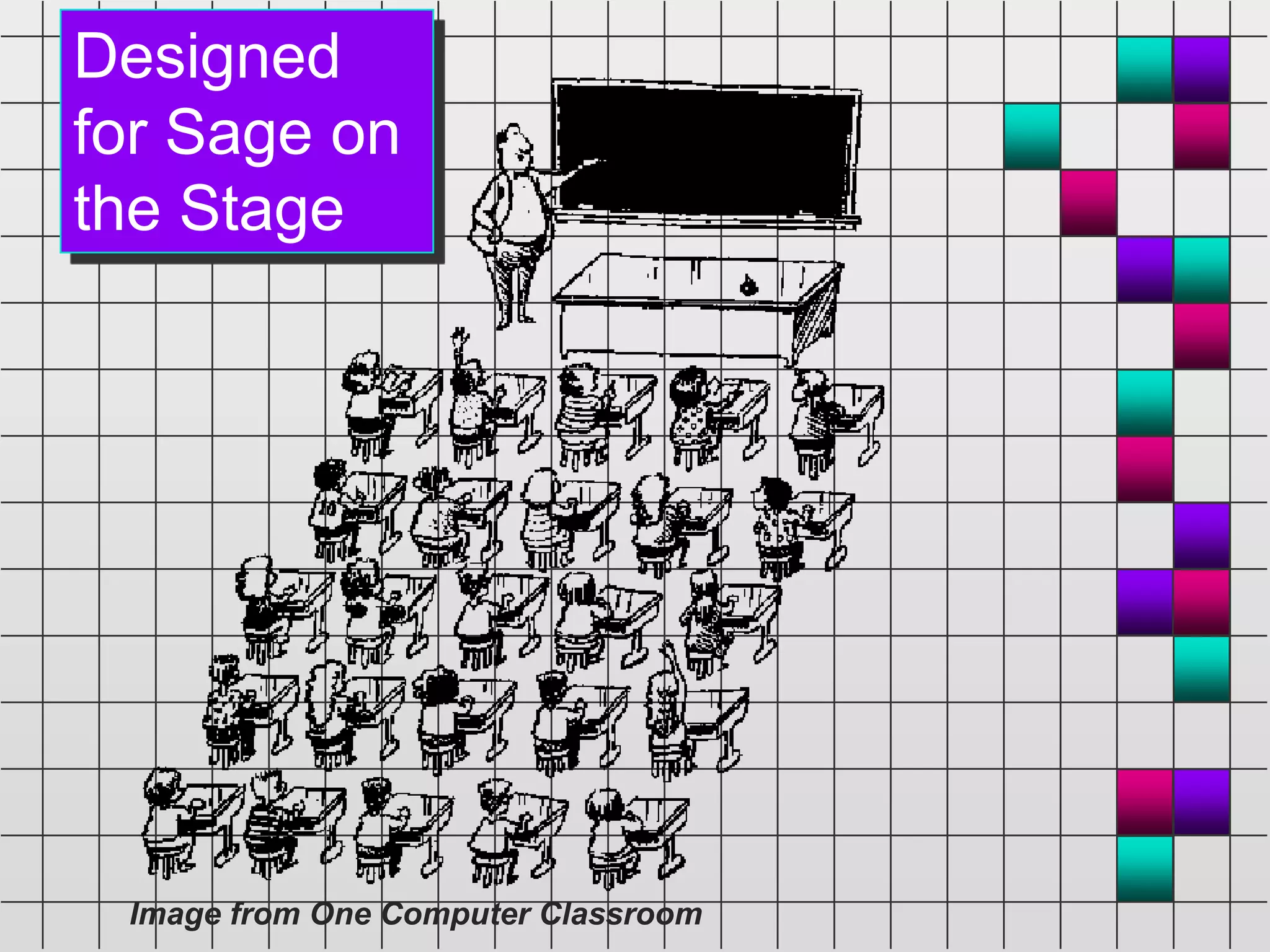
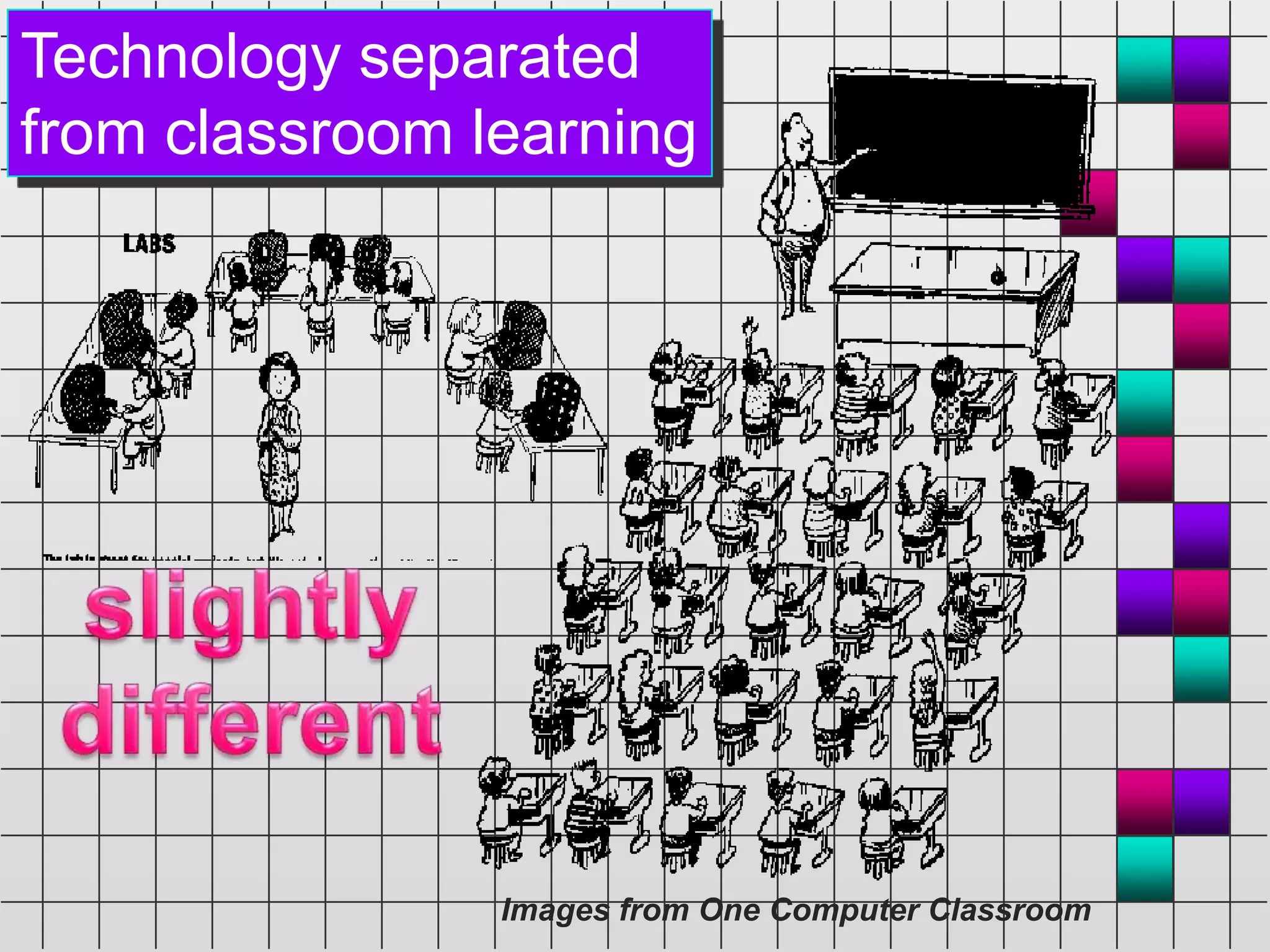
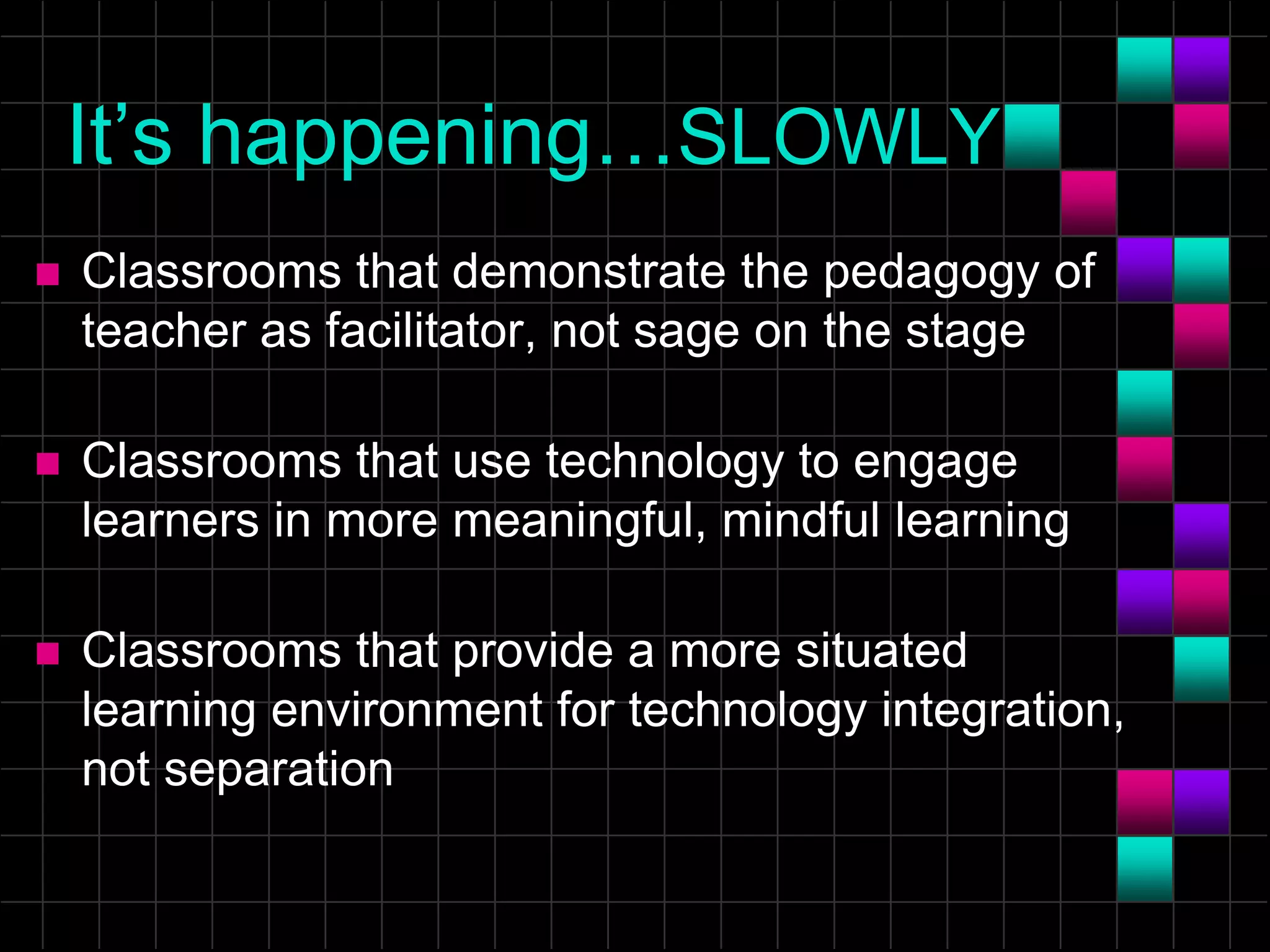
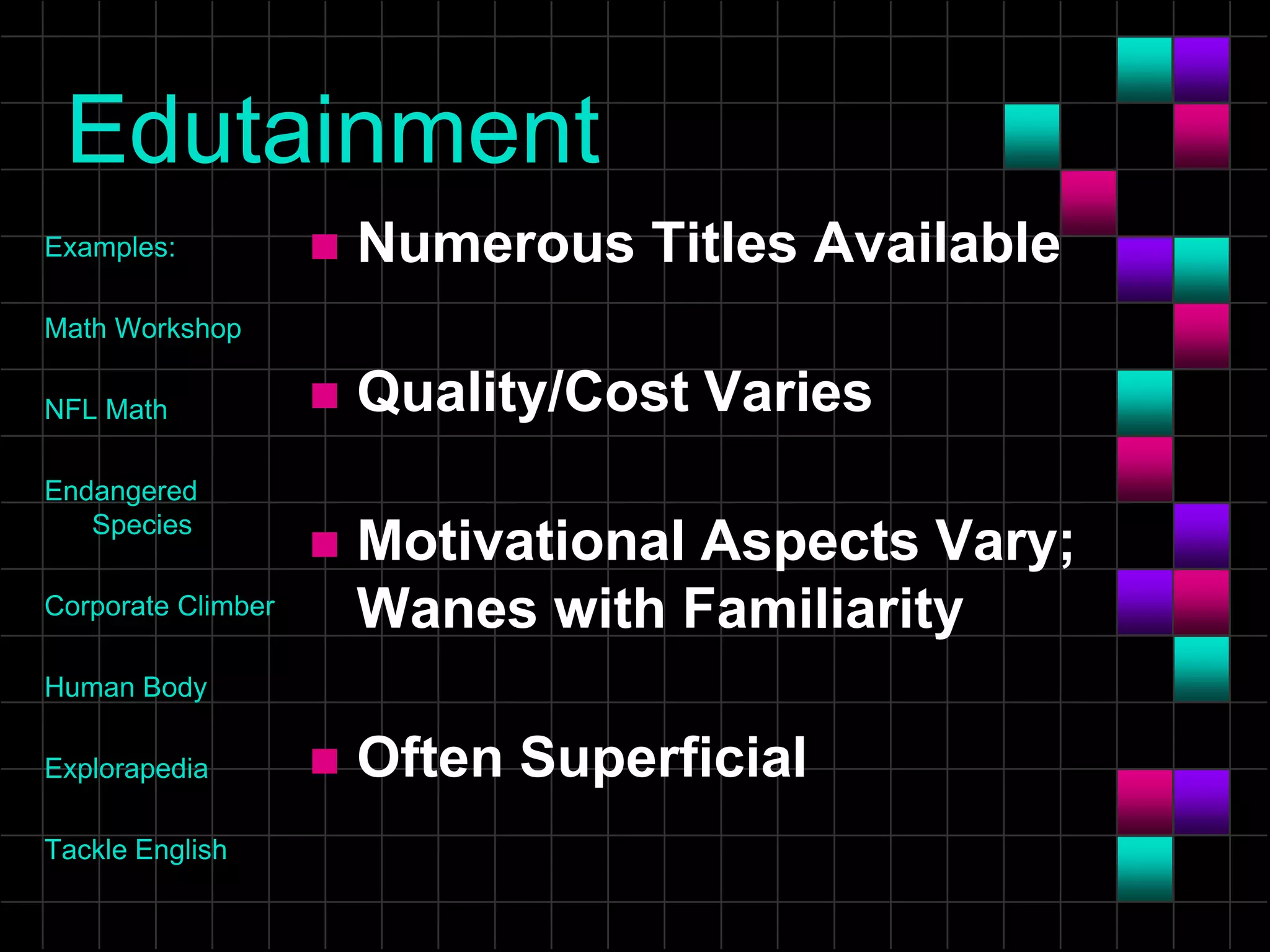
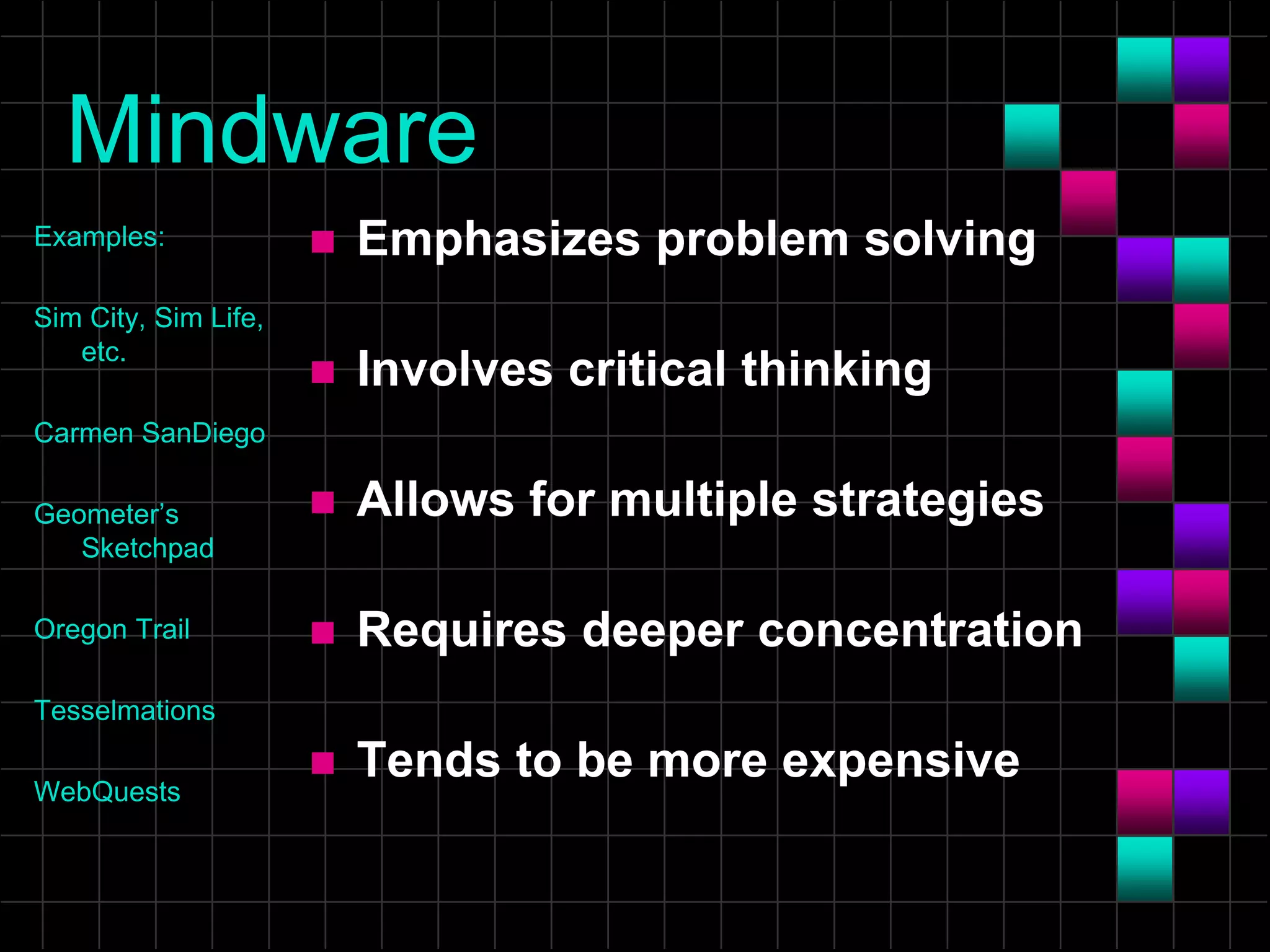
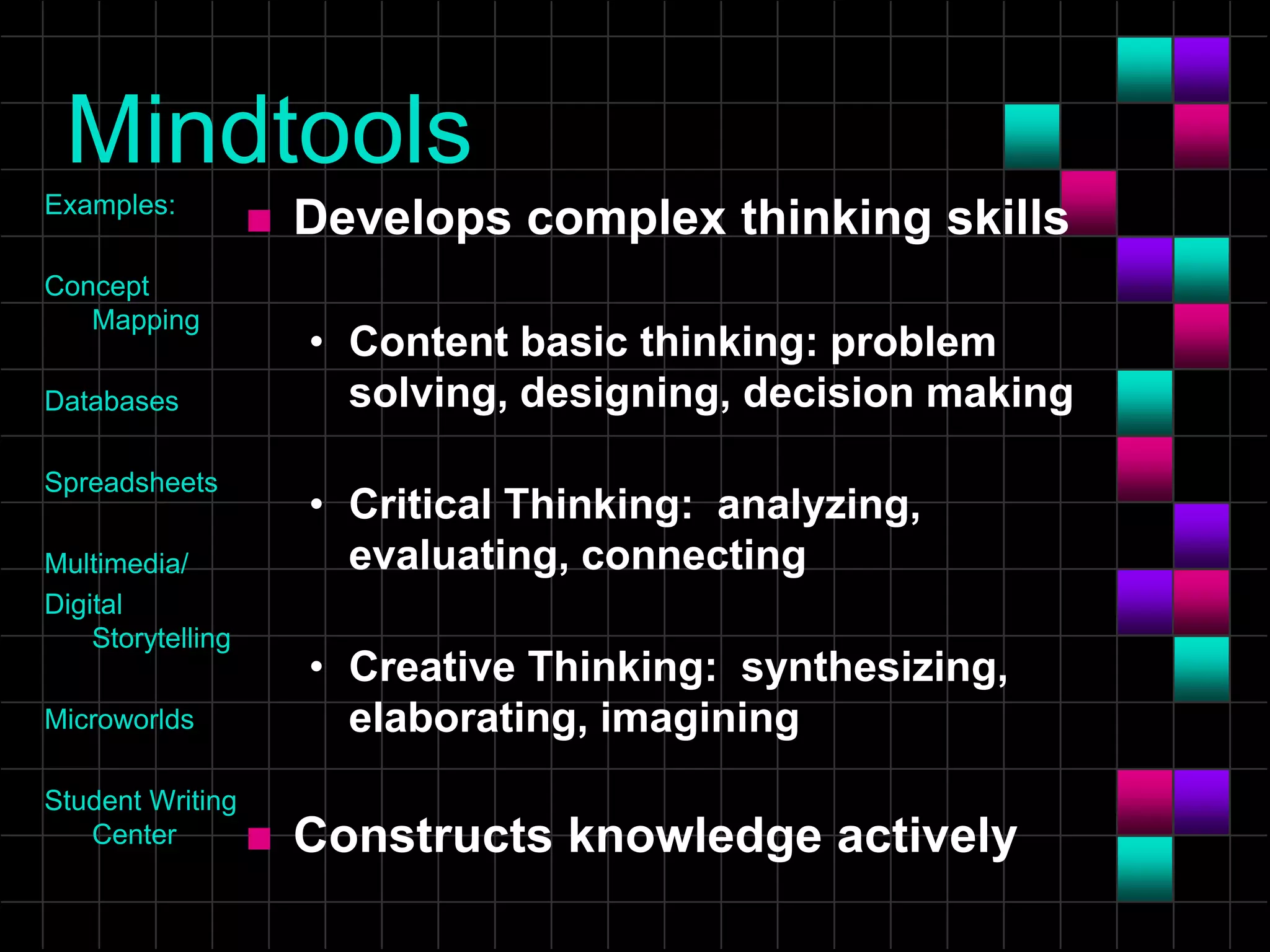
The document discusses the evolution and current state of classrooms concerning technology integration, emphasizing a shift from traditional 'sage on the stage' teaching to a more facilitator-driven approach that enhances student engagement and self-directed learning. It highlights various tools and methods, such as educational technology and mindtools, that can inspire meaningful learning experiences and improve critical thinking skills. Additionally, it advocates for rearranging technology to support contemporary learning needs rather than forcing students and educators to adapt to outdated classroom setups.